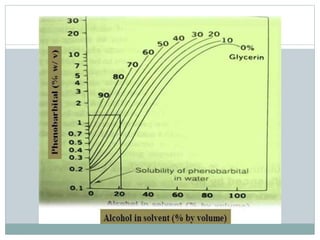
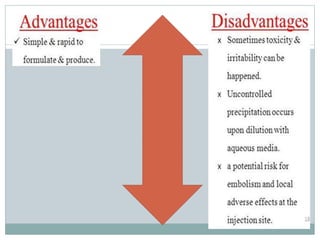
This document discusses cosolvency as a technique for enhancing the solubility of poorly soluble drugs. It defines solubility and outlines reasons for enhancing solubility, such as improving oral bioavailability. It then describes cosolvency, where a cosolvent is added to increase the solubility of a drug by creating a solution with an enhanced solubility. Common cosolvents that are non-toxic, non-irritating, and able to cross membranes include glycerine, PEG, diethyl acetamide, and ethyl alcohol. Cosolvency works by creating a solution with dielectric properties between those of water and the original solvent. It is a widely used technique that allows for parenteral formulations and improves