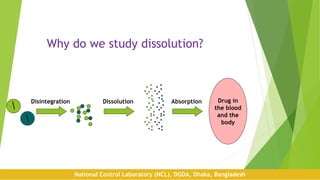
Dissolution is a test used to evaluate the rate of release of a drug substance from a dosage form. It assesses the performance of drug products and aims to be predictive of bioavailability. The first dissolution studies were reported in 1897 and focused on relating dissolution to drug absorption. Key factors that can affect dissolution include the apparatus used, temperature, media composition and pH, as well as formulation aspects like excipients. Proper procedure involves setting standardized conditions for the apparatus, media preparation, running the test, and calculating the percentage of drug dissolved within a specified time period.