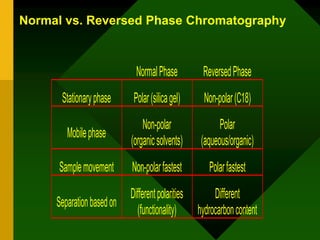
HPLC is a form of column chromatography that separates compounds based on their polarity and interaction with the stationary phase. It utilizes a pump to push the mobile phase and analytes through a column under high pressure. Various detectors can then provide the retention time of analytes as they exit the column. Key aspects of HPLC include the types of columns, mobile phases, and detectors used, which are selected based on the compounds being analyzed. HPLC is commonly used to analyze biological, pharmaceutical, environmental, and forensic samples.