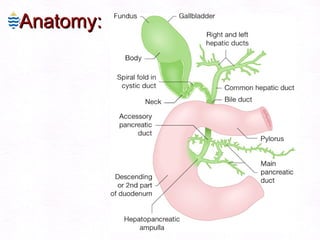
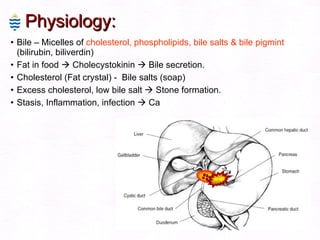
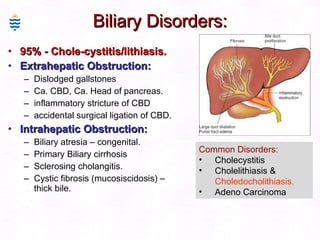
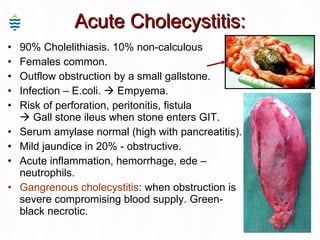
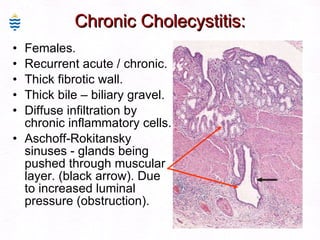
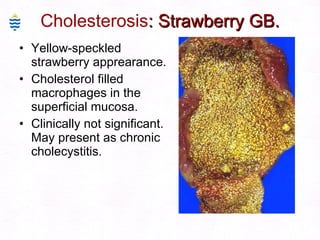
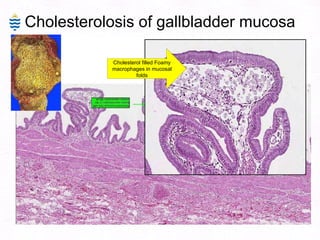
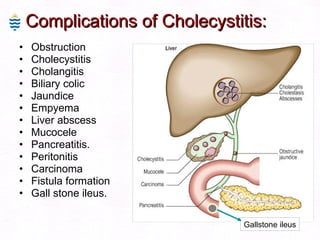
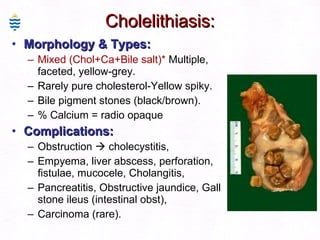
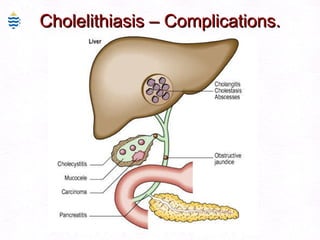
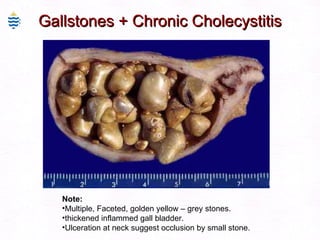
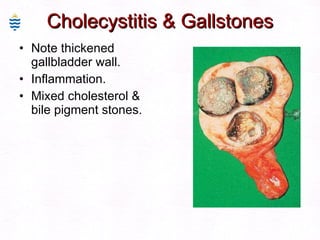
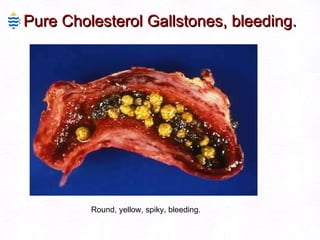
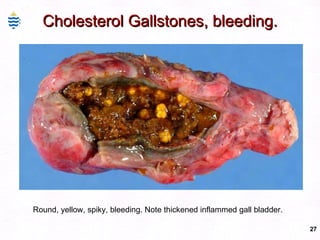
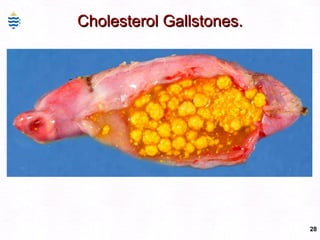
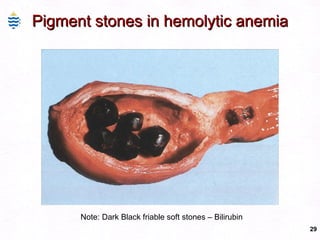
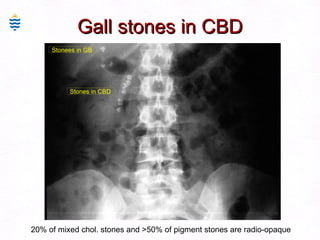
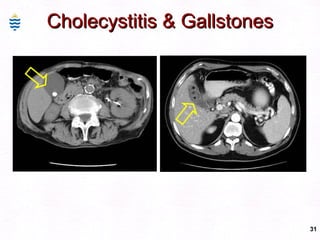
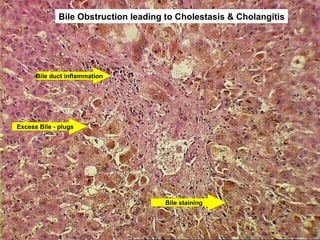
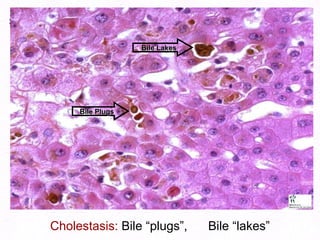
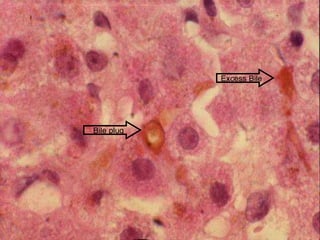
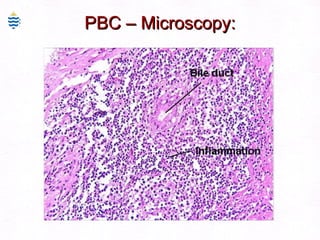
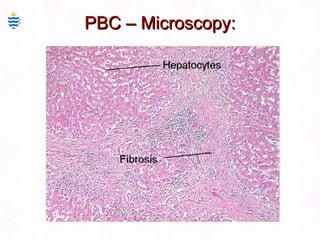
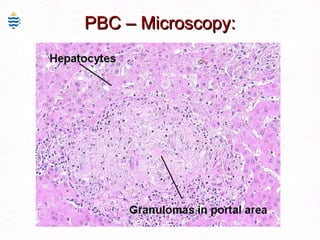
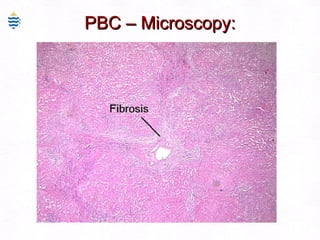
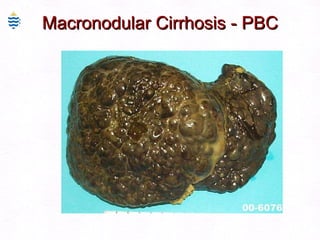
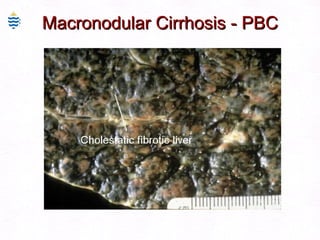
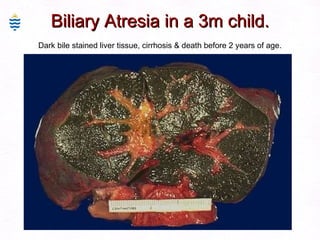
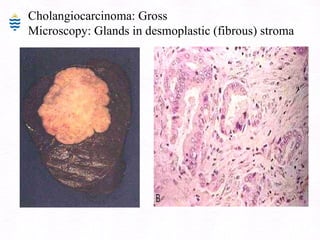
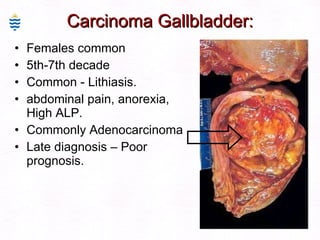
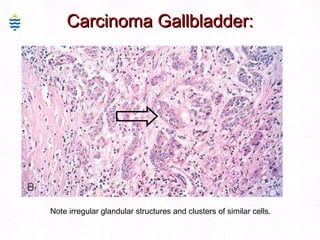
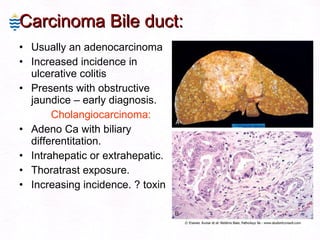
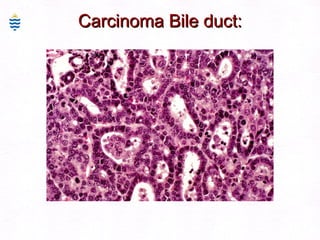
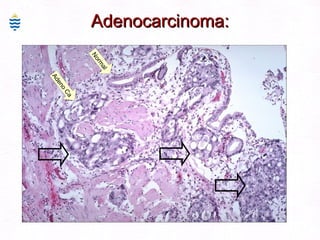
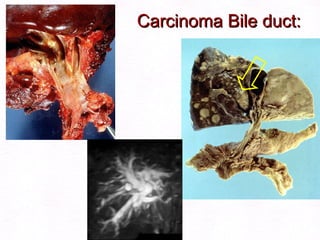
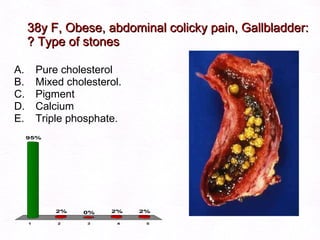
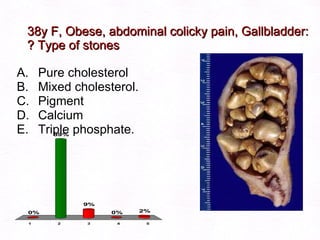
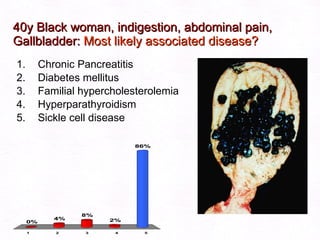
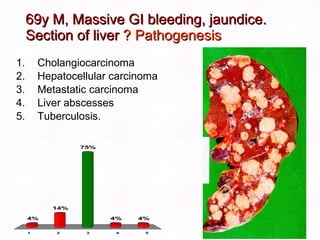
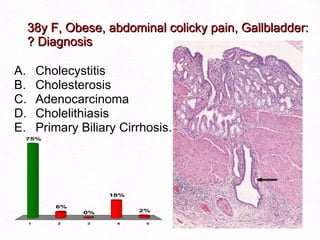
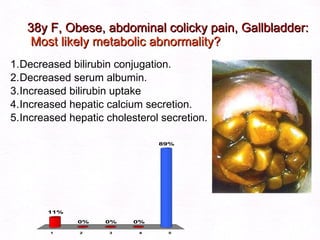
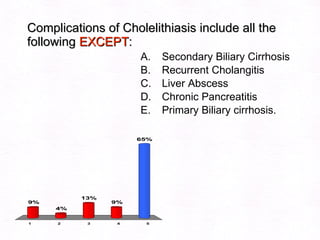
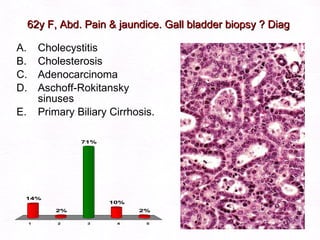
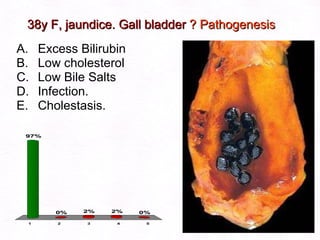
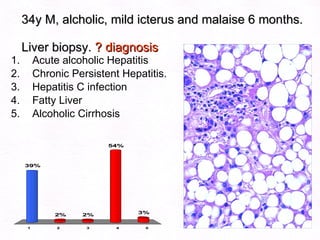
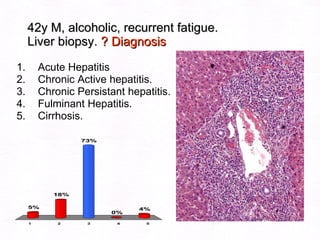
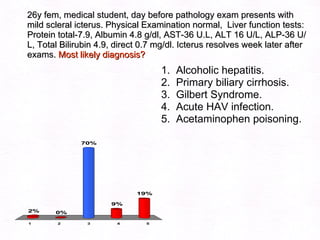
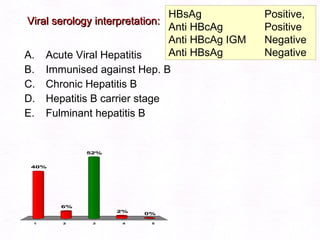
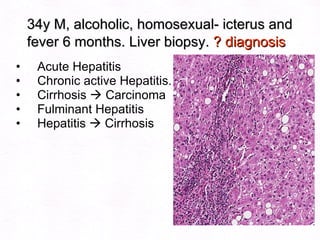
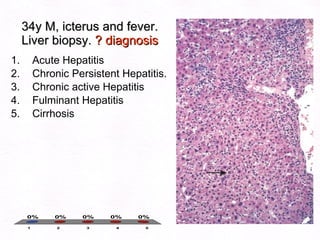
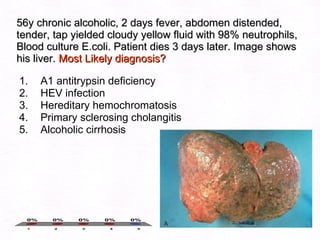
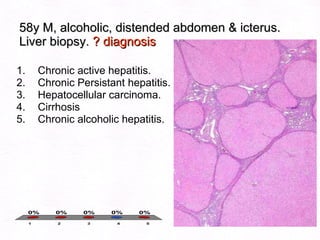
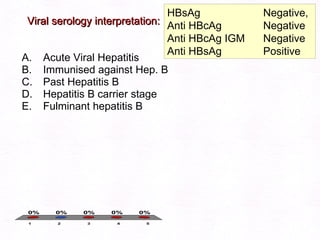
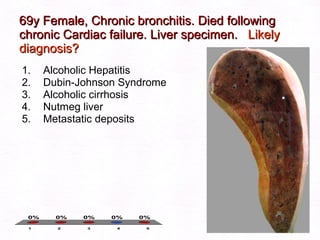
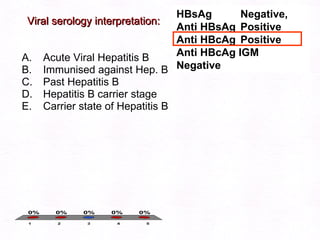
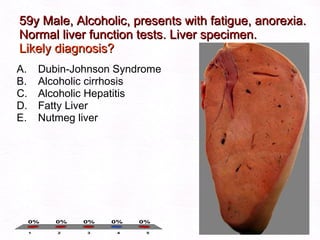
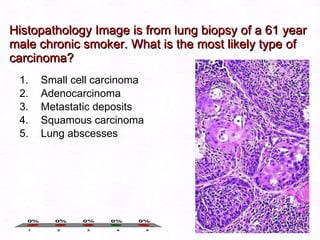
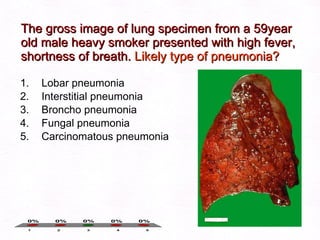
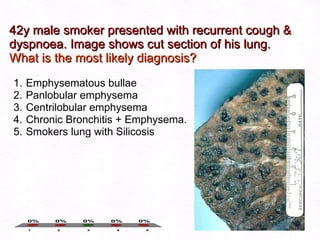
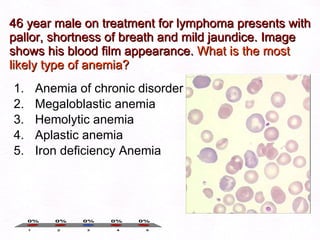
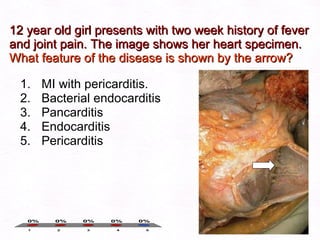
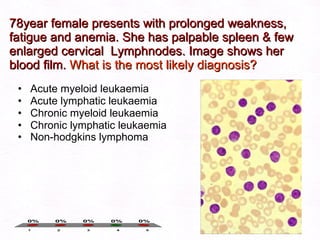
This document contains information about a patient visit. A 42-year-old real estate agent named Fay approached the assistant at a charity function with abdominal problems and was advised to see the assistant at their surgery. The document then provides detailed information about Fay's medical history, symptoms, lab results, and differential diagnoses. It discusses conditions like gallstones, cholecystitis, liver disease, and more.