1. The document discusses various gallbladder diseases including cholelithiasis, acute cholecystitis, ascending cholangitis, gallstone ileus, and porcelain gallbladder.
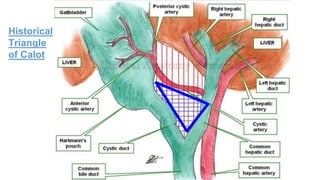
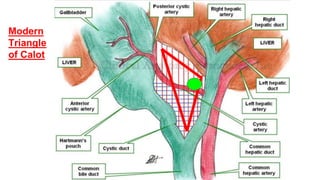
2. It provides details on the presentation, workup, diagnosis and management of these conditions including anatomy, imaging findings, medical and surgical treatment options.
3. Case examples are presented and summarized to demonstrate the clinical approach to patients with different gallbladder issues.