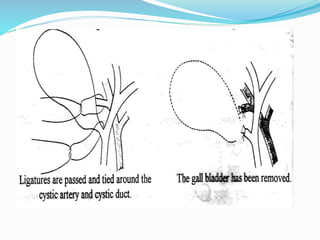
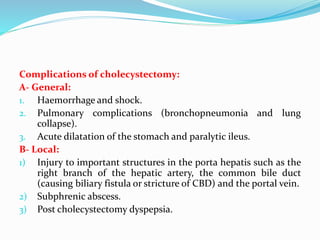
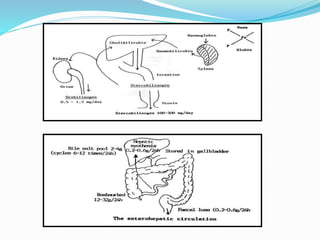
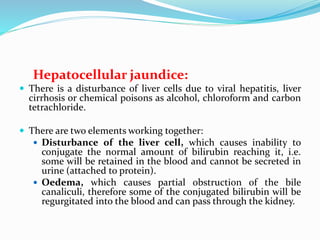
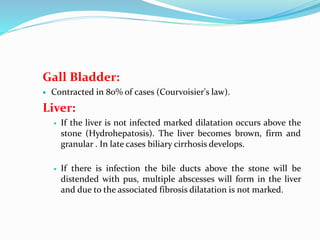
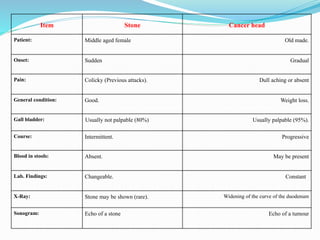
Chronic cholecystitis encompasses various conditions affecting the gall bladder, primarily characterized by gall stones in 95% of cases. Diagnosis involves recognizing symptoms in middle-aged females, while treatment options include medical management and surgical cholecystectomy, with laparoscopic surgery being the preferred method. Complications may arise from gall stones, leading to further conditions such as inflammation and jaundice.