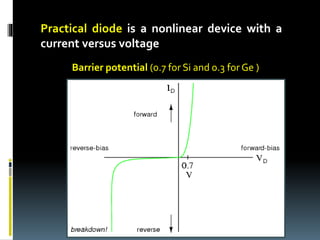
The document provides an extensive overview of diodes, detailing their construction, operation, characteristics, and various applications such as rectification, regulation, clippers, clampers, and special-purpose diodes like Zener and Schottky diodes. It covers key concepts such as forward and reverse biasing, threshold voltage, and breakdown voltage, while also explaining methods for analyzing diode circuits and their role in electronic devices. Additionally, the document includes diagrams and equations to illustrate the principles discussed, as well as review questions to reinforce understanding.