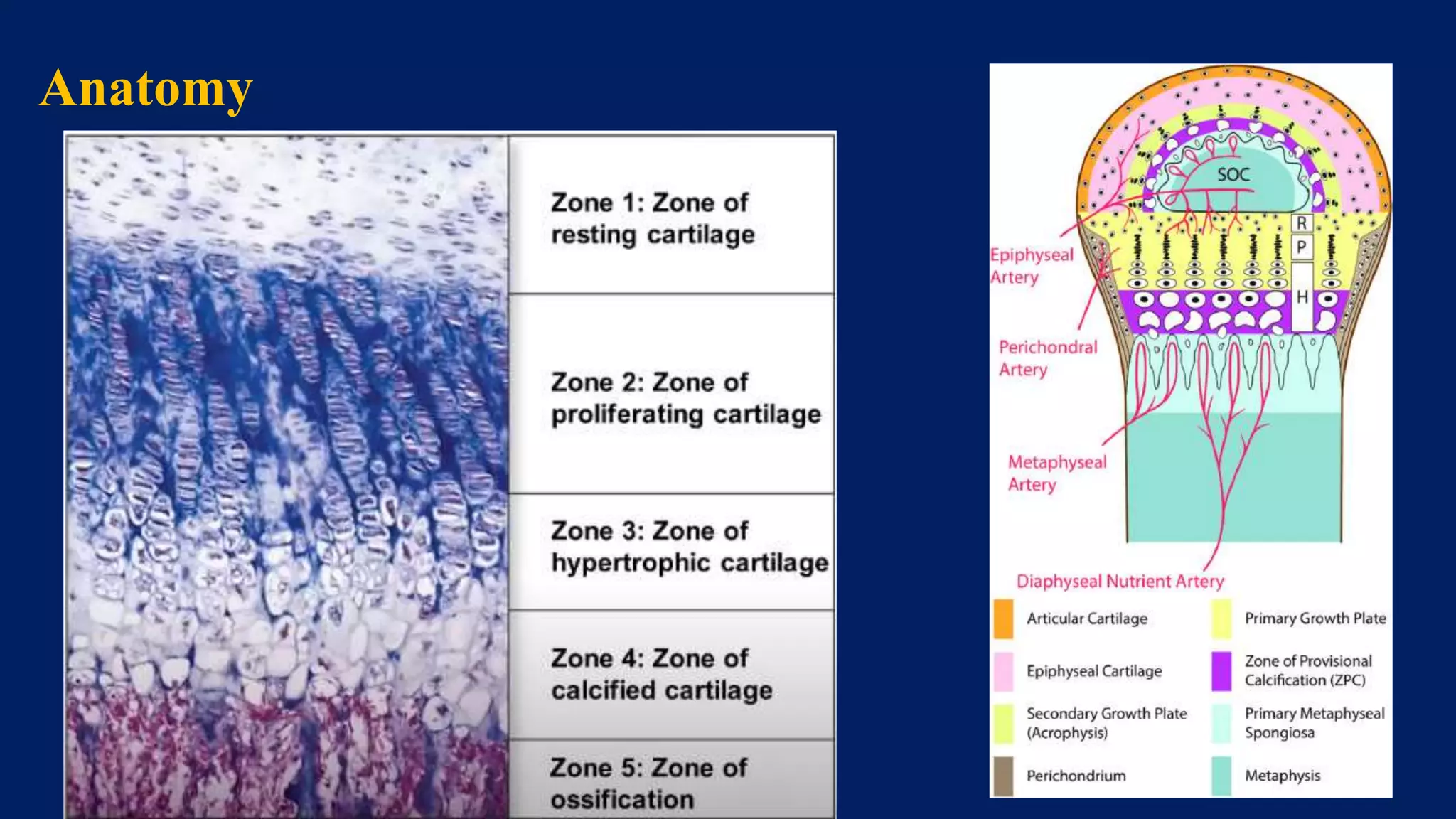
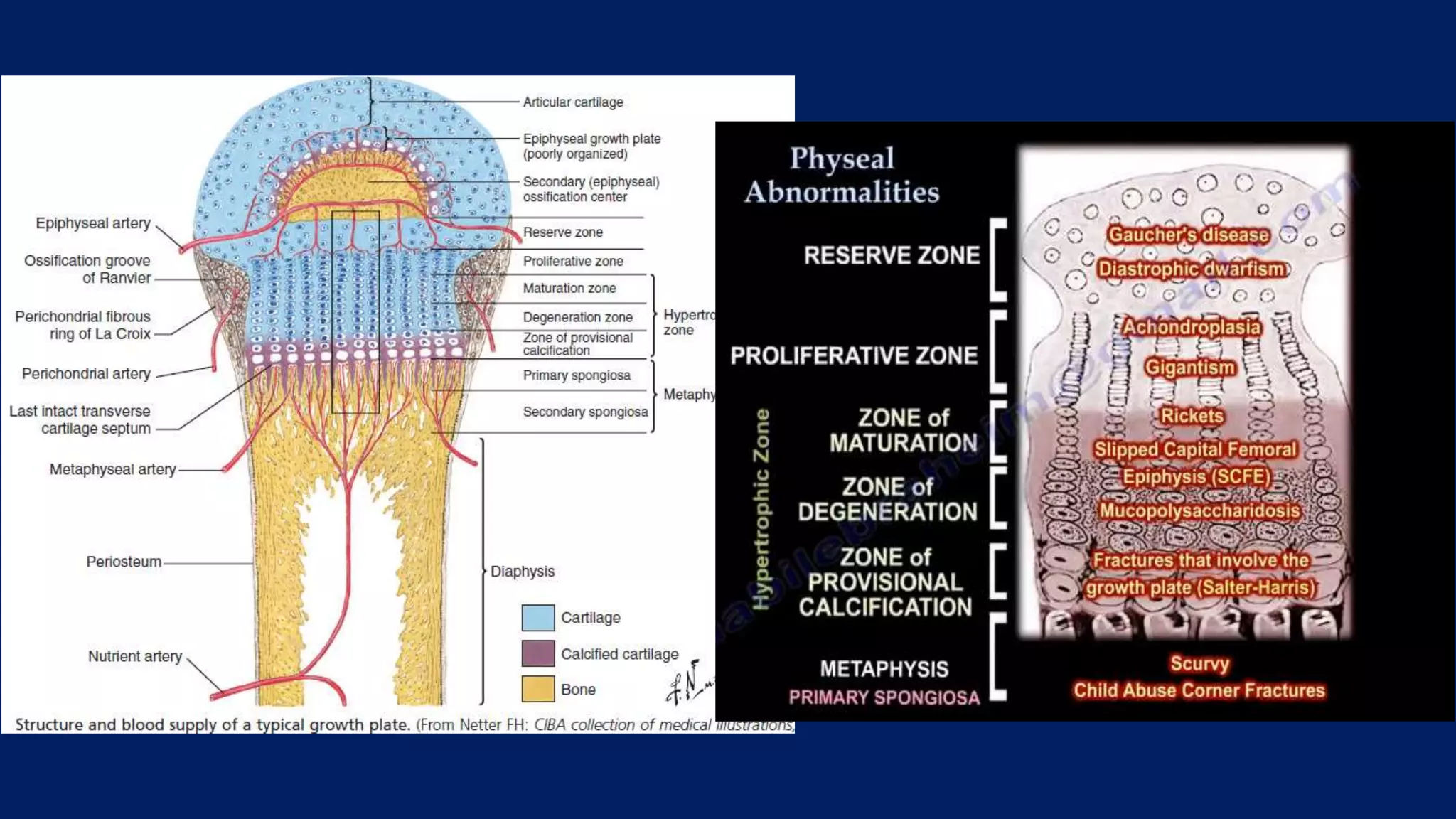
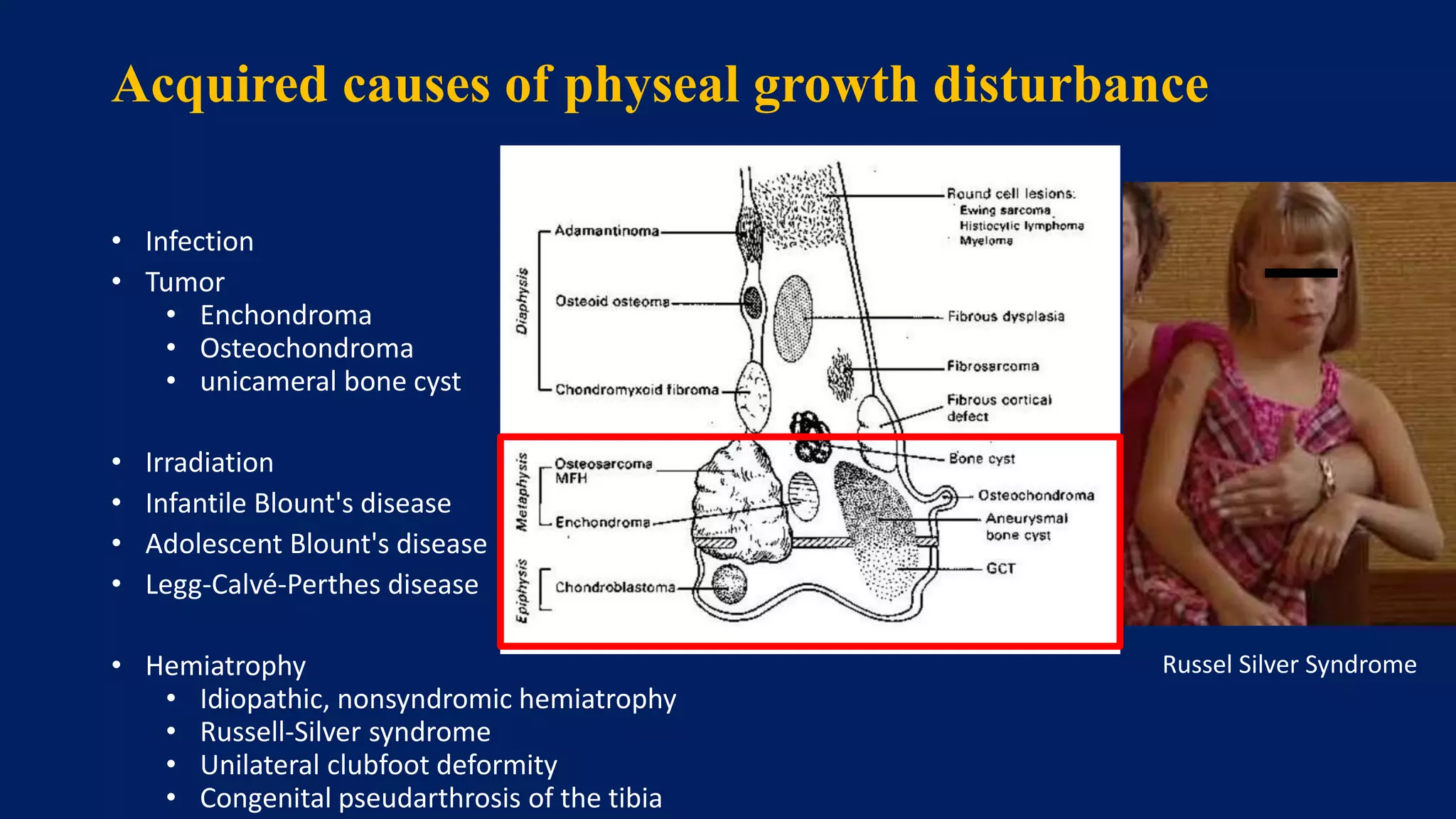
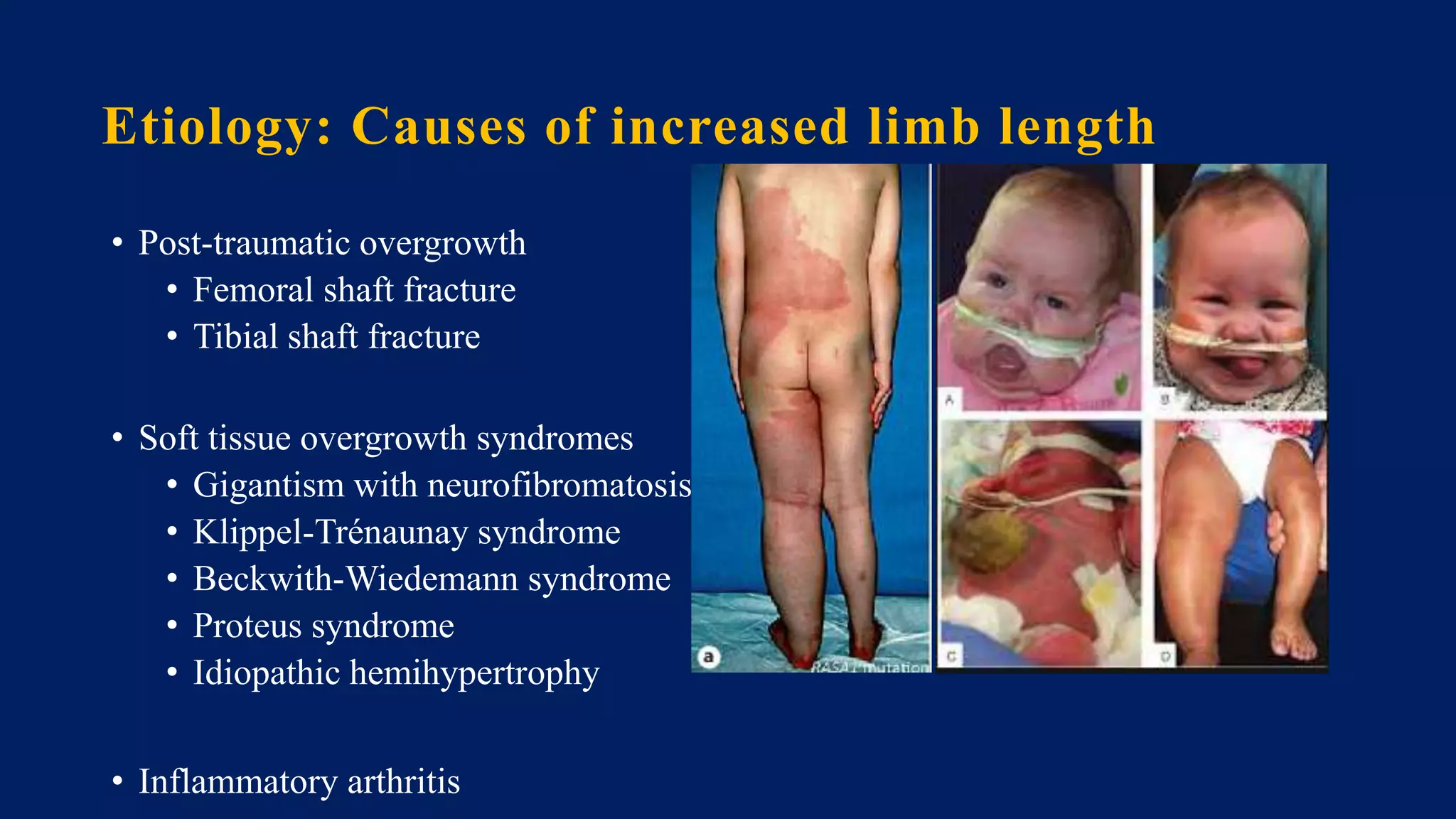
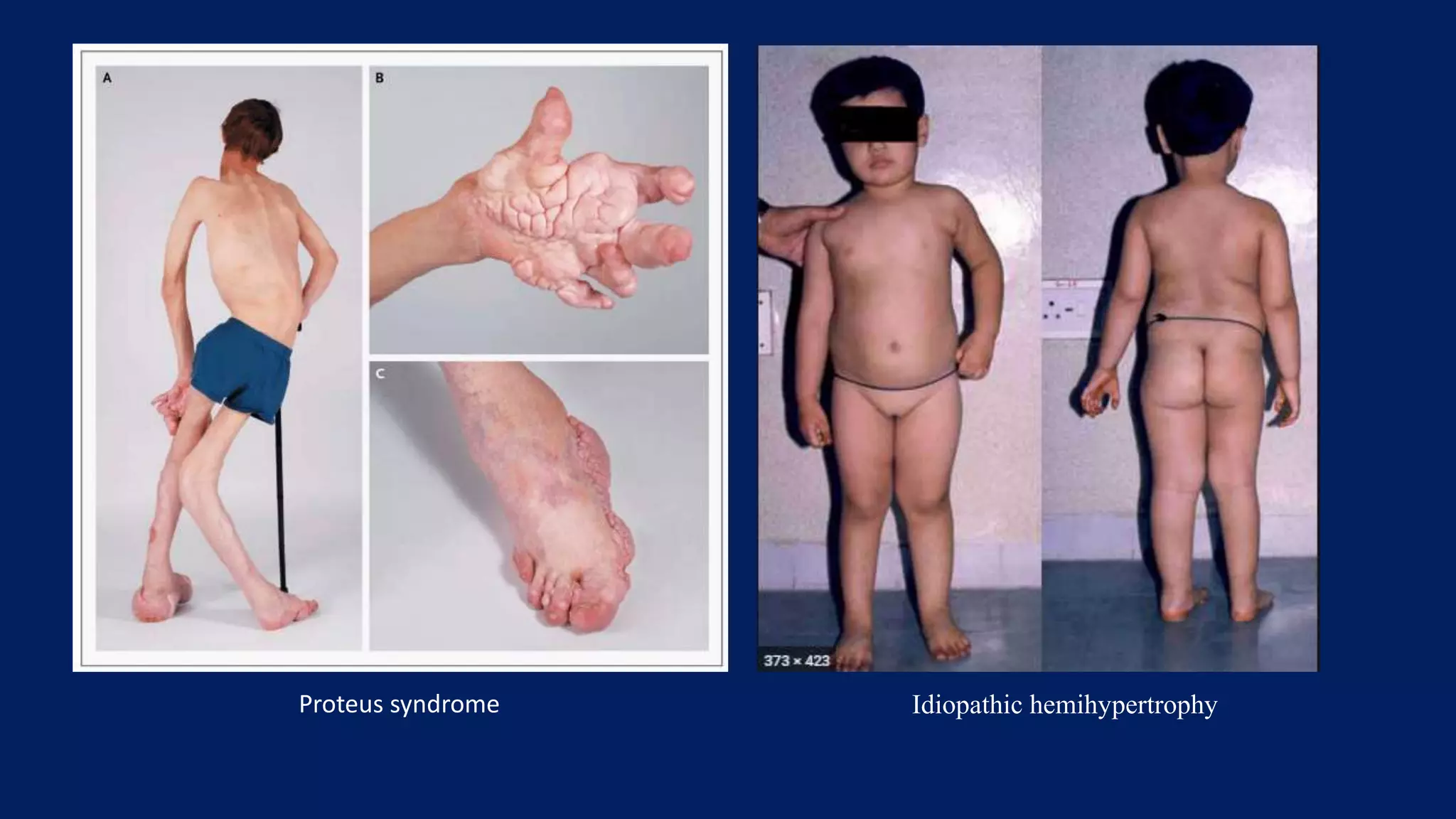
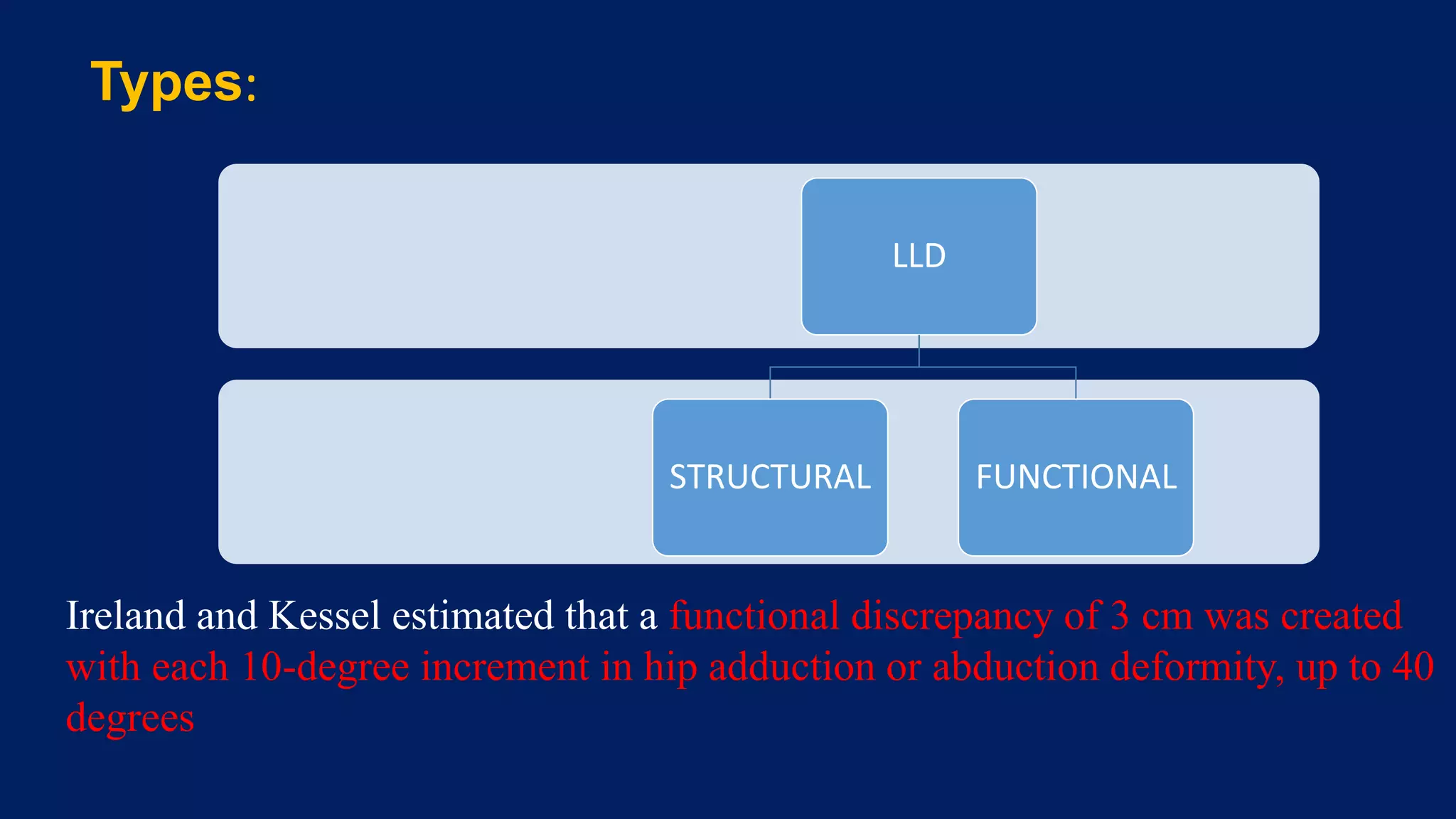
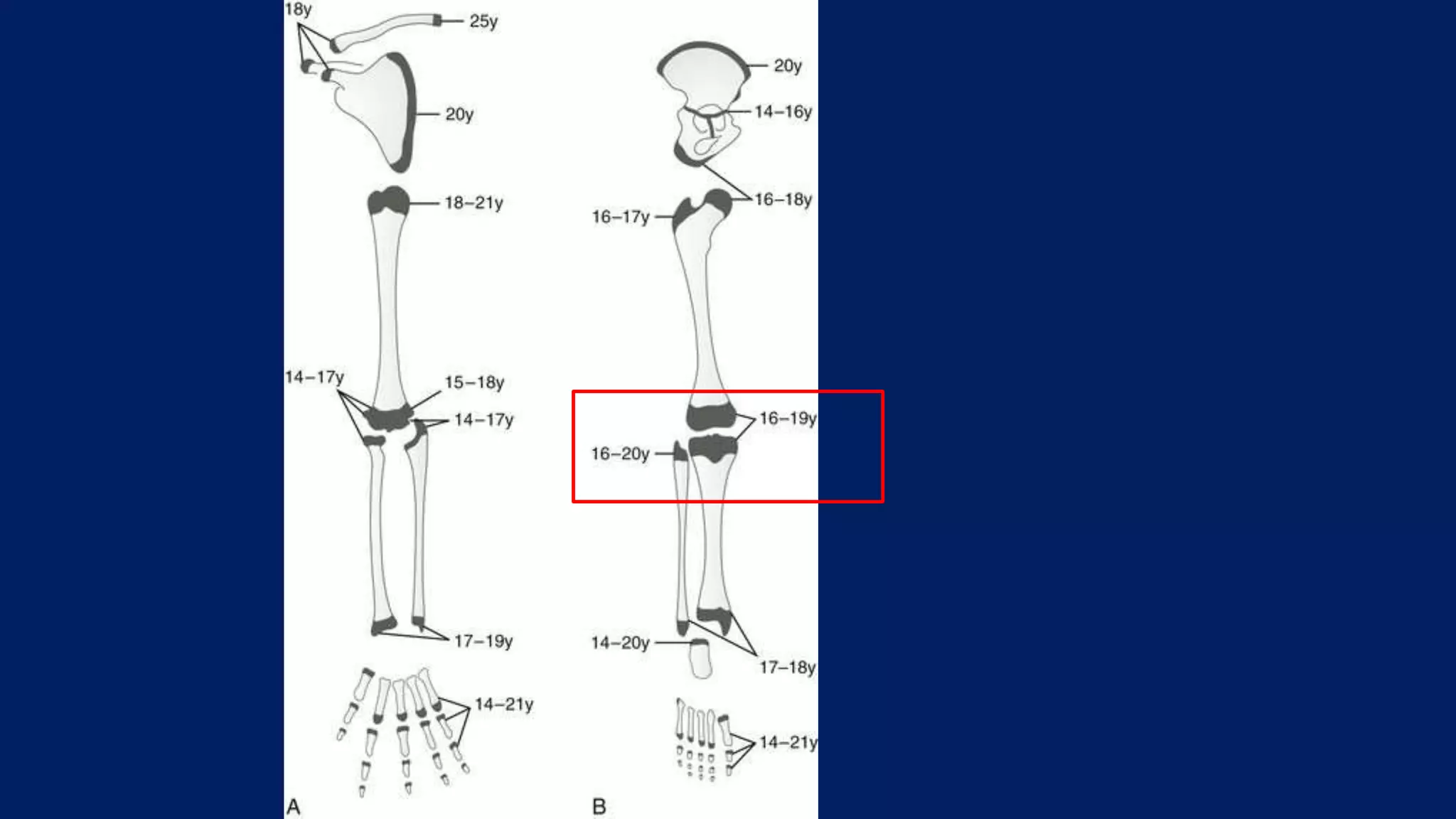
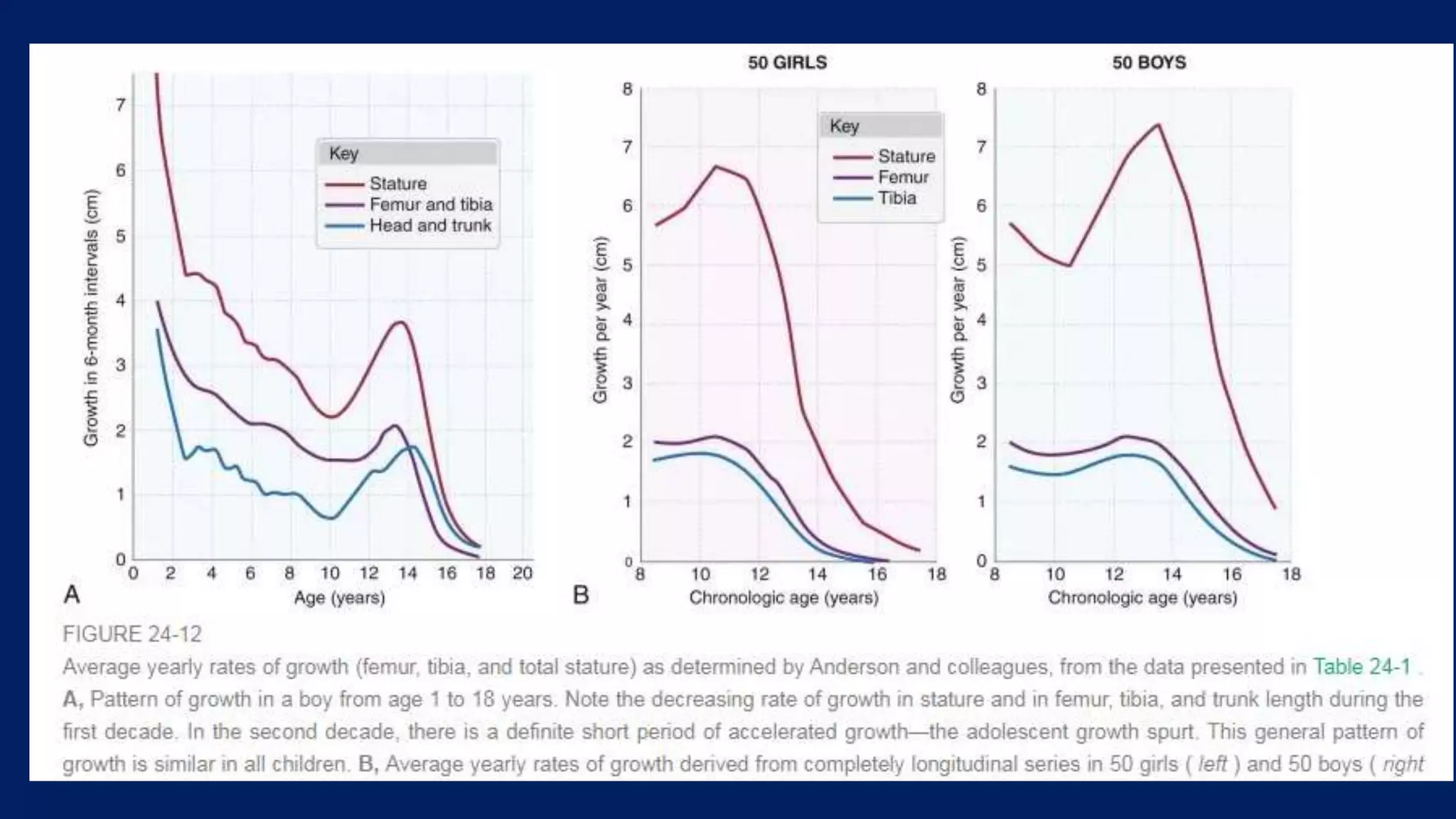
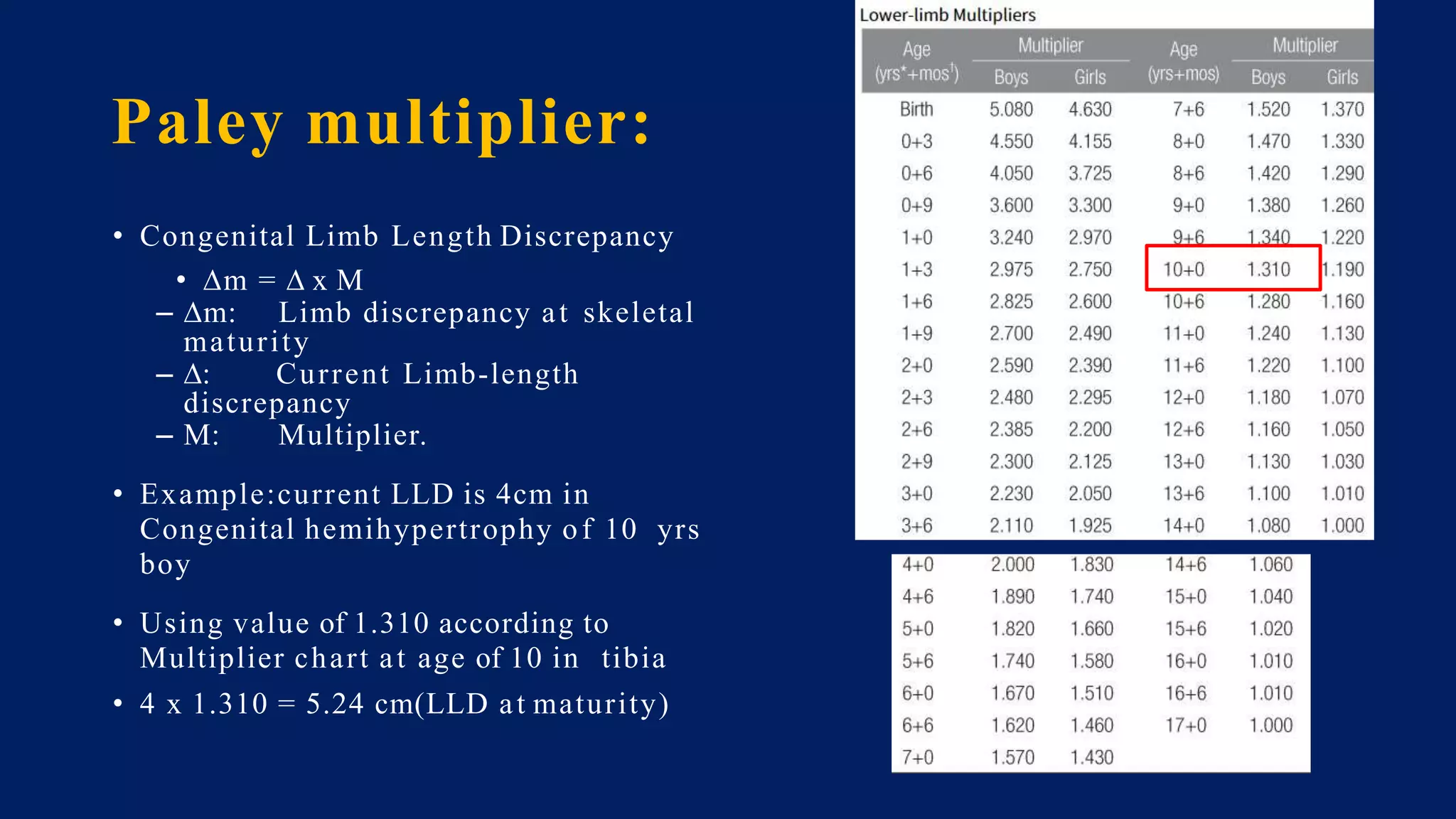
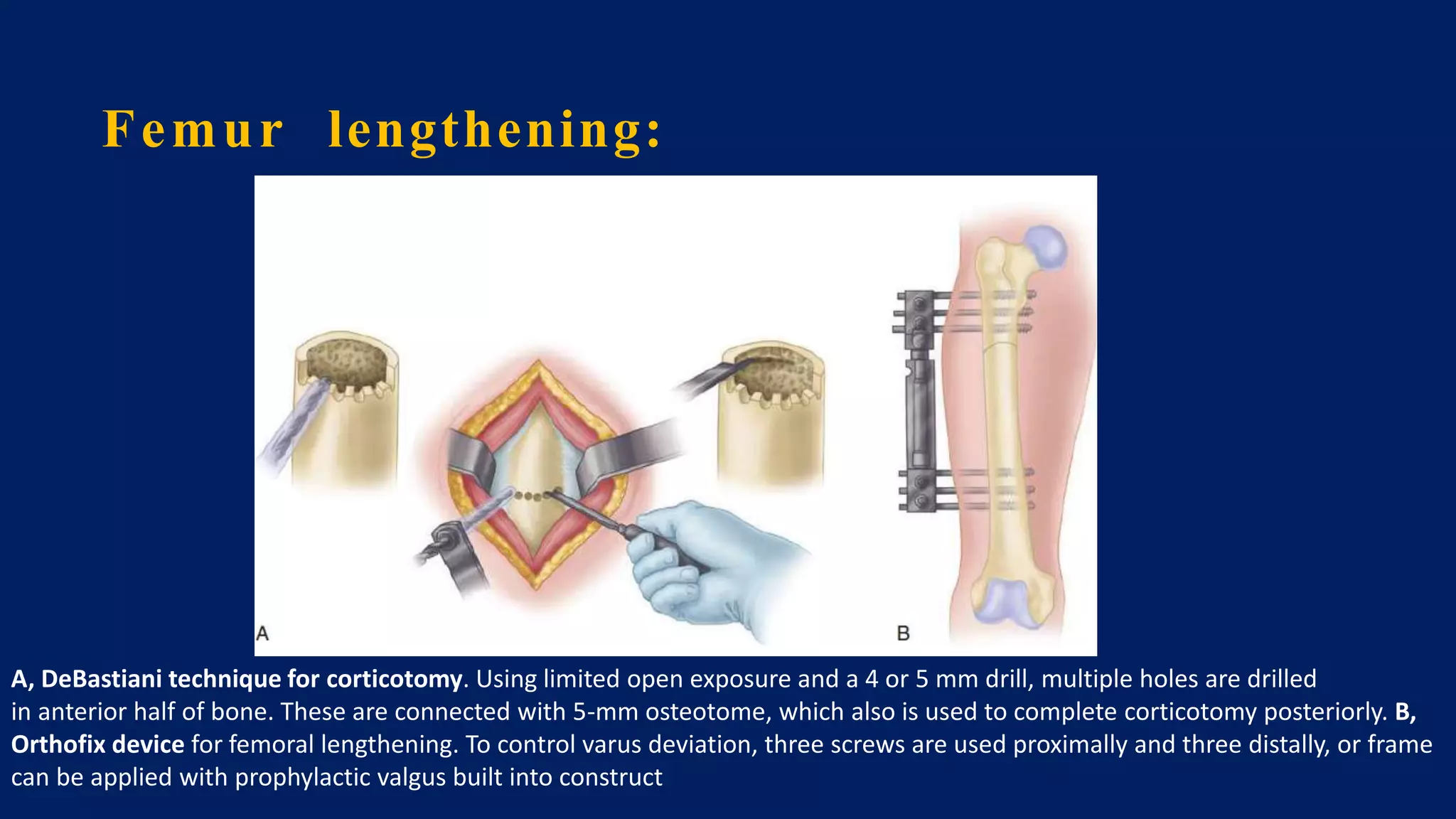
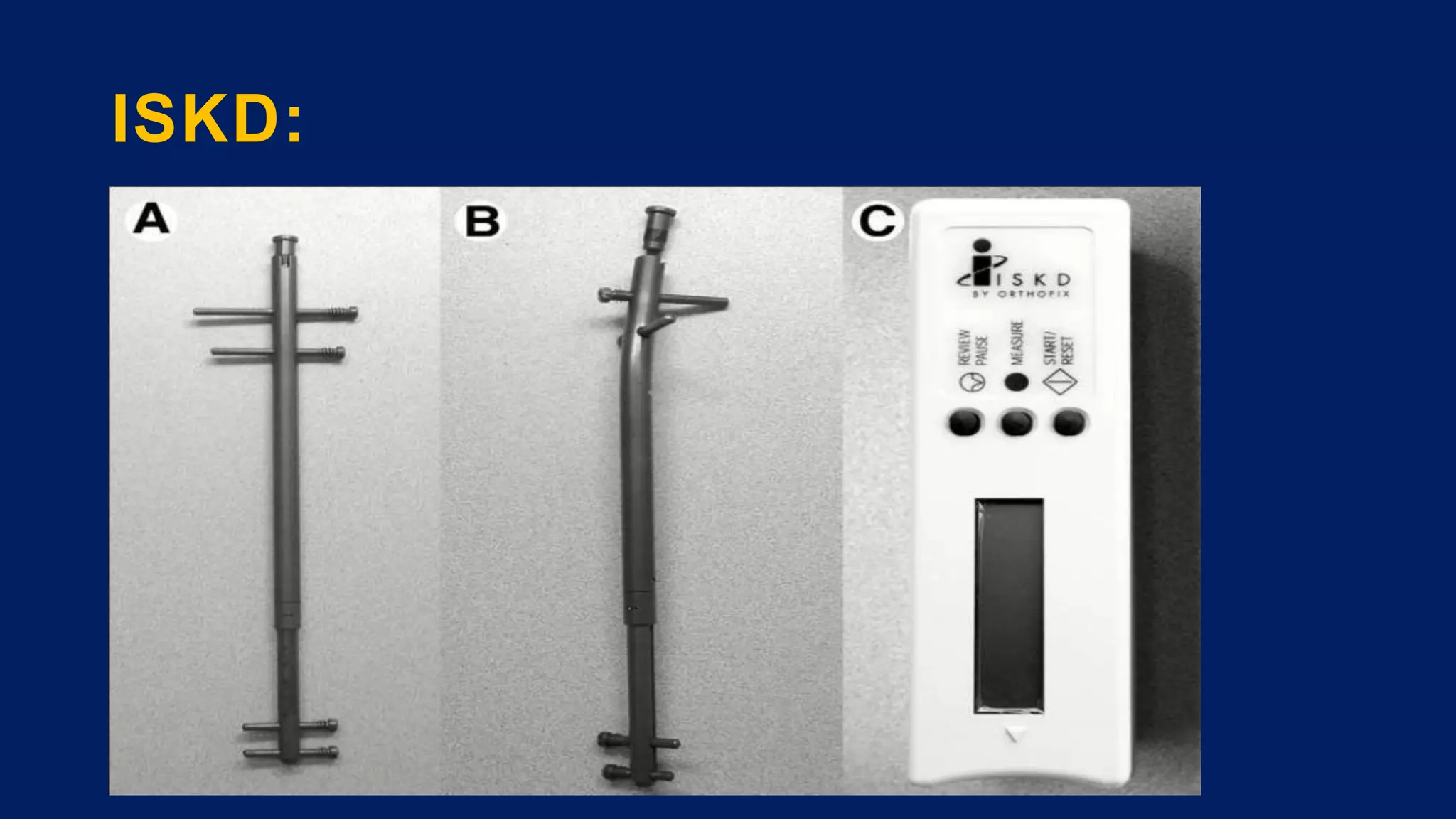
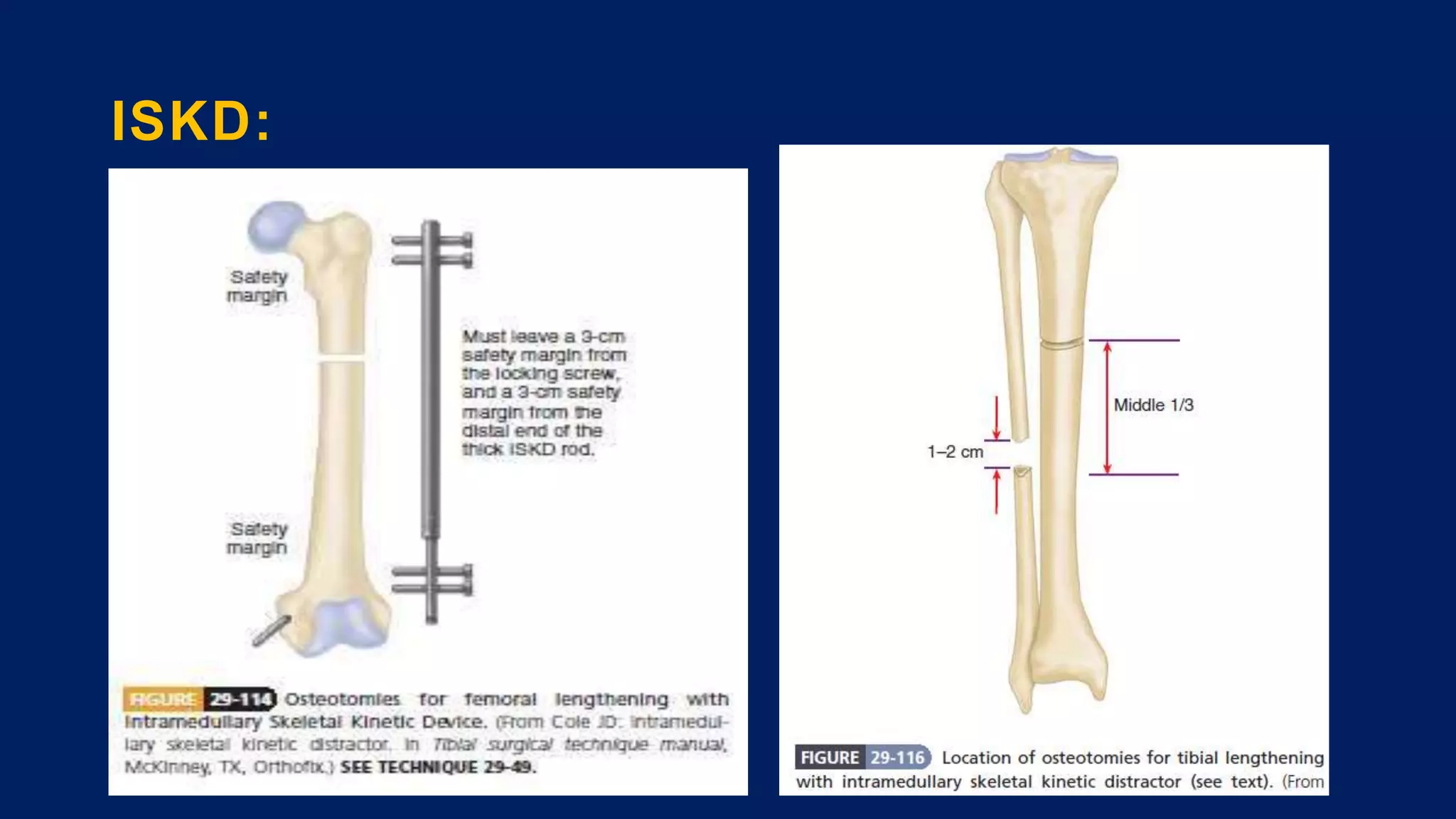
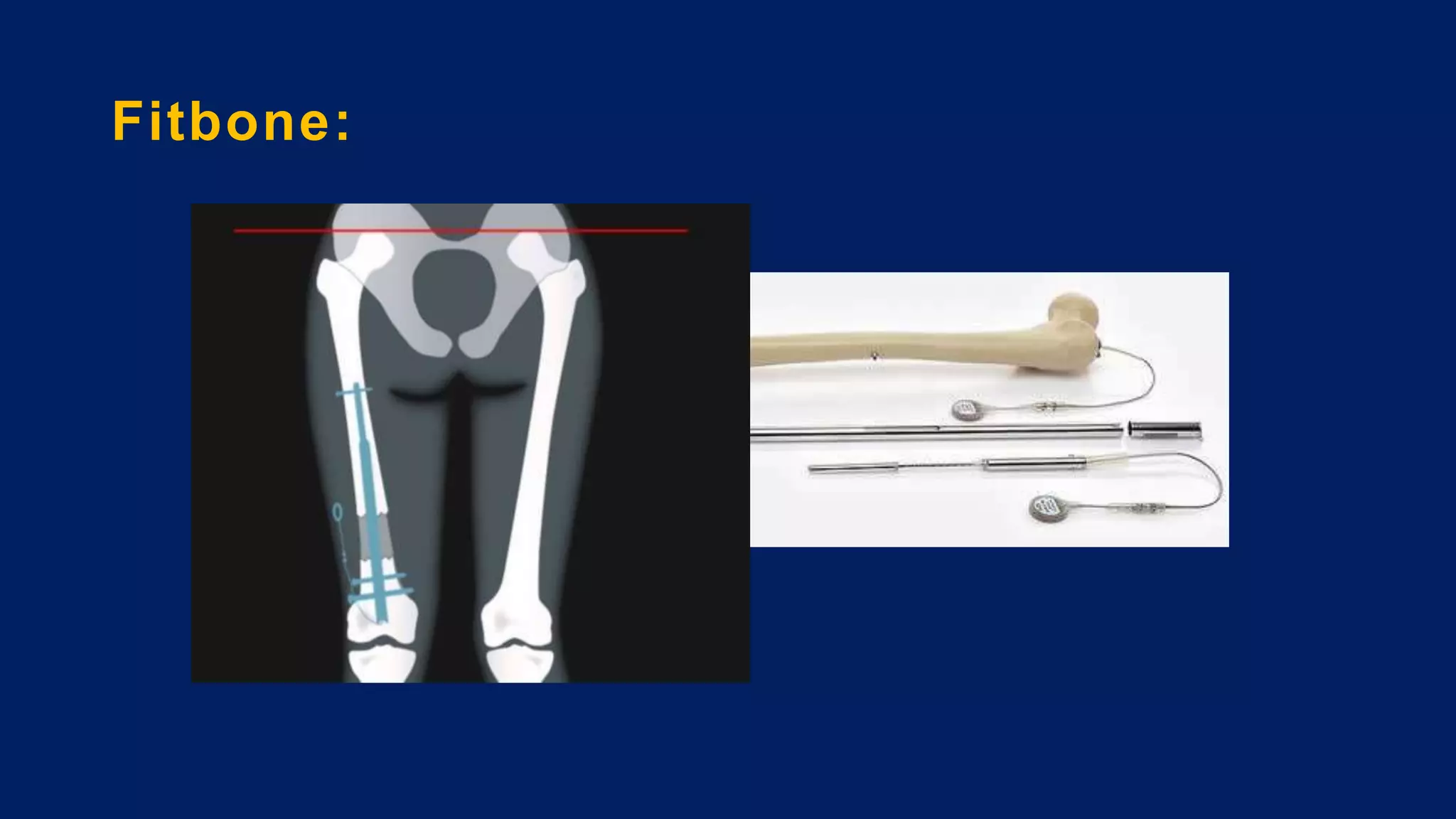
1) Limb length discrepancy (LLD) can be congenital or acquired and causes include trauma, infections, tumors, or bone diseases. It is classified as mild (<3cm), moderate (3-6cm), or severe (>6cm) based on the magnitude of inequality.
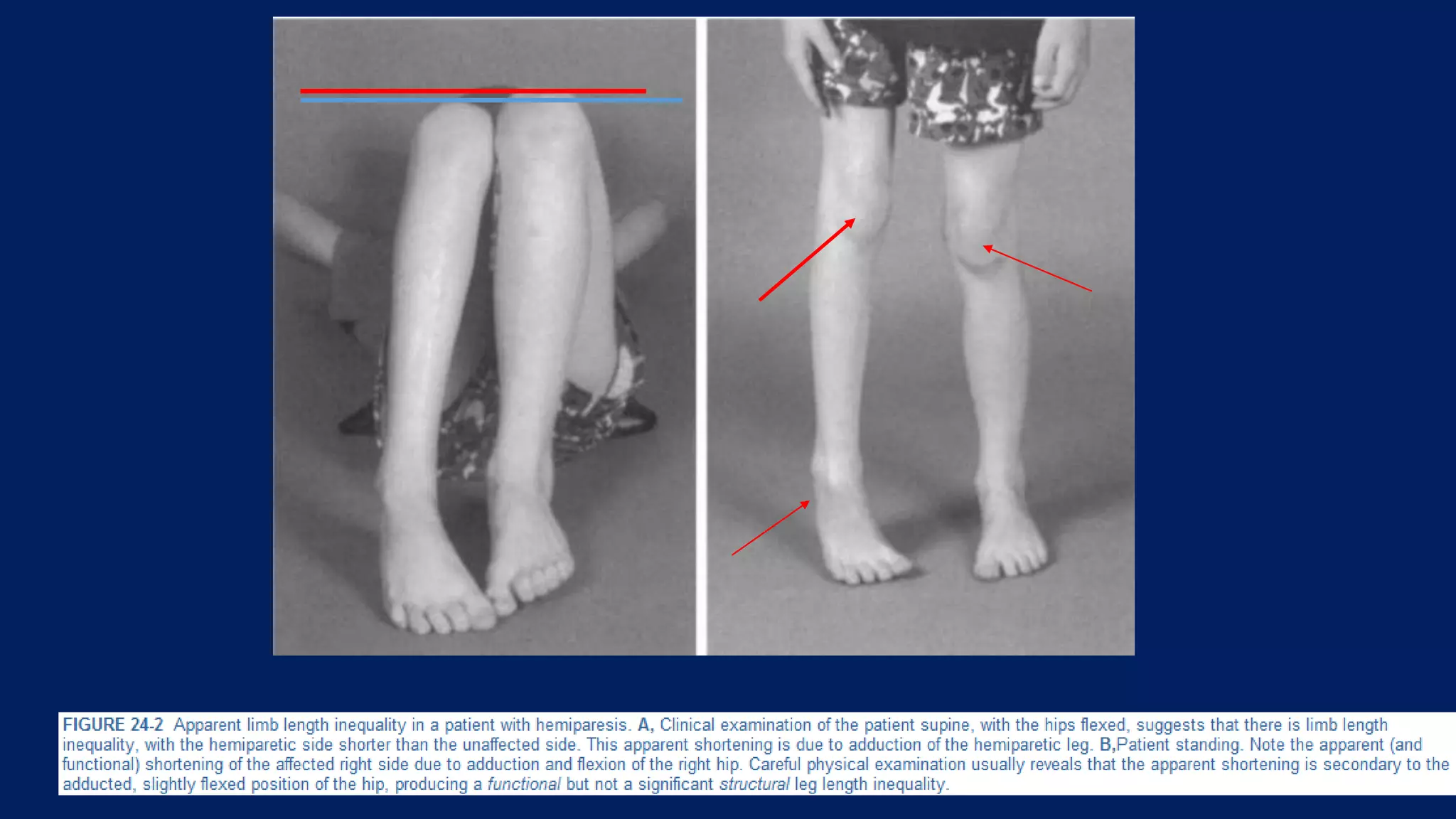
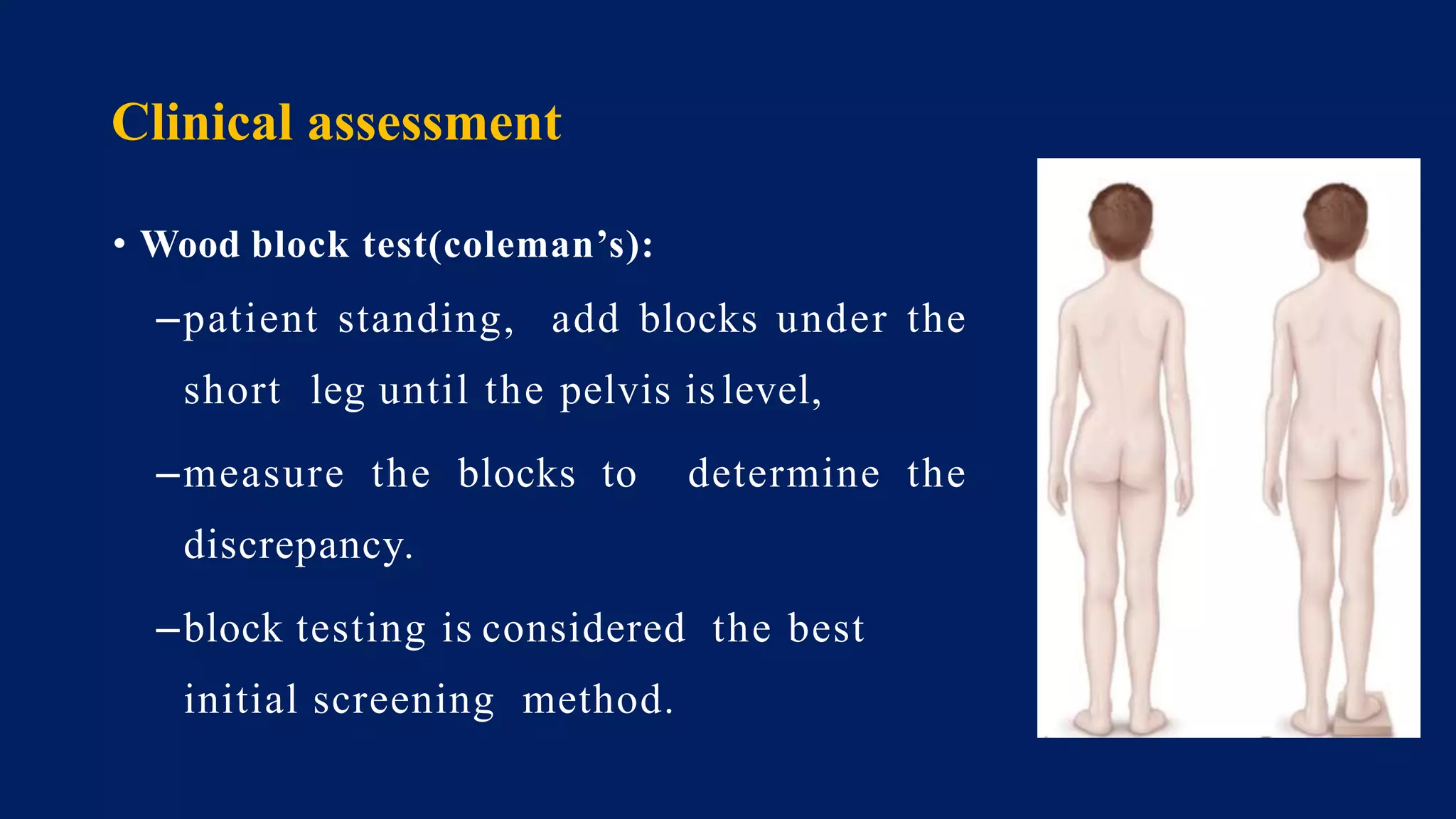
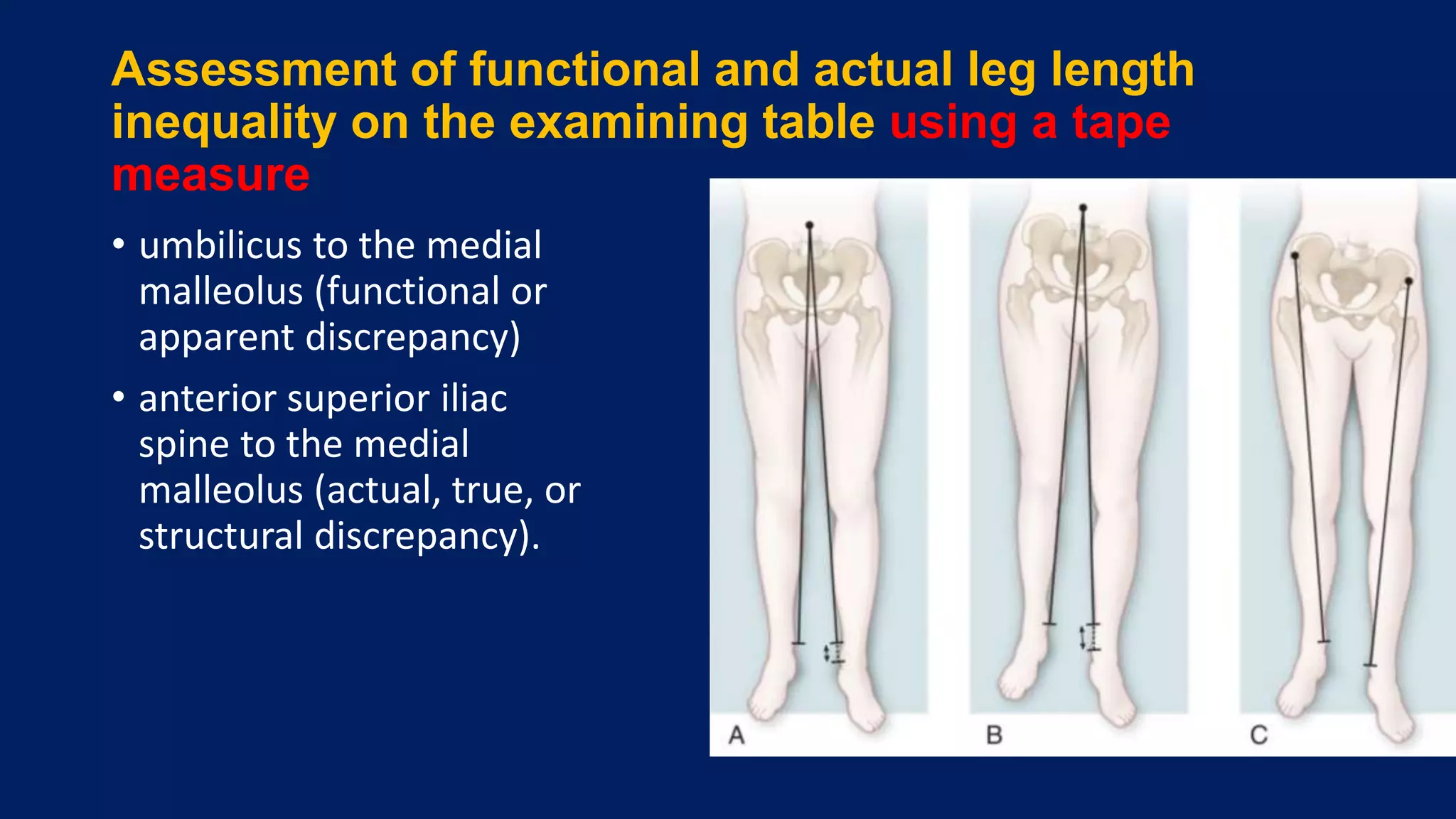
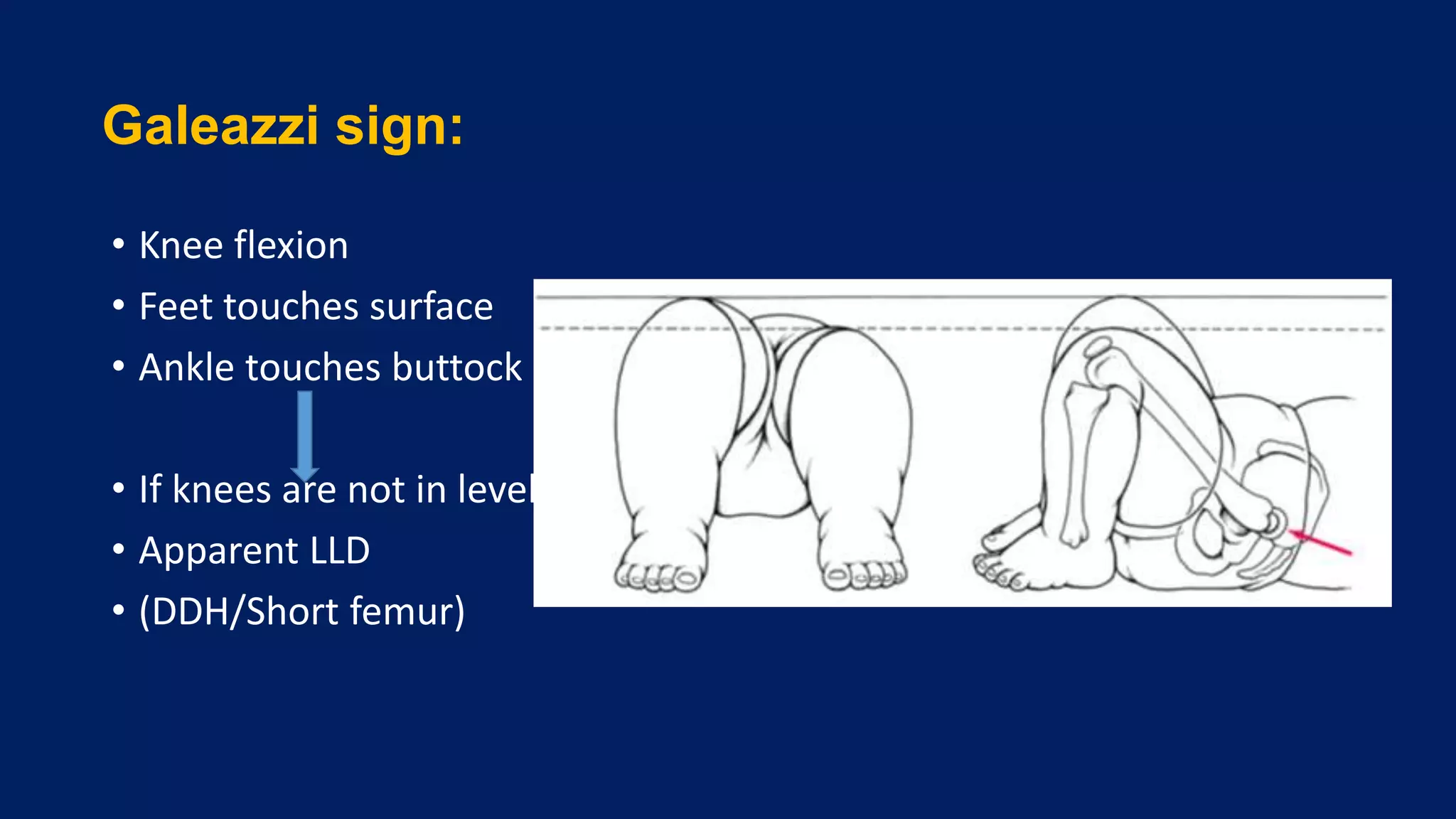
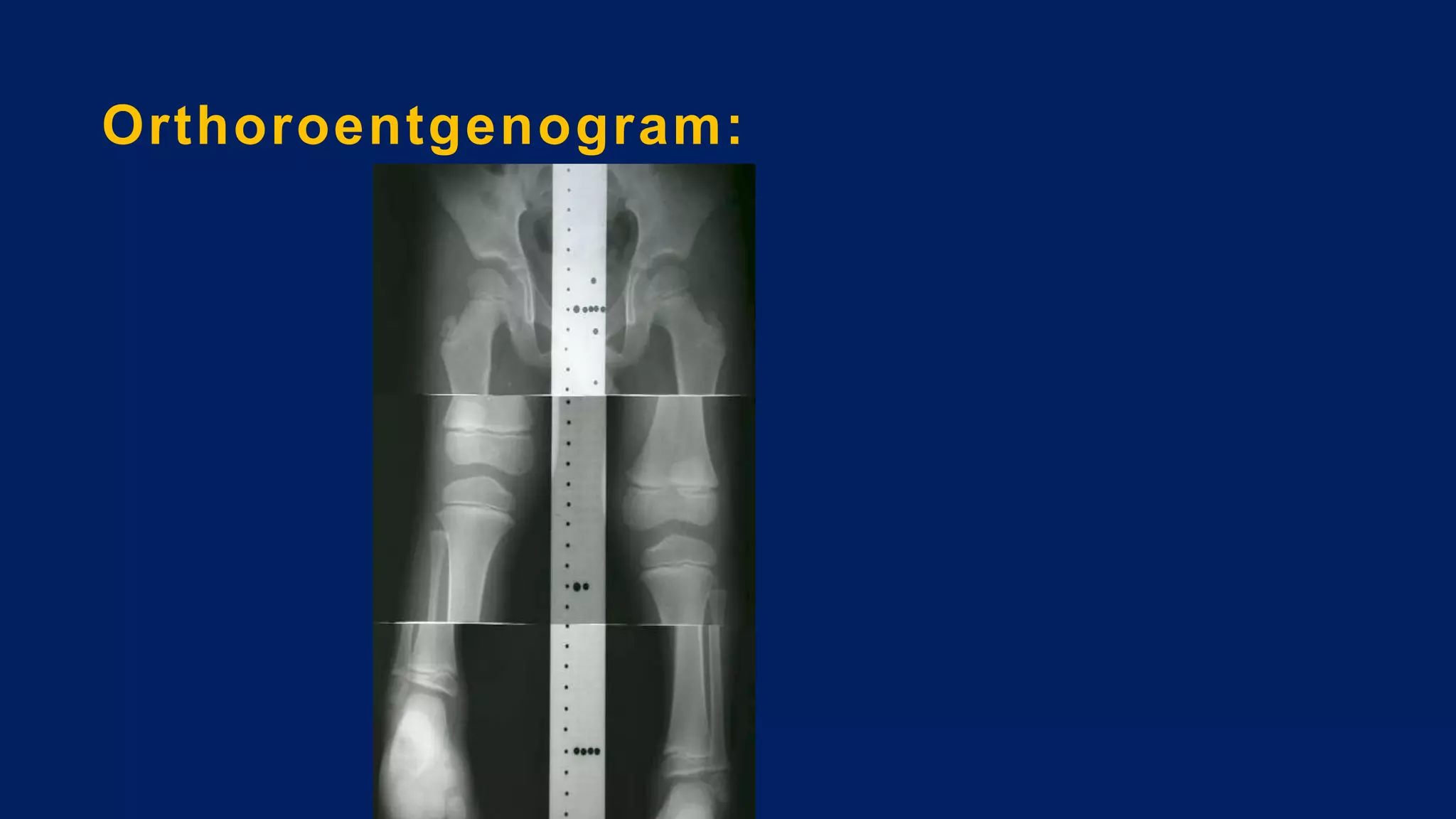
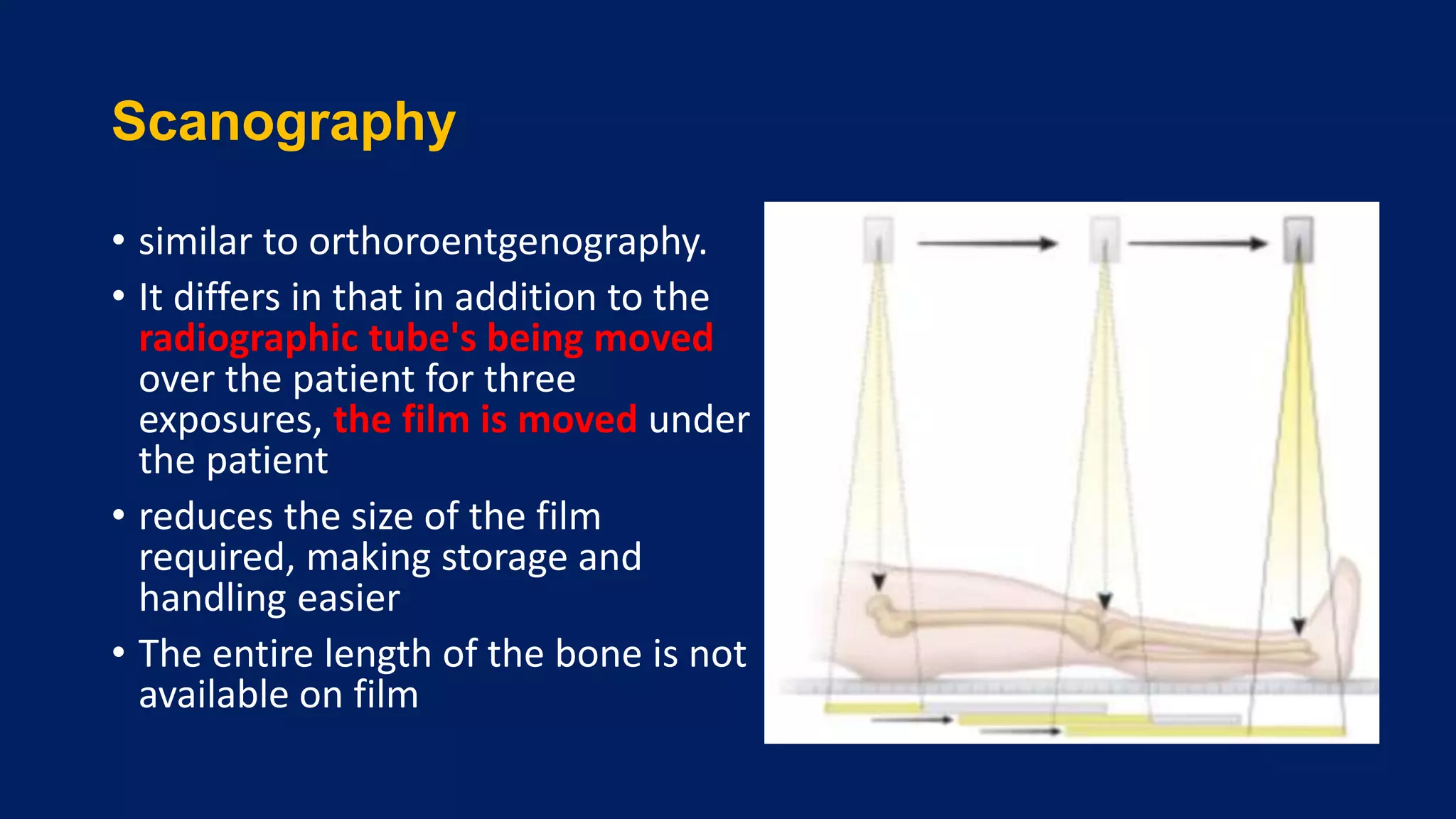
2) Assessment of LLD involves history, physical exam including block tests and measurements, and imaging like radiographs. Compensations can include gait disturbances, back pain, and deformities.
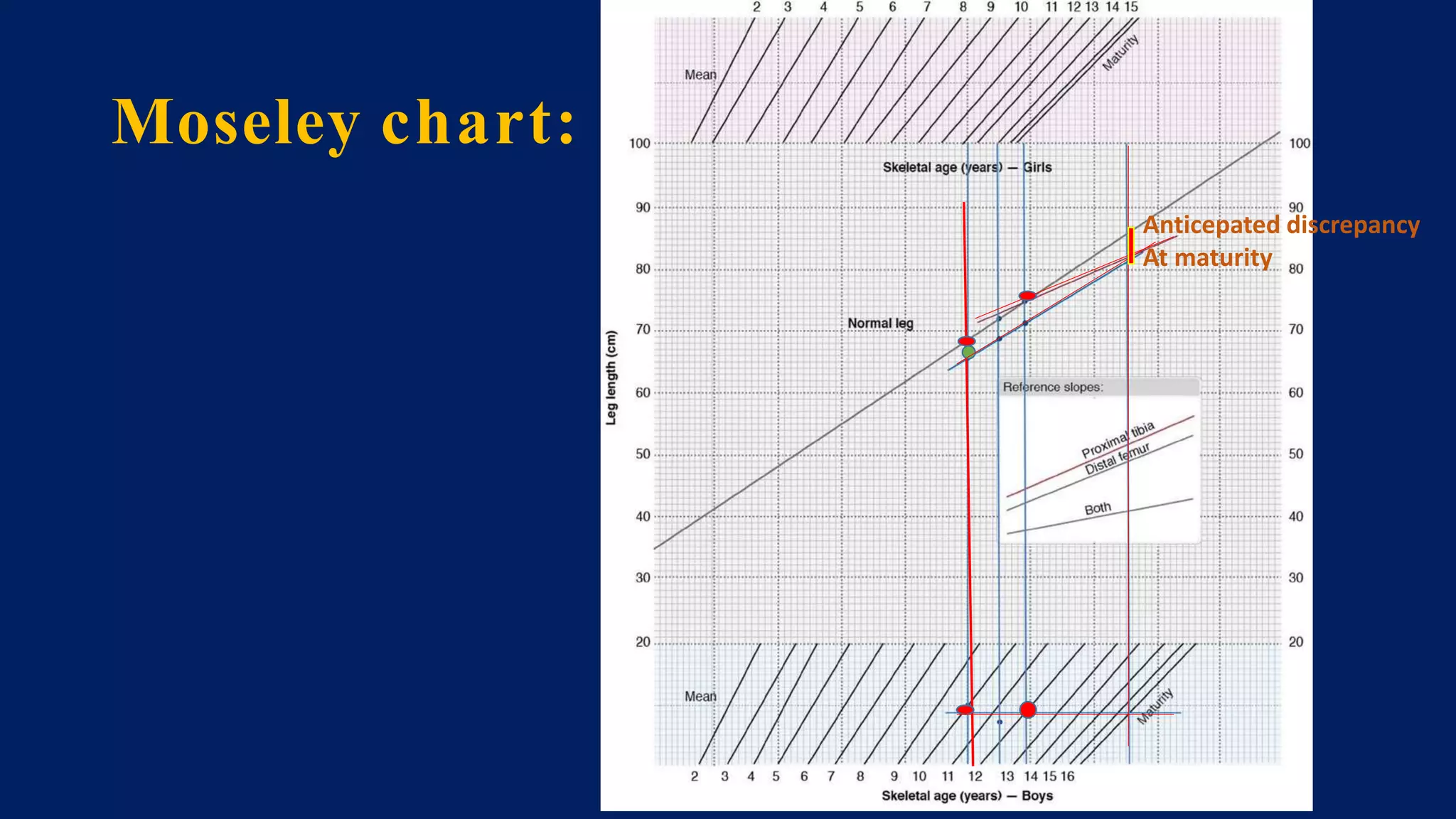
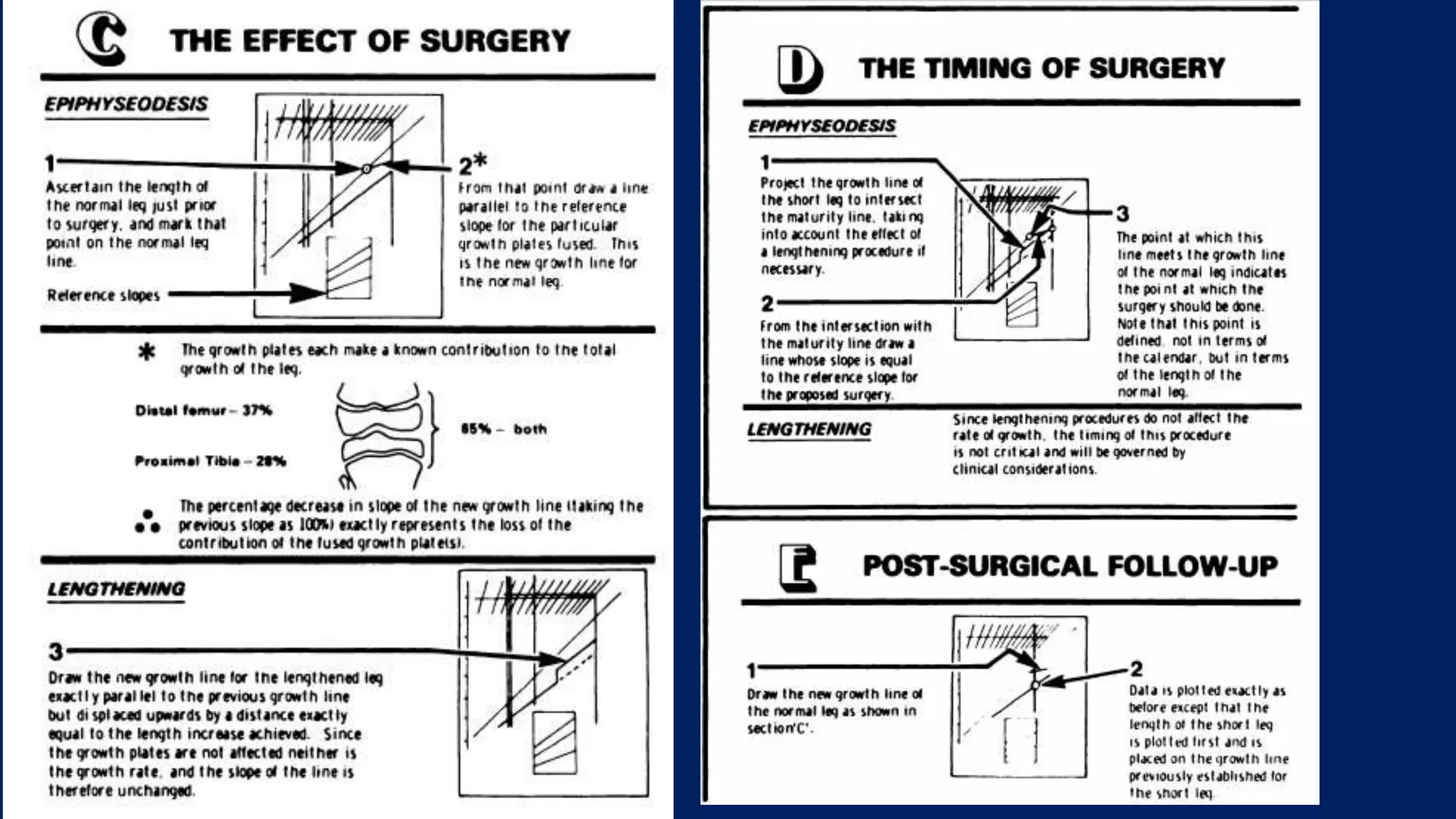
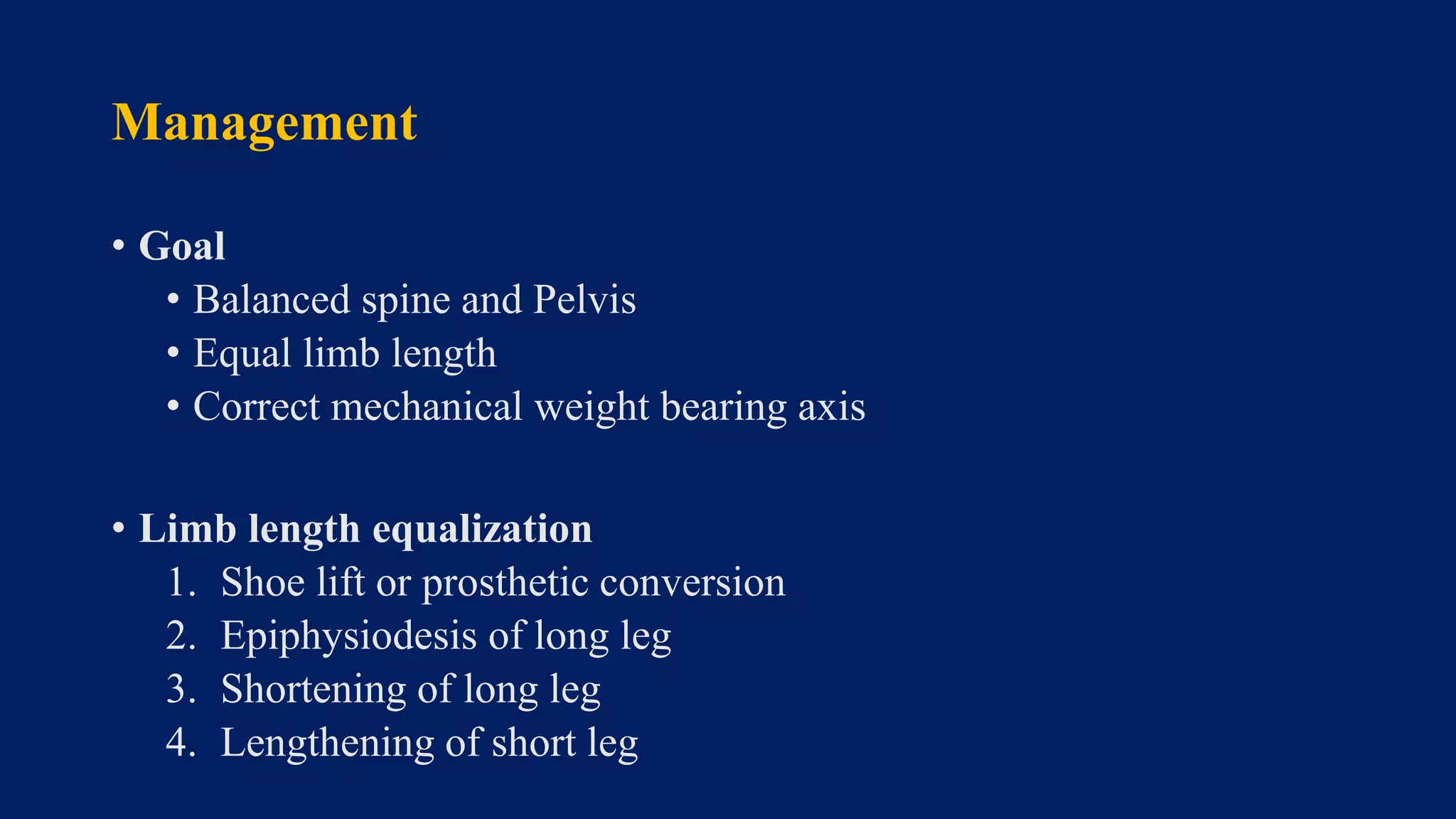
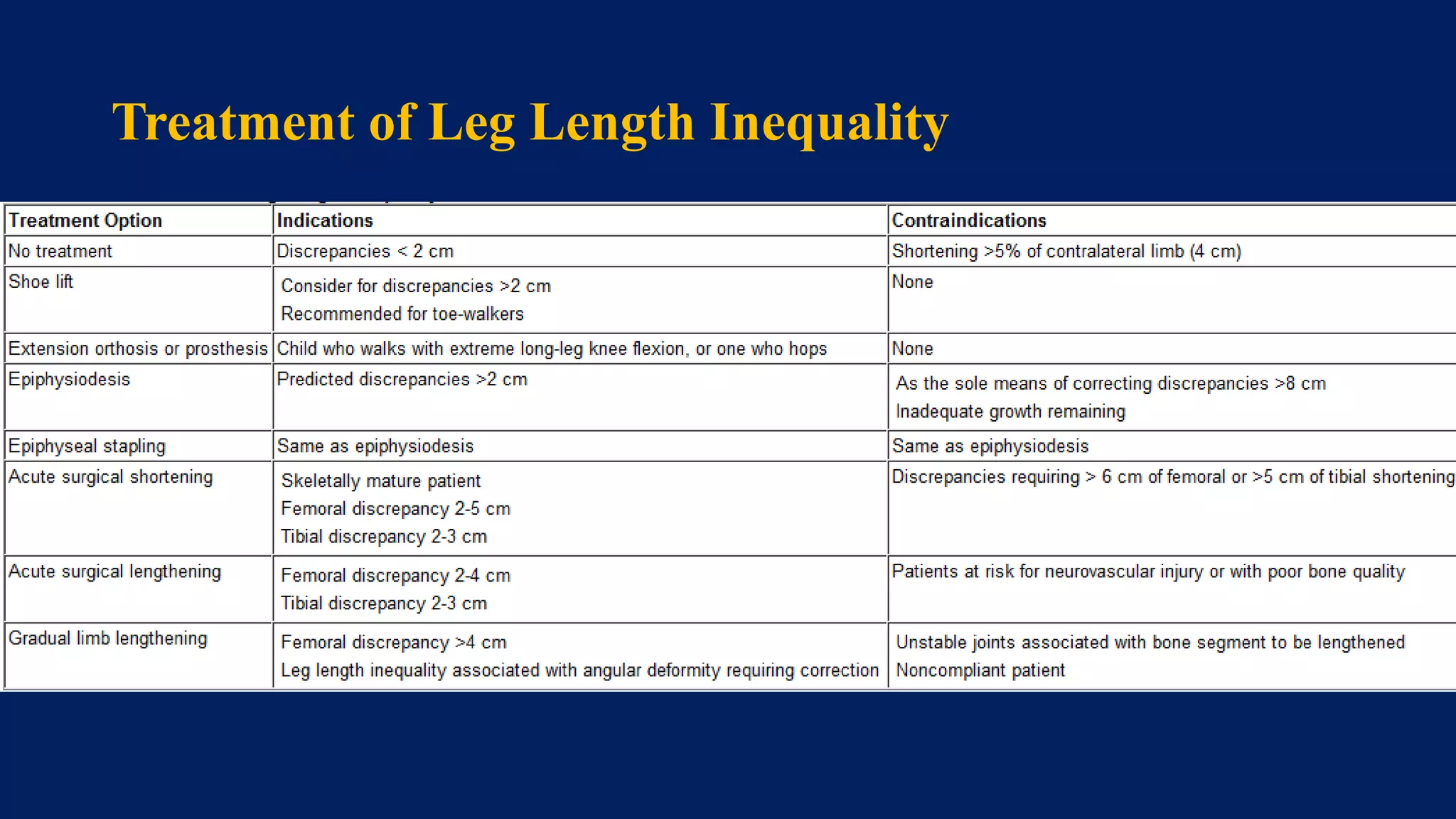
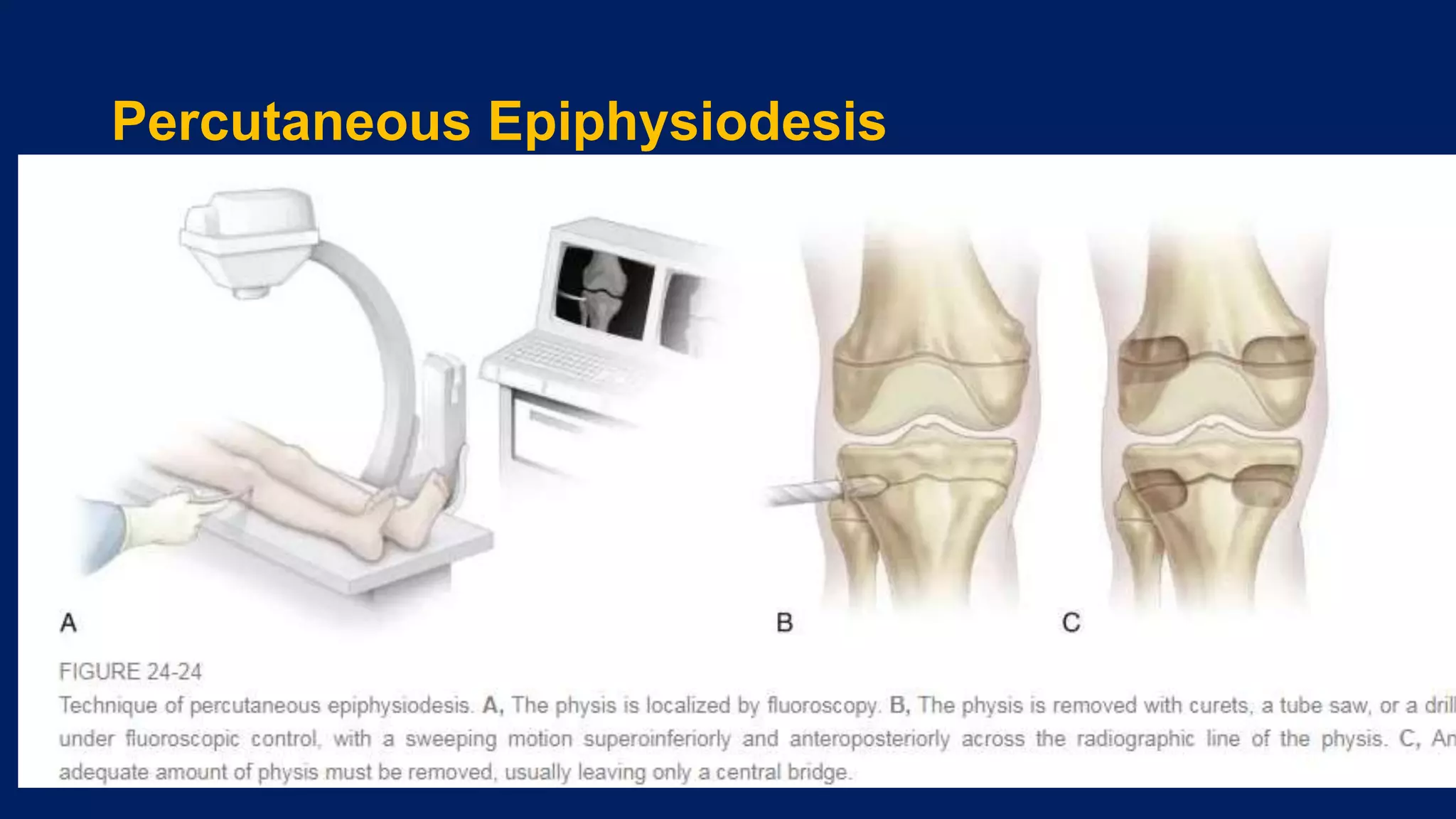
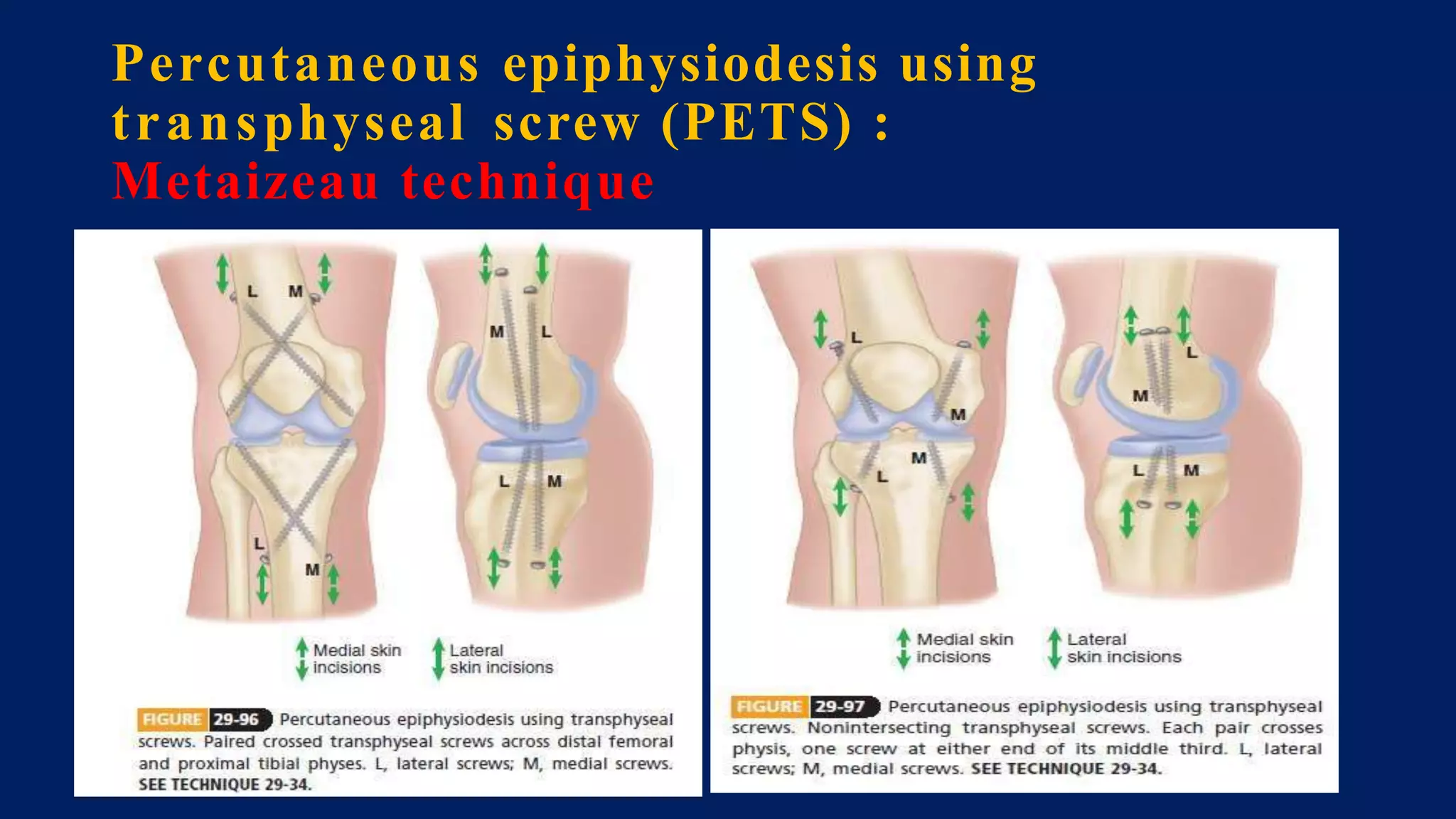
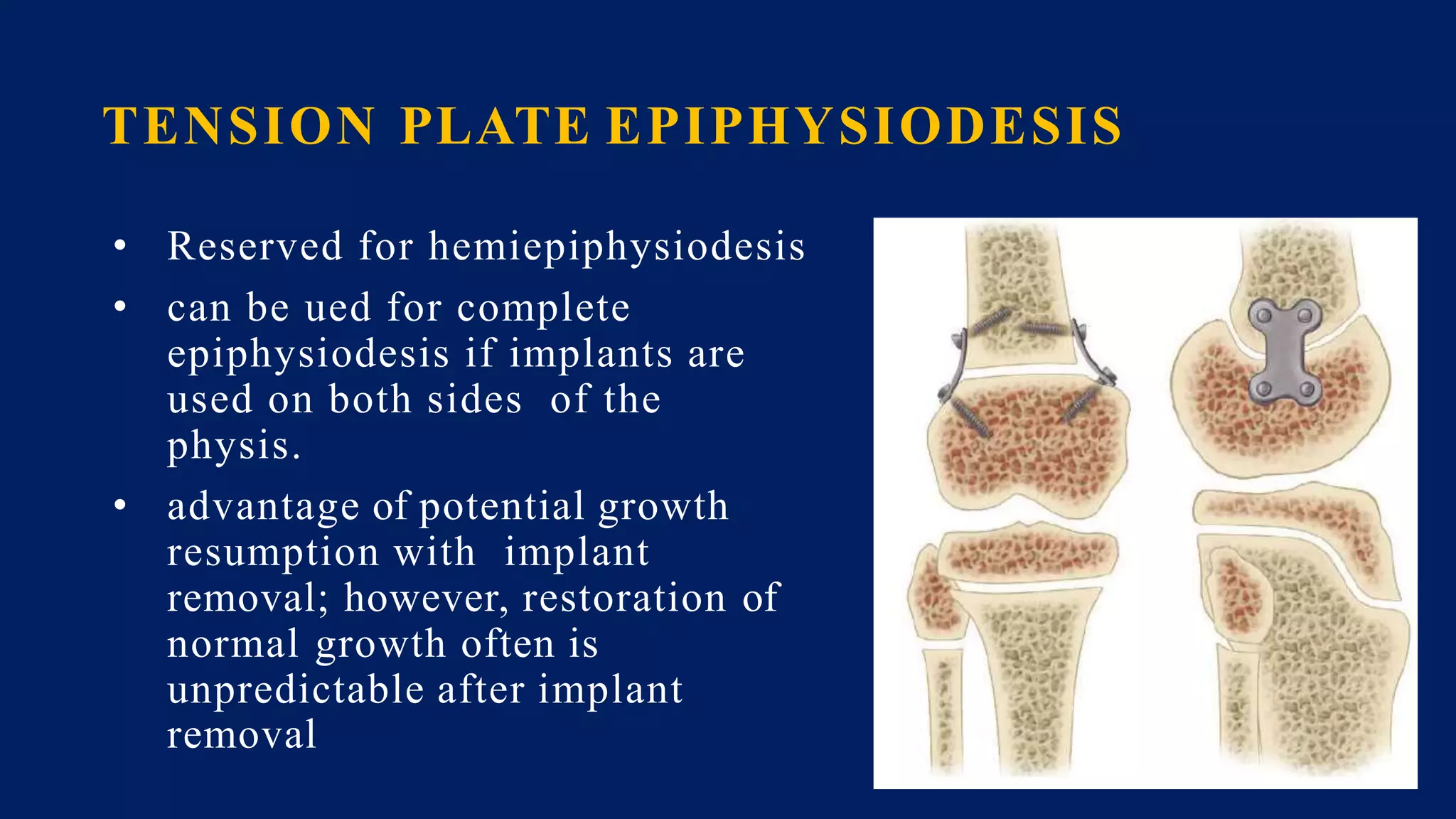
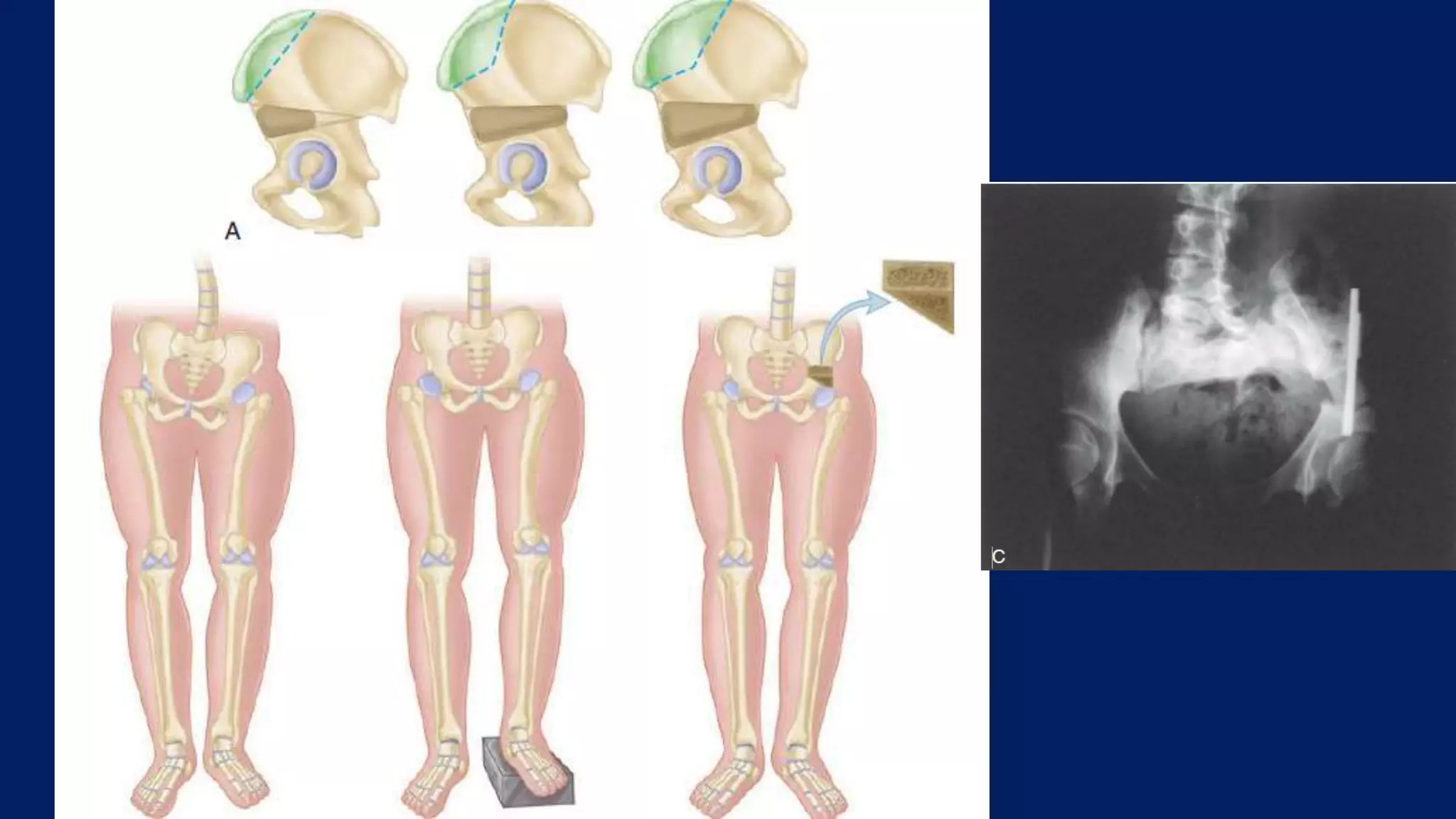
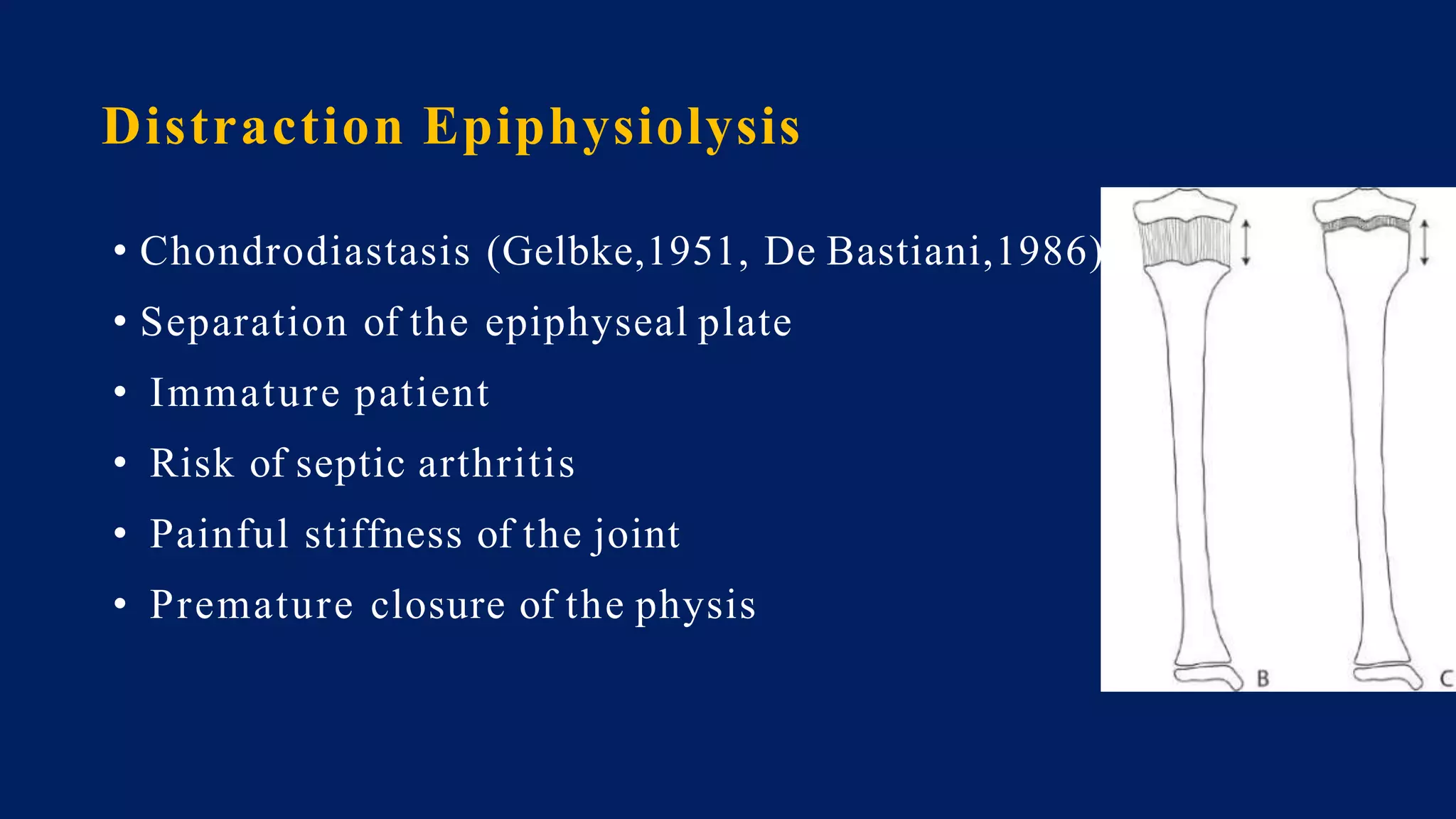
3) Management depends on skeletal maturity and can include shoe lifts, epiphysiodesis to slow long bone growth, acute shortening/lengthening procedures, or gradual lengthening with external or internal fixation devices.