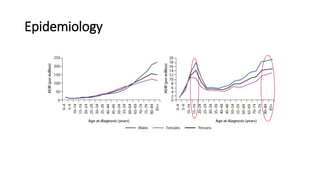
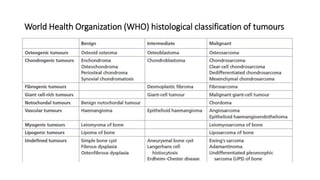
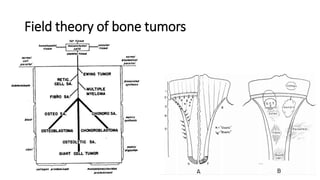
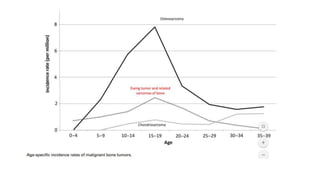
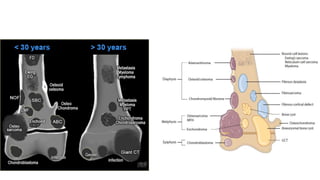
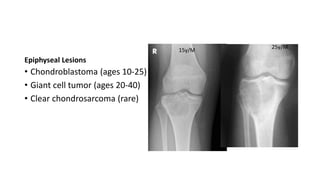
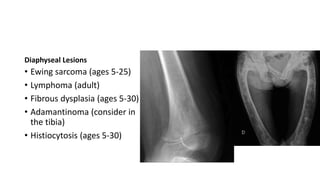
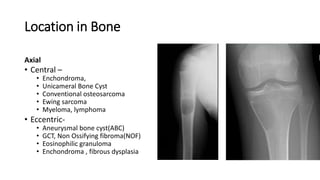
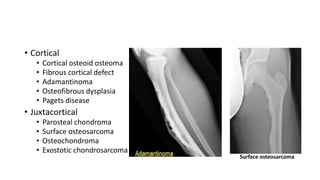
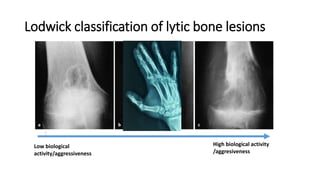
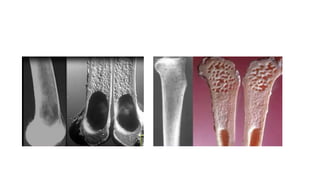
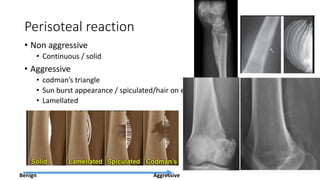
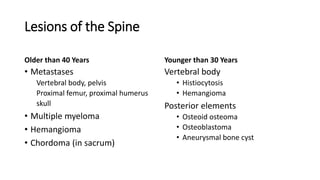
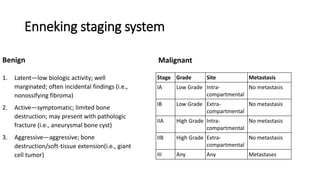
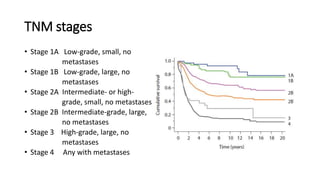
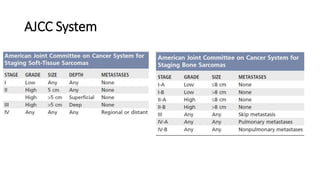
- Bone tumors can be benign, intermediate, or malignant lesions. They are classified based on factors like aggressiveness, metastatic potential, and histological grade.
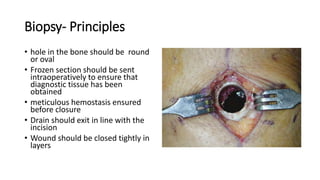
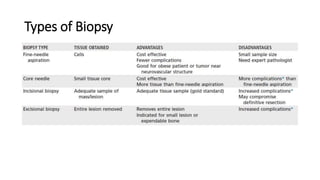
- Imaging tools like x-rays, CT, MRI, and radionuclide scanning are used to evaluate bone tumors and detect any metastases. Biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosis.
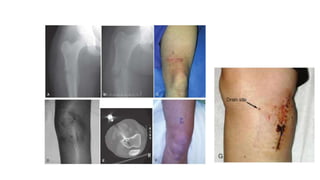
- Treatment depends on the type and stage of the bone tumor. It may involve surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination. The goal is to make the patient disease-free while preserving function and limb salvage when possible.