This document discusses child development and developmental assessments. It covers the following key points:
1. Child development involves growth in four main areas: gross motor, fine motor, personal-social, and language. Development follows a typical sequence but rates vary between children.
2. Developmental assessments evaluate a child's skills and compare them to typical ages and milestones. They are used to identify delays, provide support and interventions, and reassure parents of normal development.
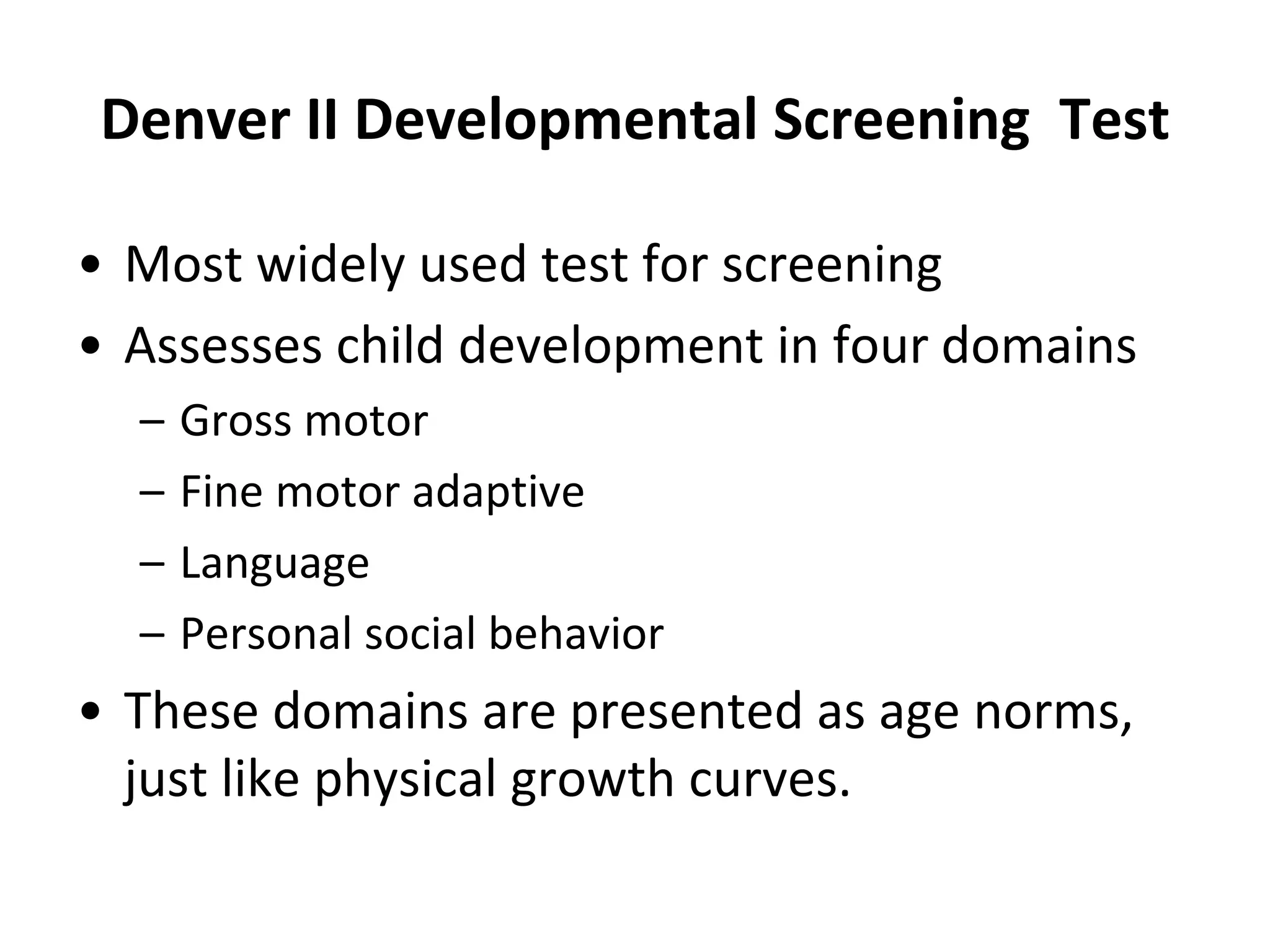
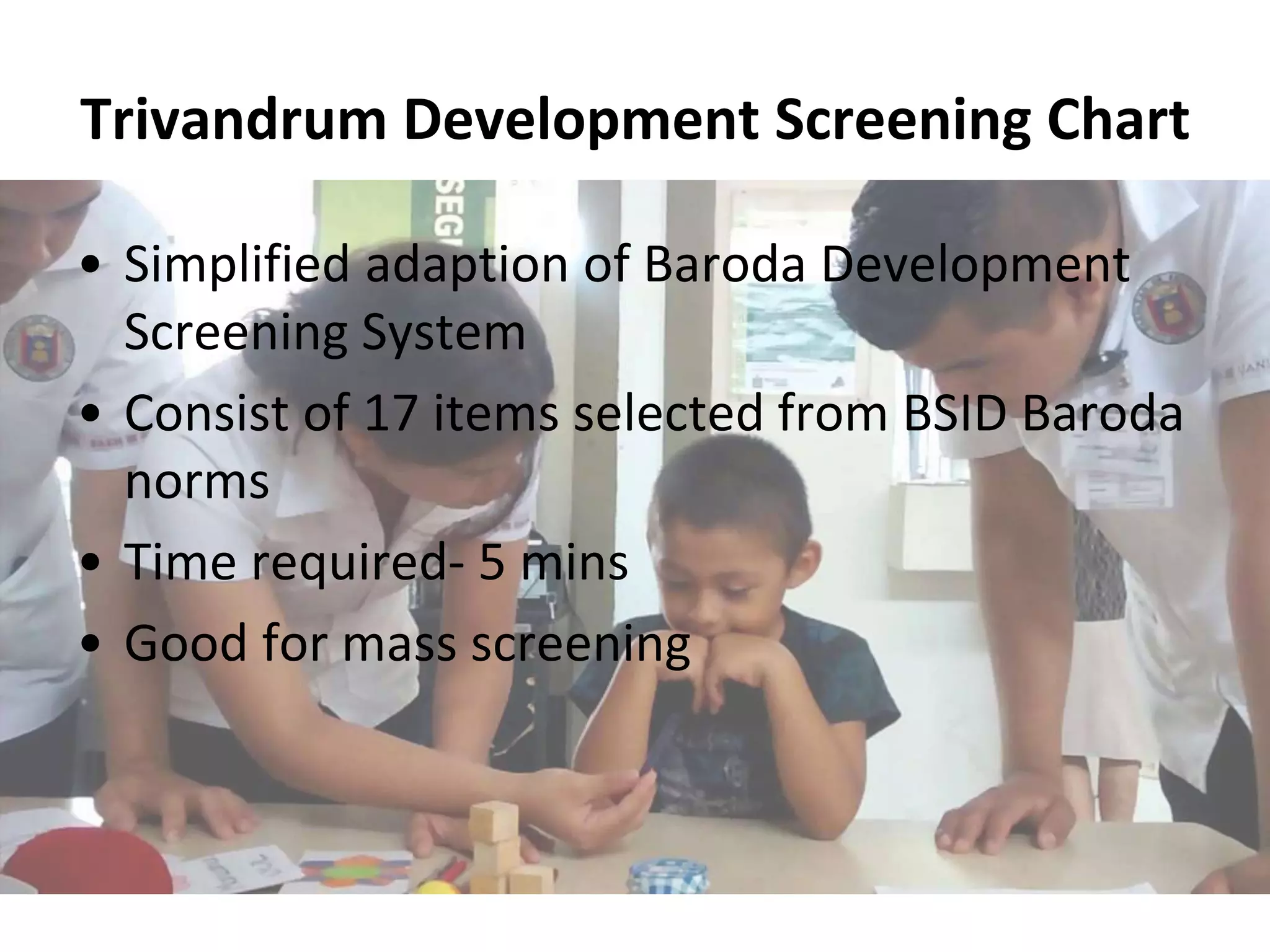
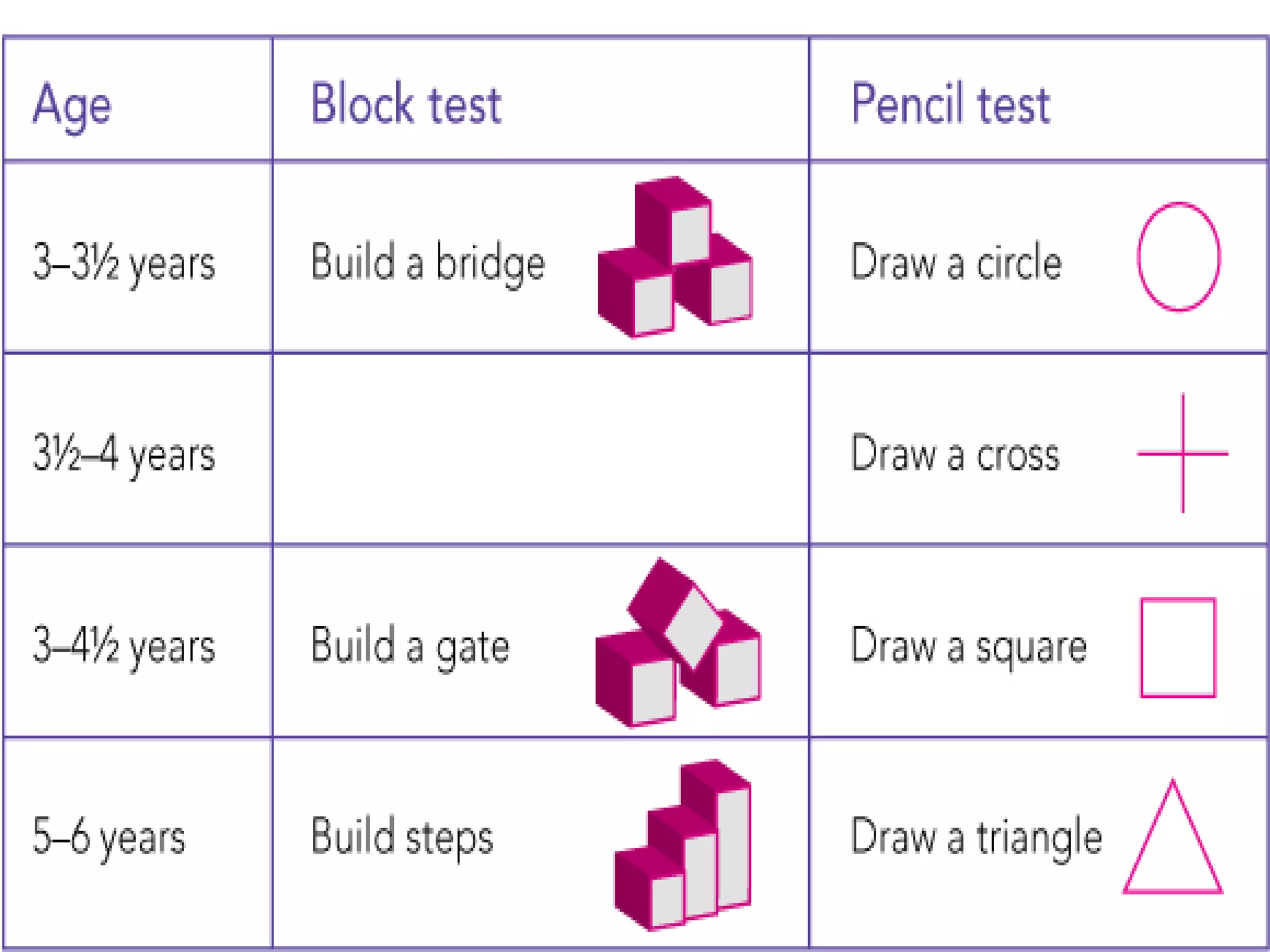
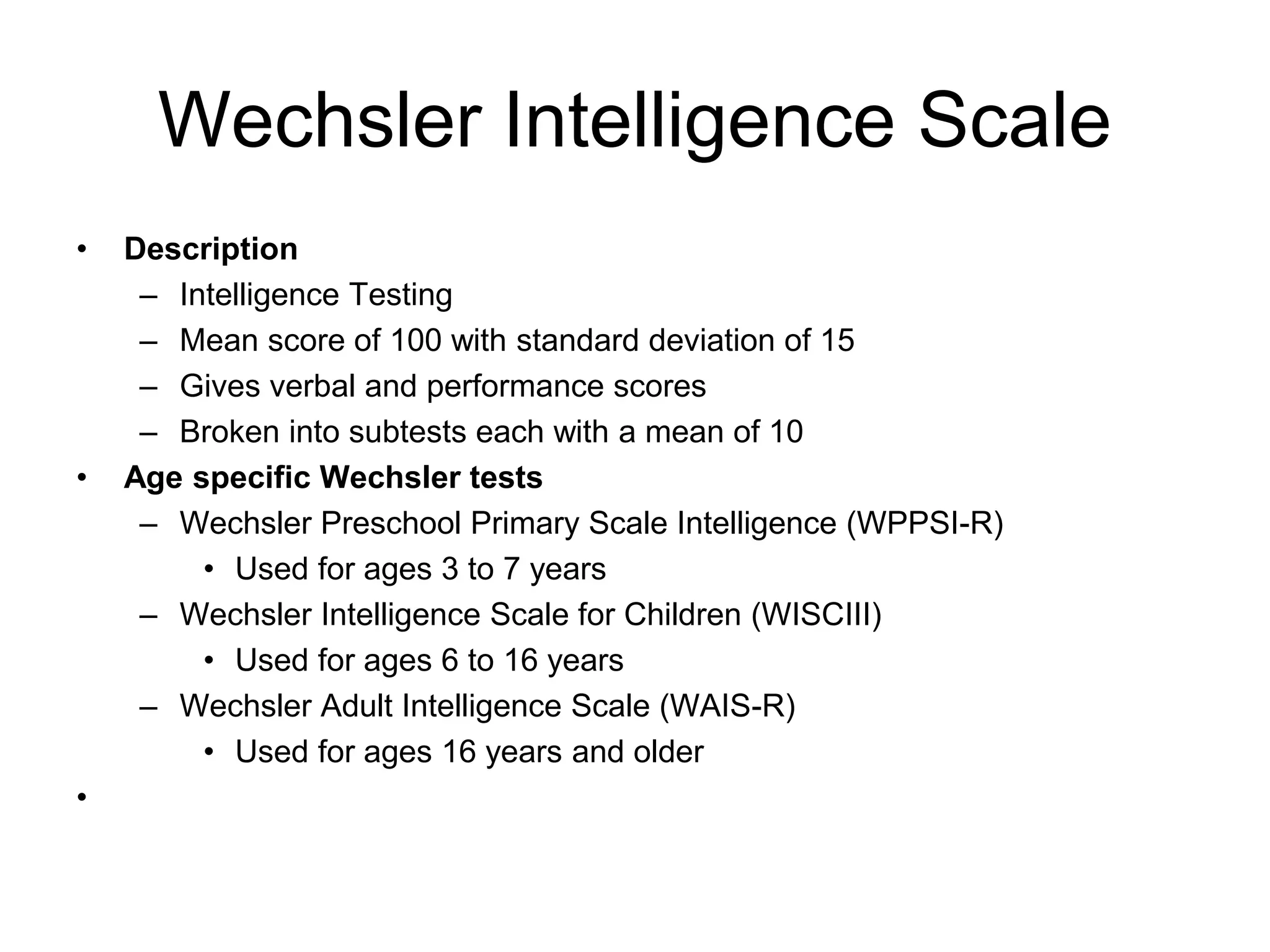
3. Common developmental screening tests include Denver-II, Ages and Stages Questionnaire (ASQ), and Phatak's Baroda Screening Test. Definitive tests like Bayley Scales and Wechsler Scales are used