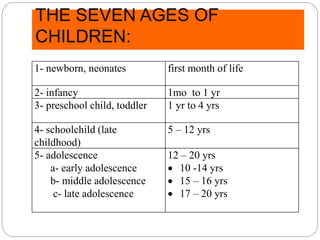
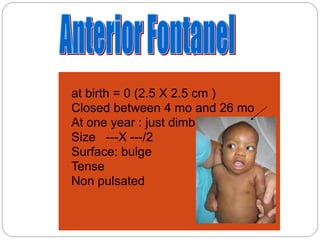
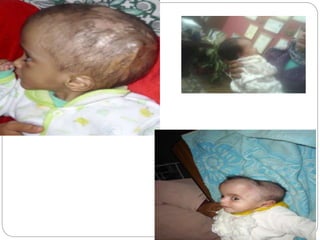
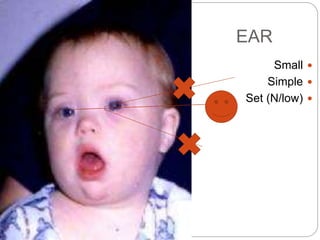
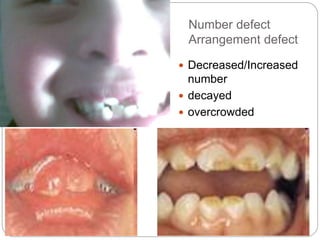
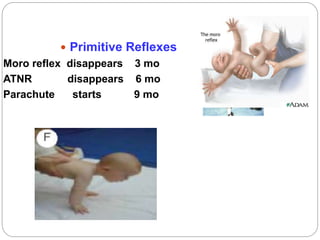
This document provides an extensive overview of pediatric neurology, emphasizing the developmental stages of children from newborns to late adolescence. It outlines essential practices for evaluating and communicating with children, detailing key considerations for medical history, clinical examination, and differential diagnosis of neurological conditions. The text also covers specific anatomical and assessment details relevant to pediatric patients, such as head measurements, facial features, and the assessment of neurological function.