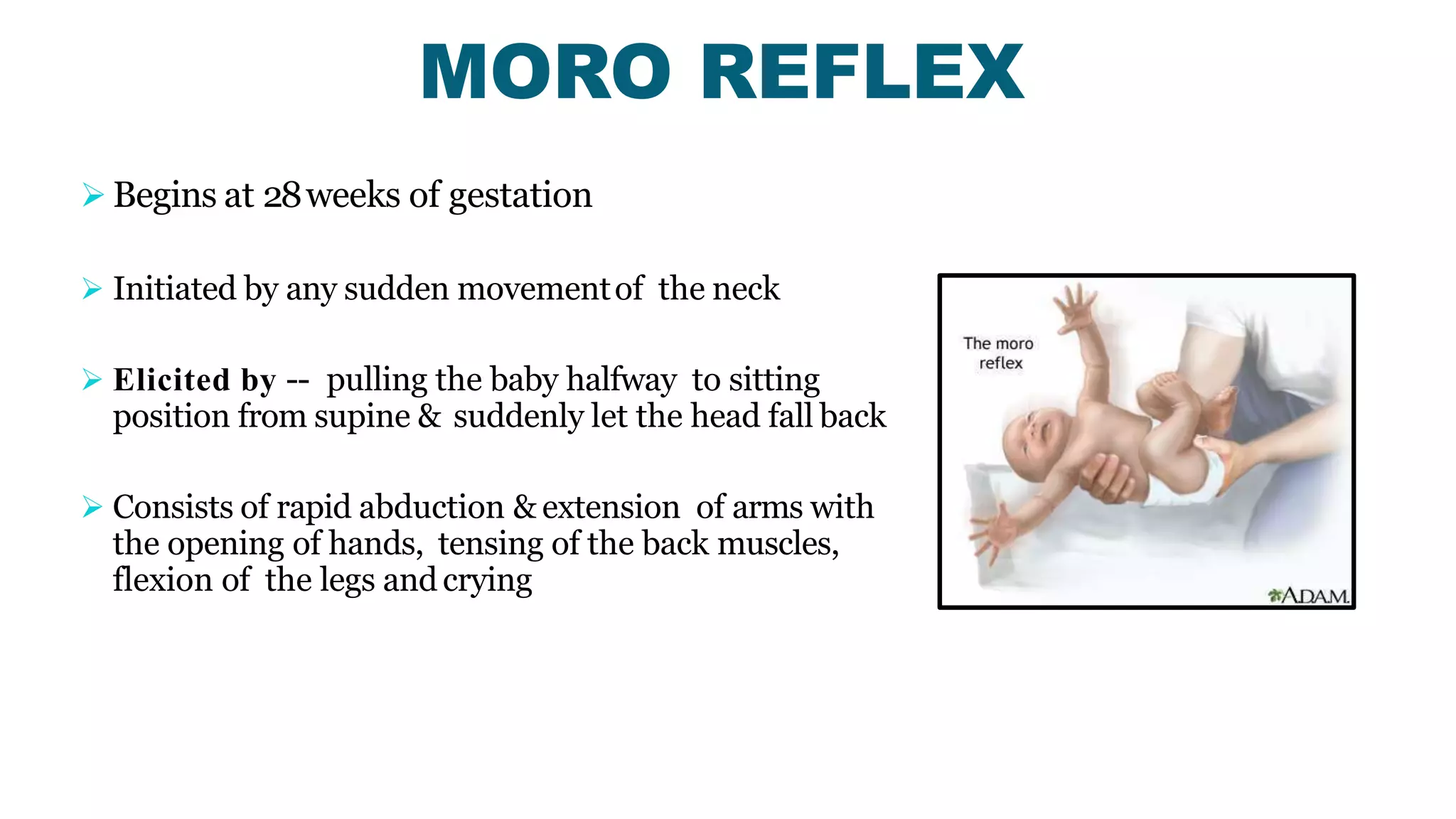
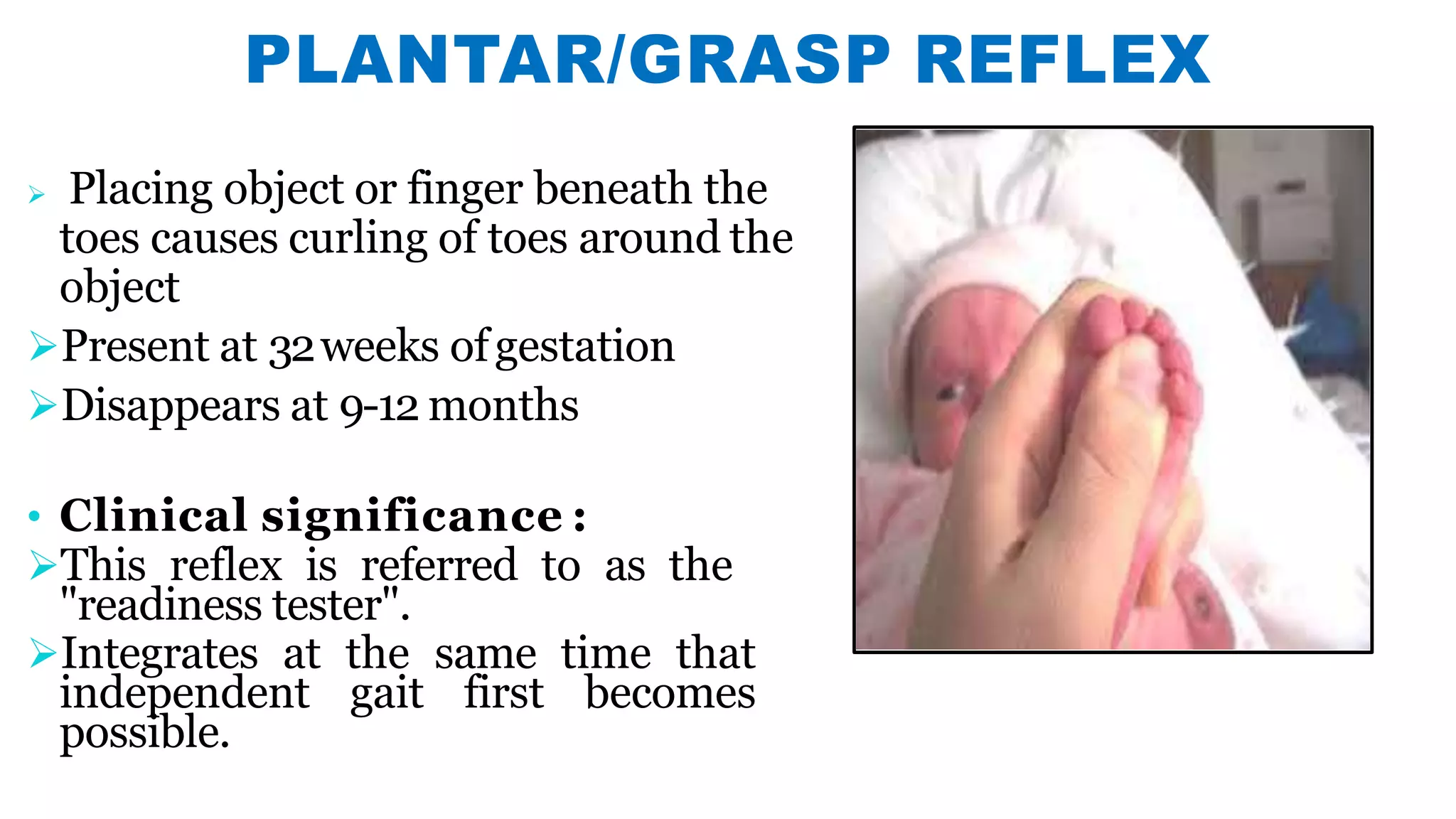
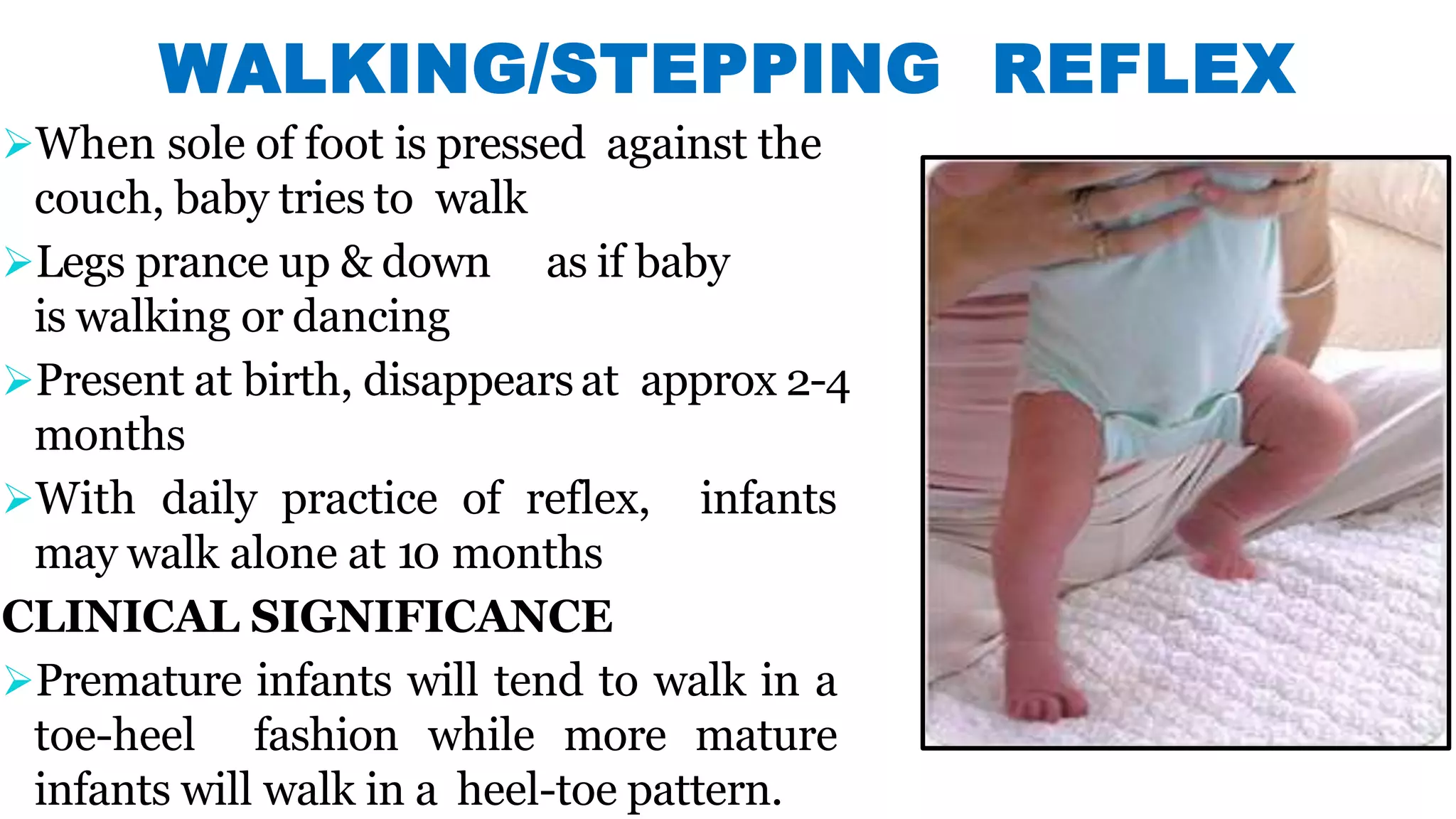
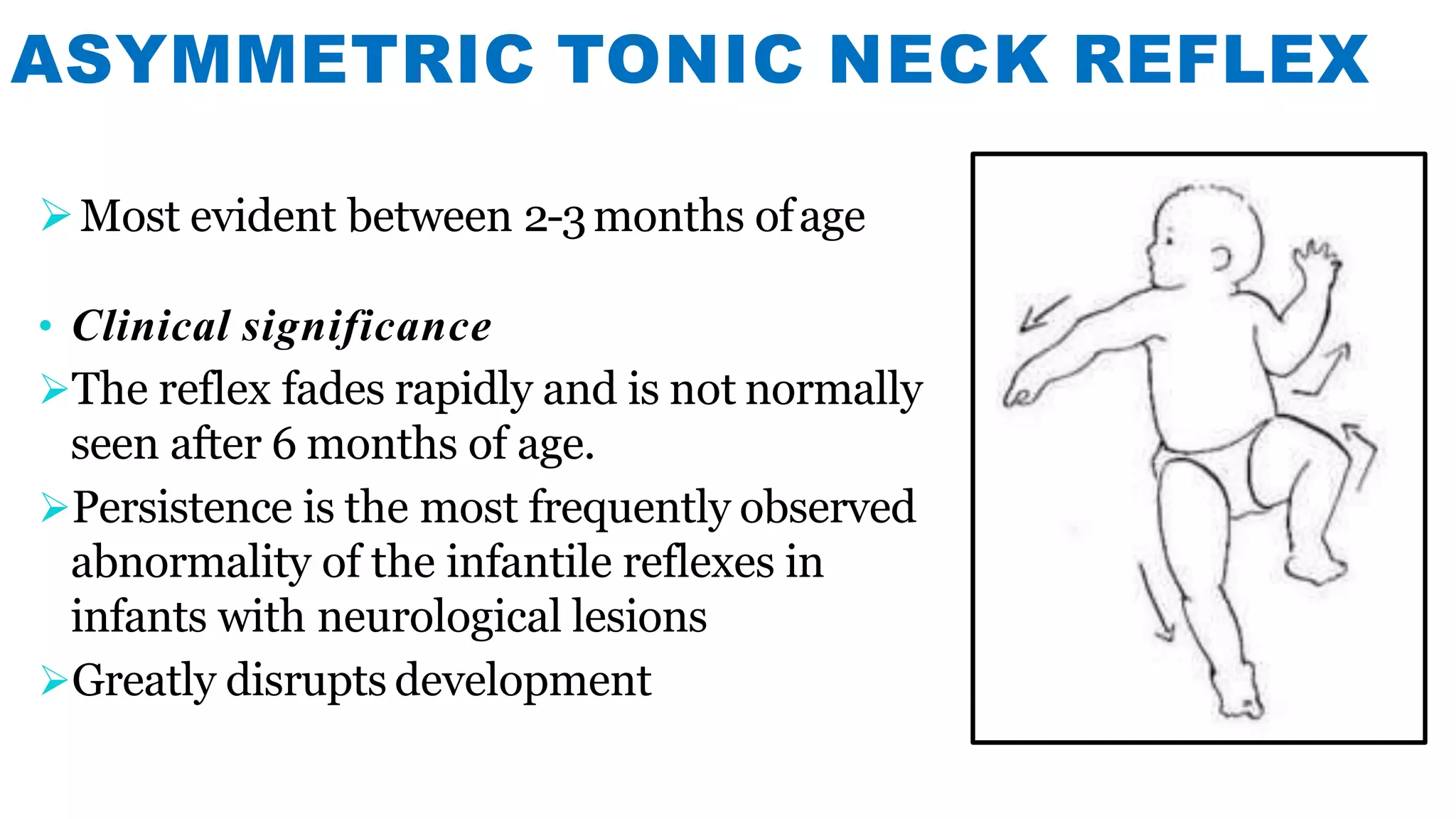
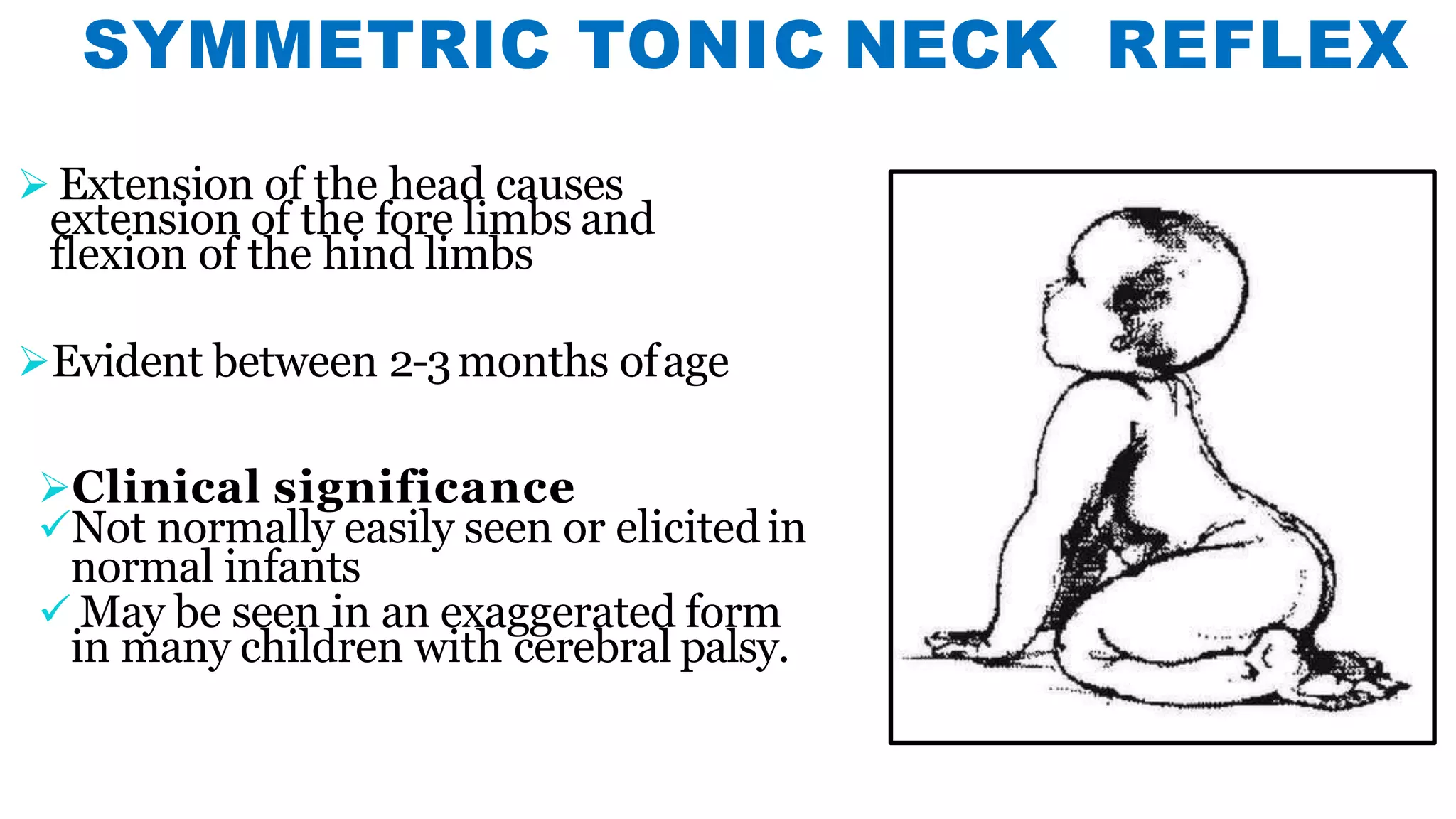
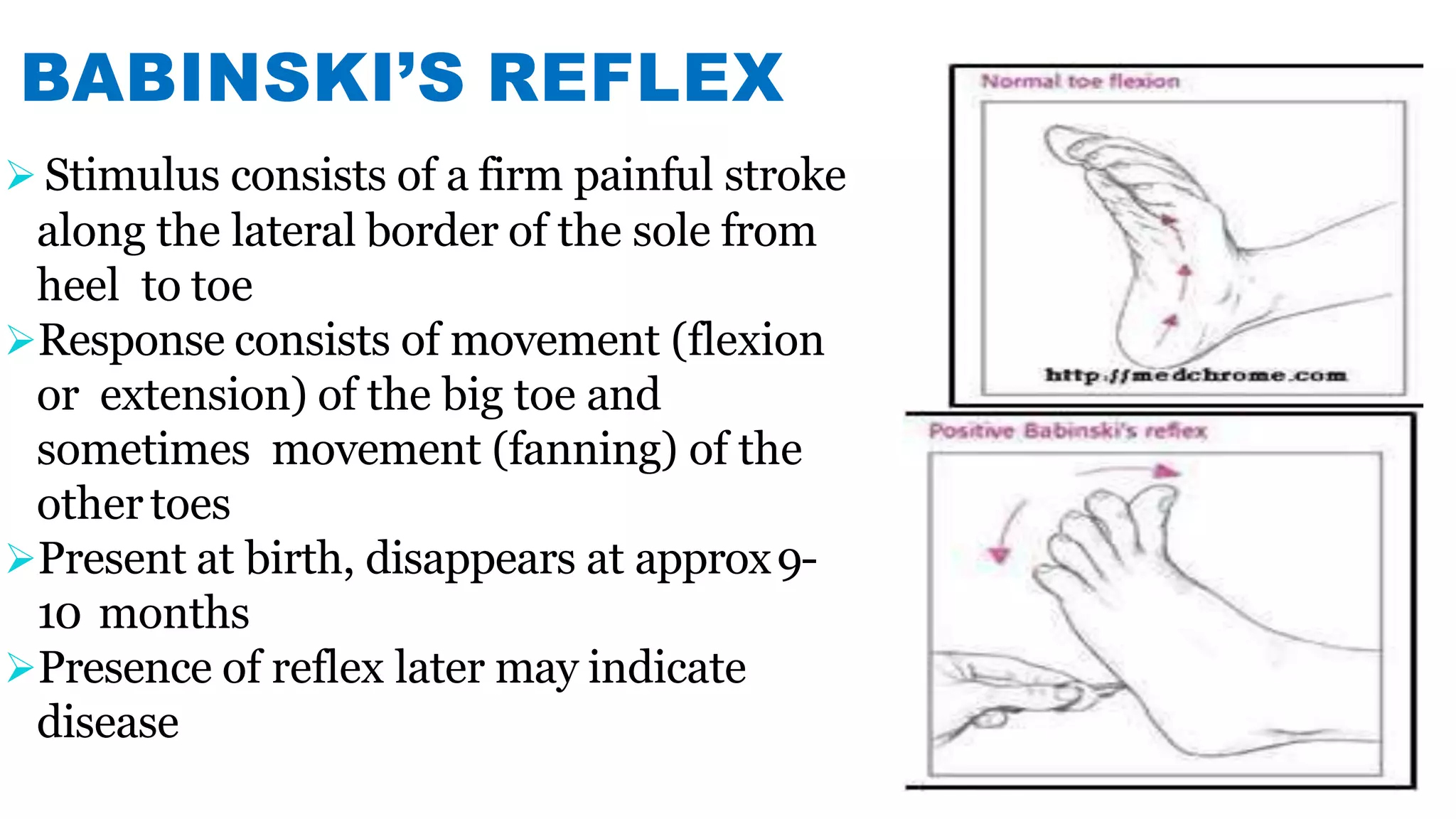
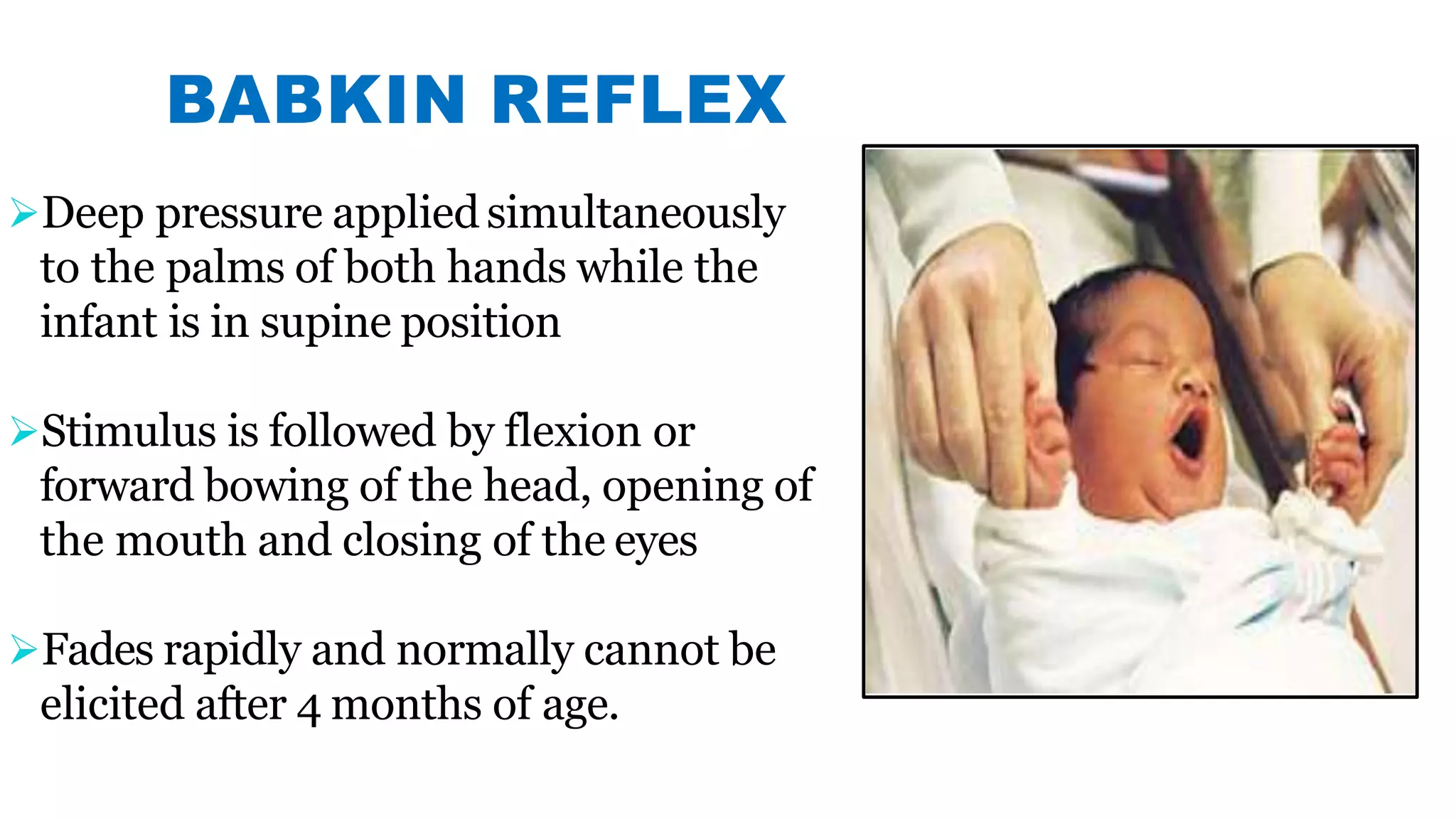
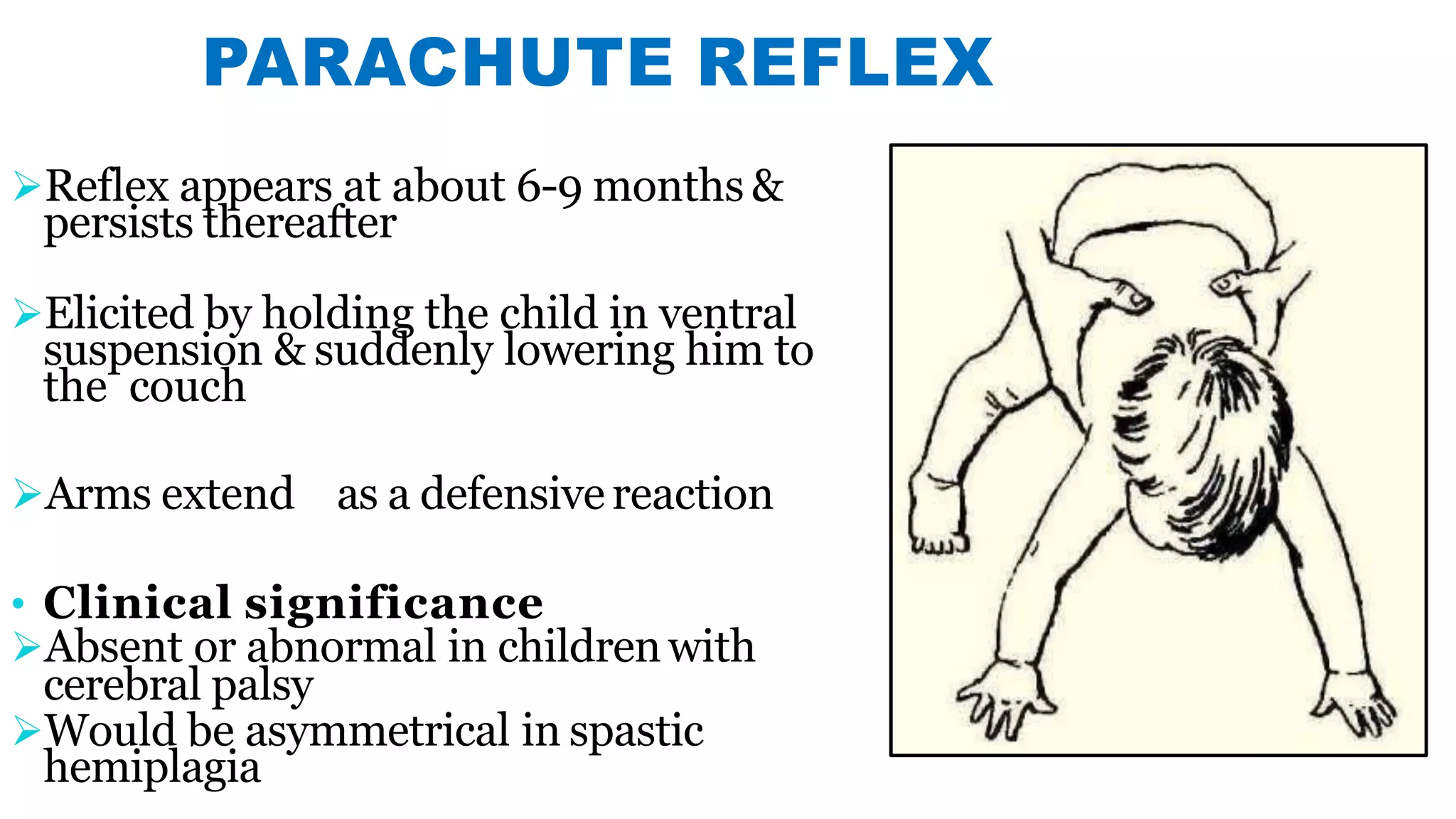
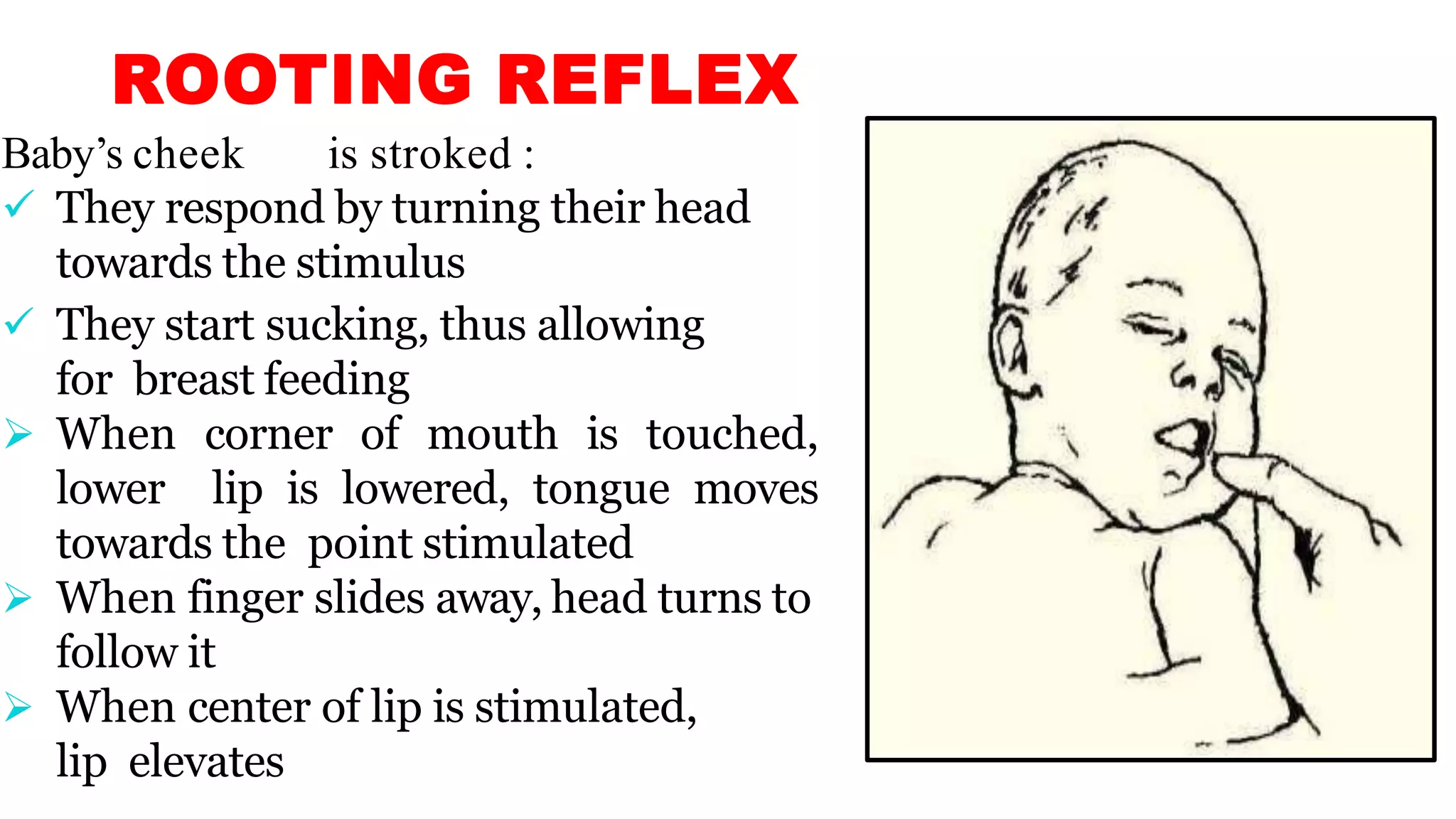
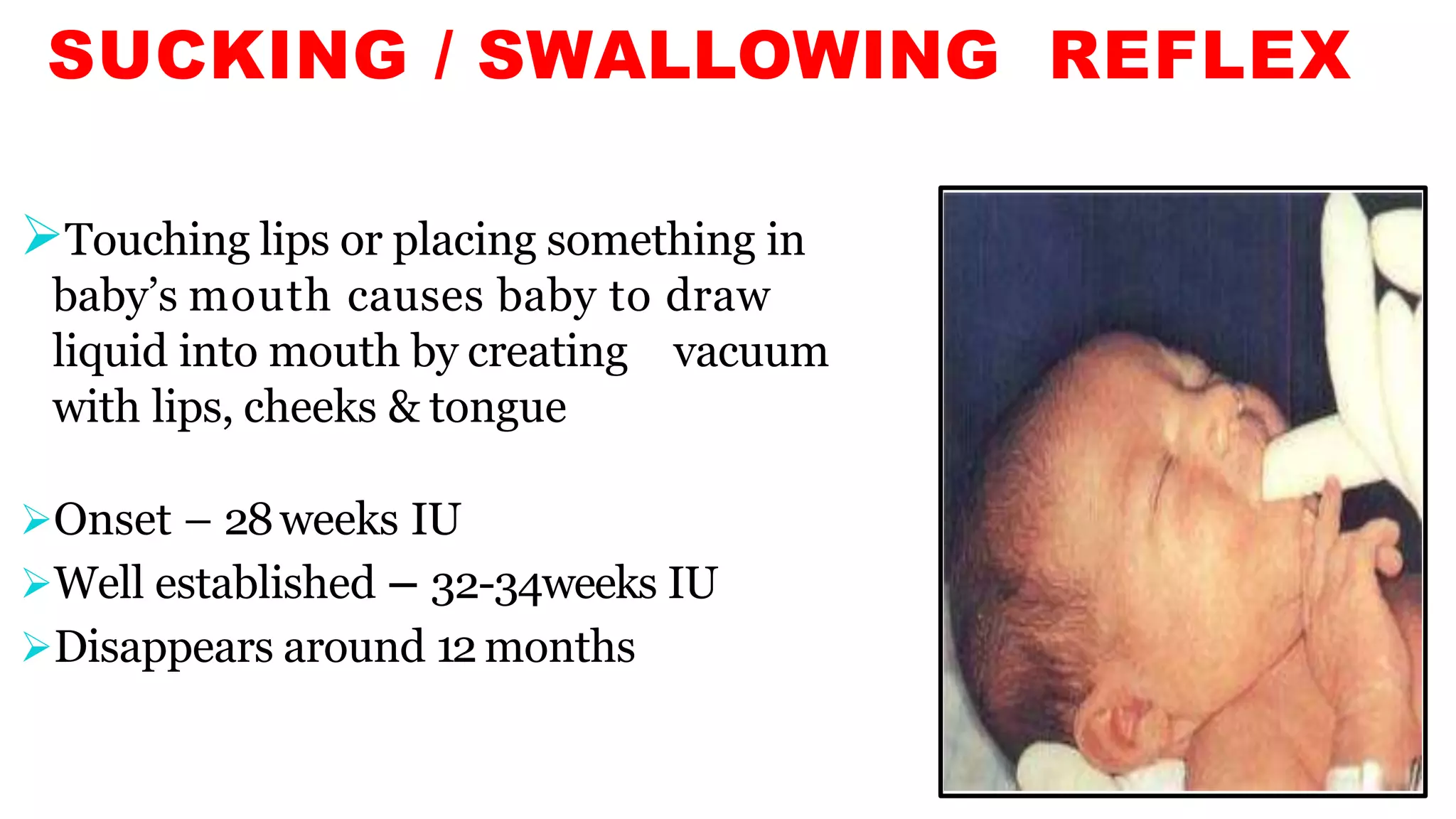
Newborn reflexes are involuntary responses that help newborns survive. The document lists and describes several important reflexes including the Moro reflex, palmar grasp reflex, plantar grasp reflex, asymmetric tonic neck reflex, Babinski's reflex, rooting reflex, sucking reflex, and gag reflex. These reflexes begin developing in the womb and help with functions like breathing, grasping, swallowing, and protecting sensitive organs. Their presence and function provide insights into neurological development and maturity in newborns.