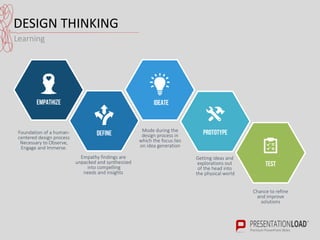
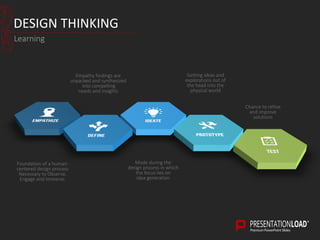
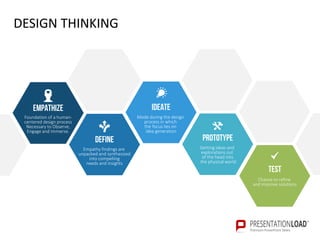
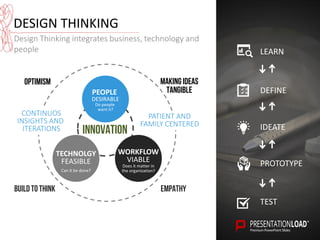
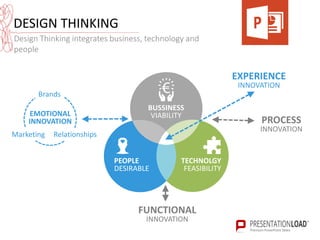
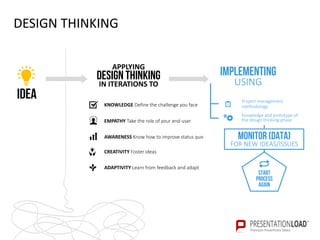
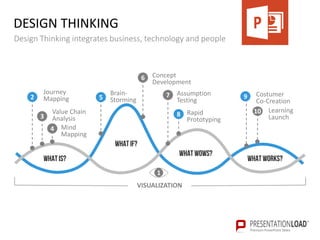
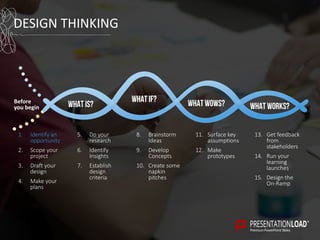
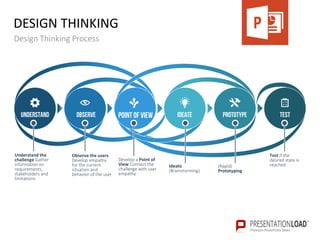
The document provides a comprehensive overview of design thinking, emphasizing its human-centered and collaborative approach to problem-solving. It outlines various modes of the design thinking process, including empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test, highlighting their purposes and methodologies. Additionally, it discusses the integration of business, technology, and user needs, advocating for an iterative process to continually improve solutions based on user feedback and insights.