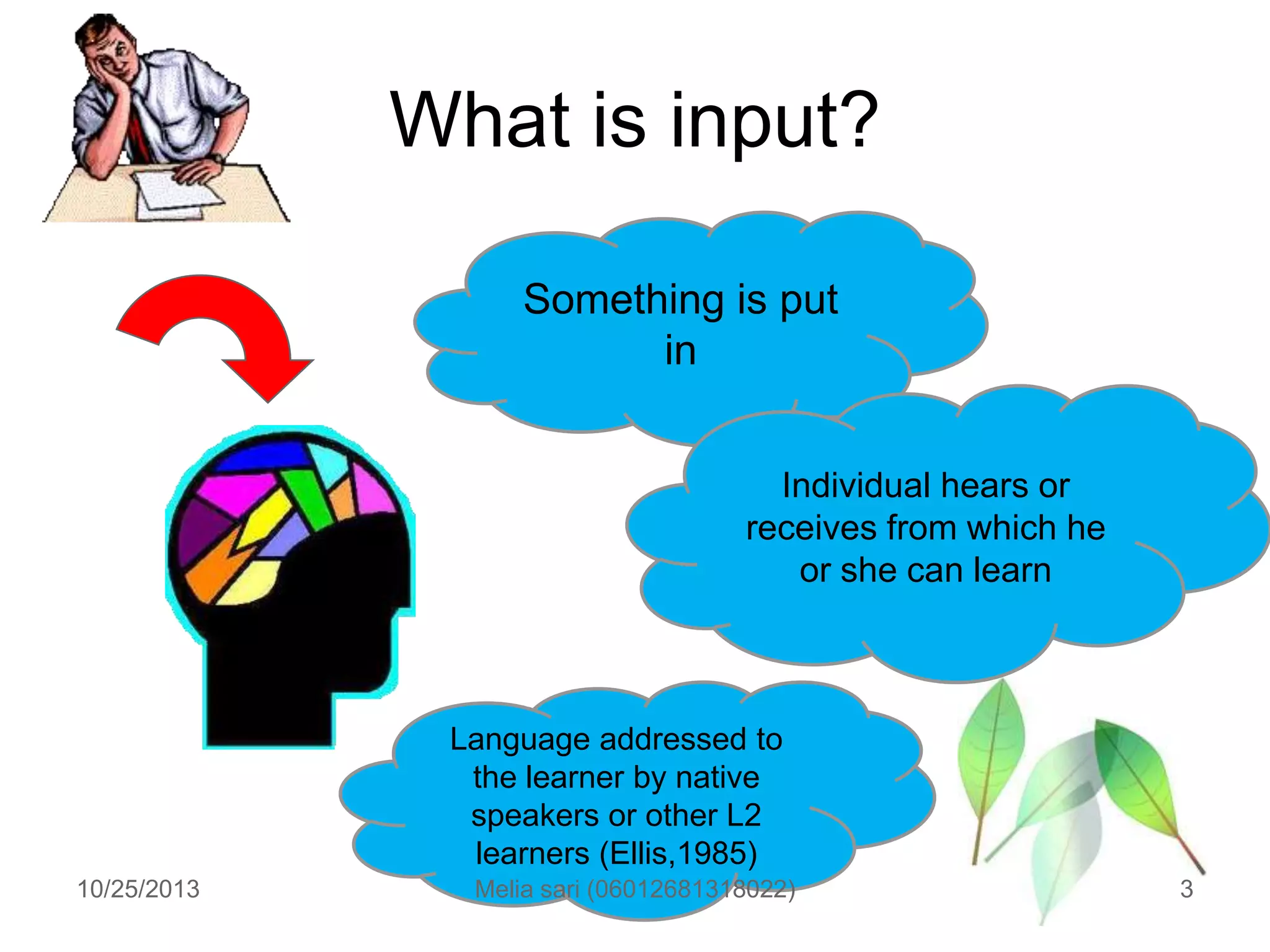
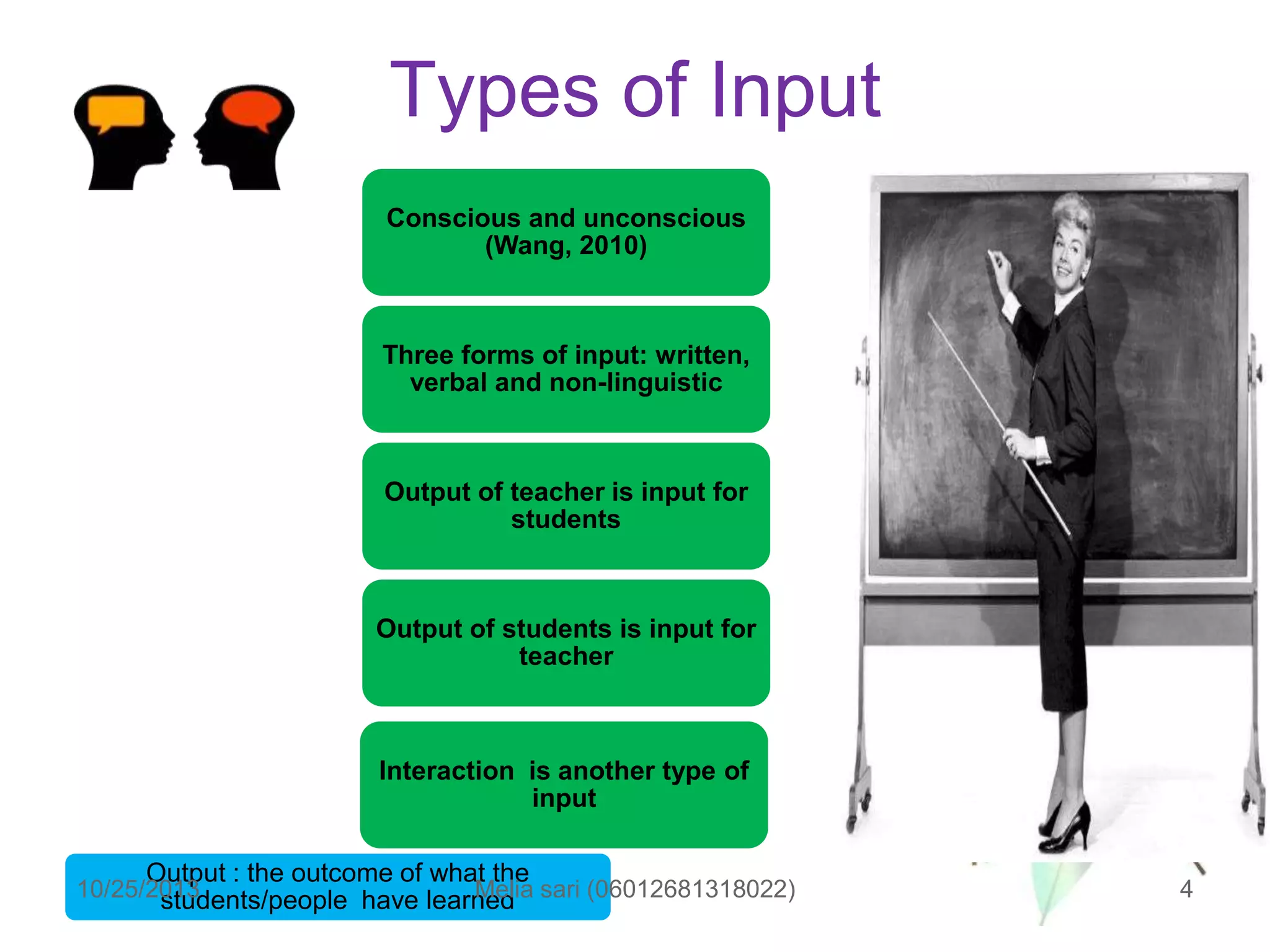
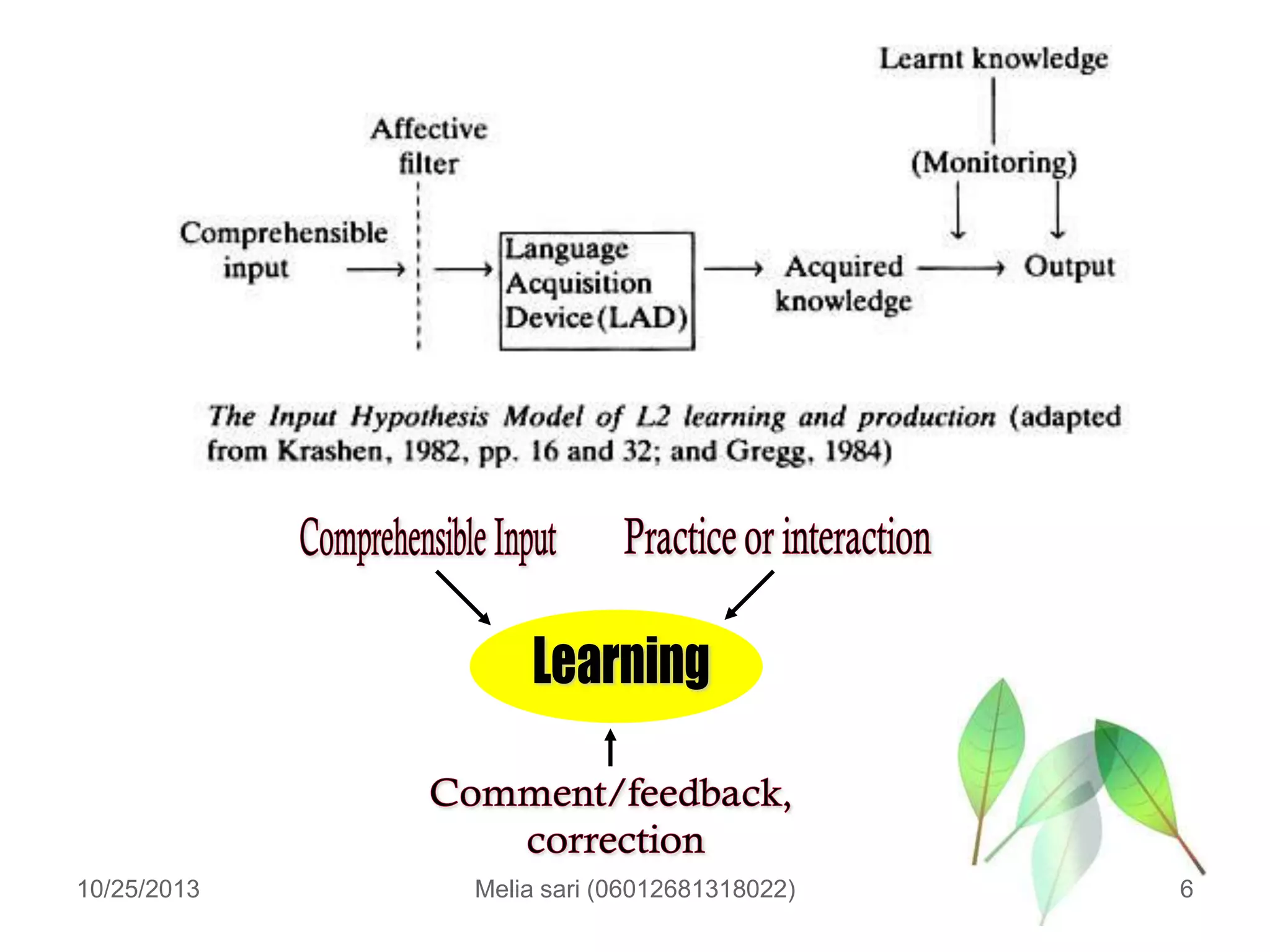
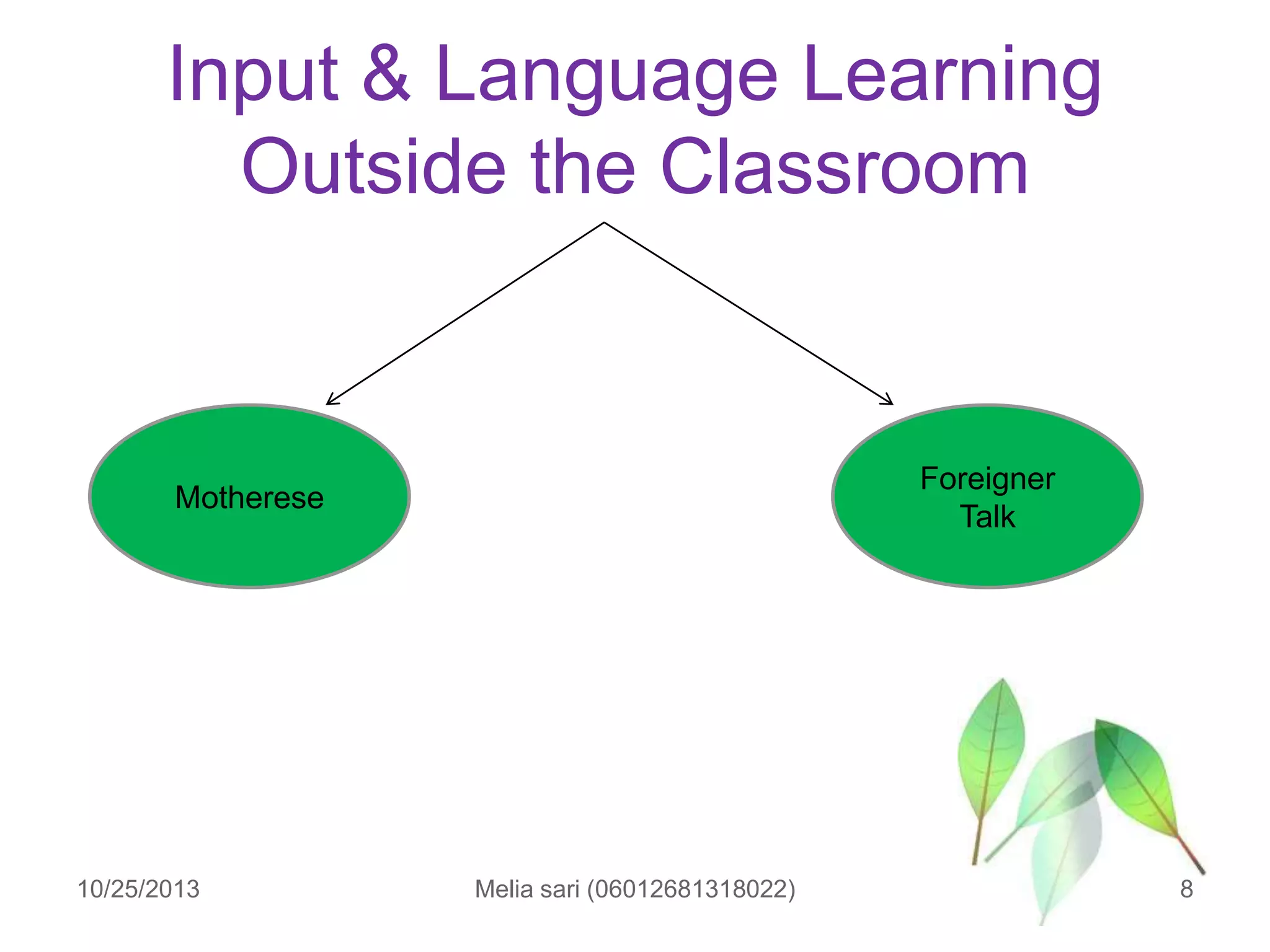
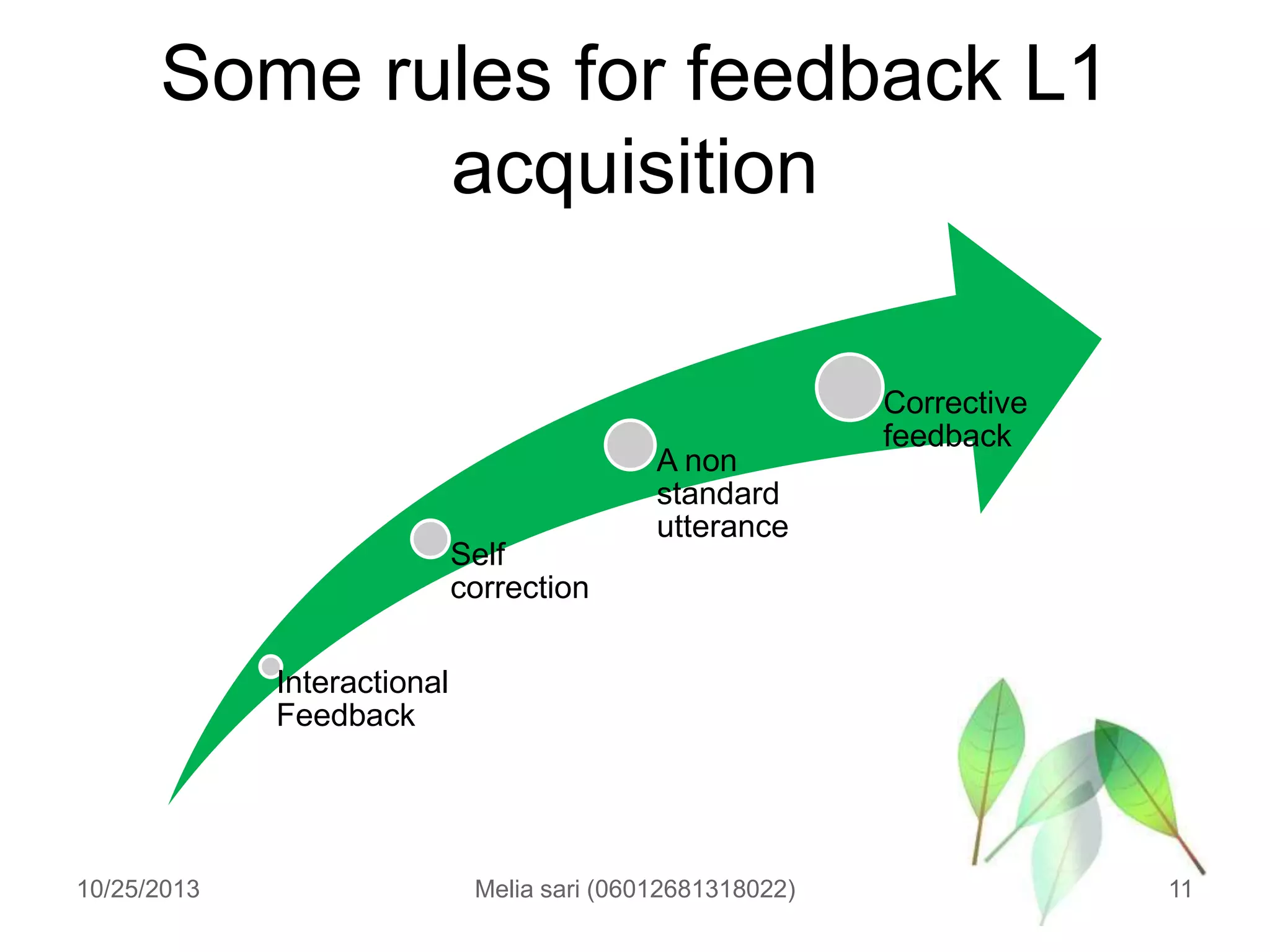
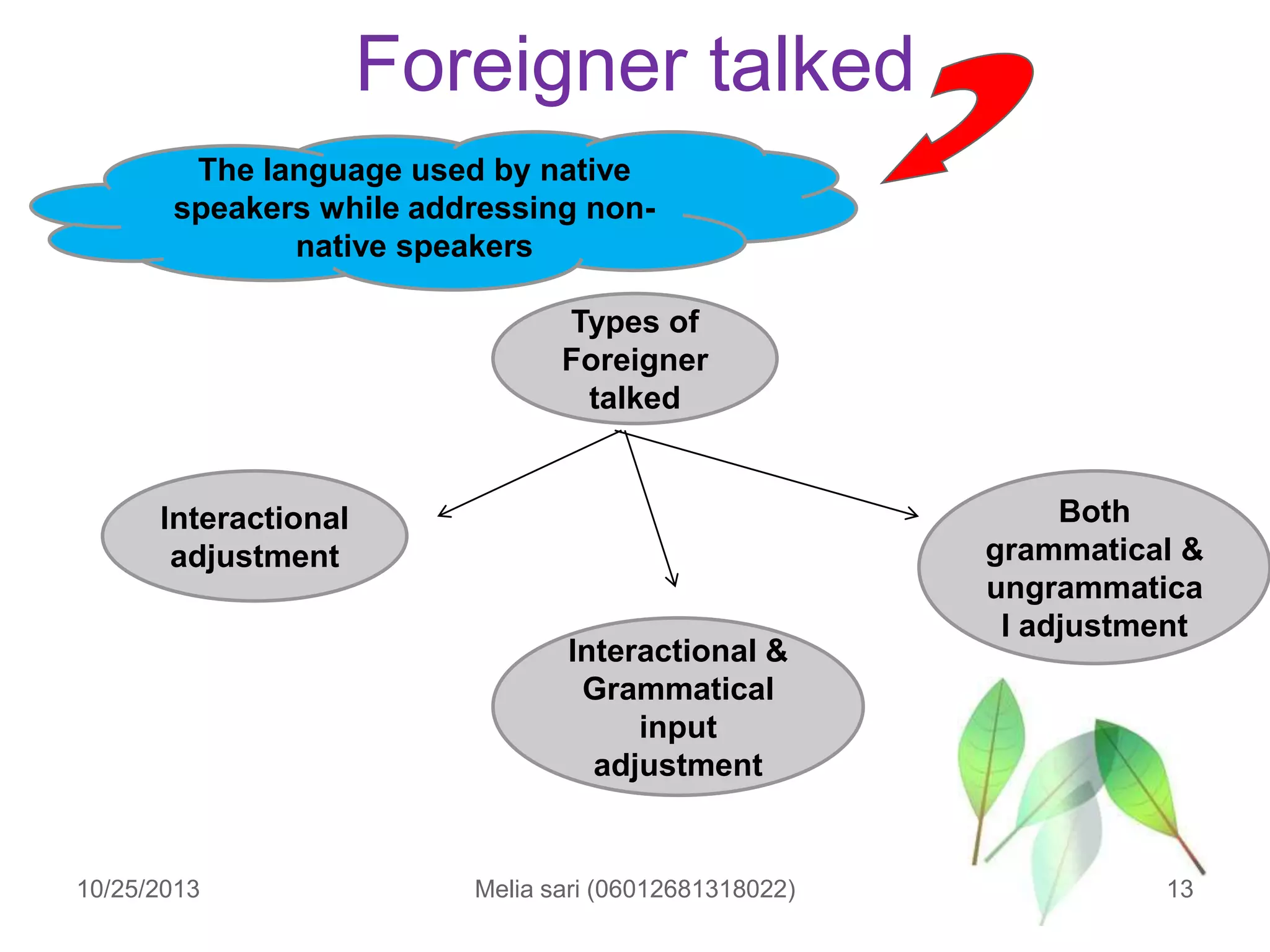
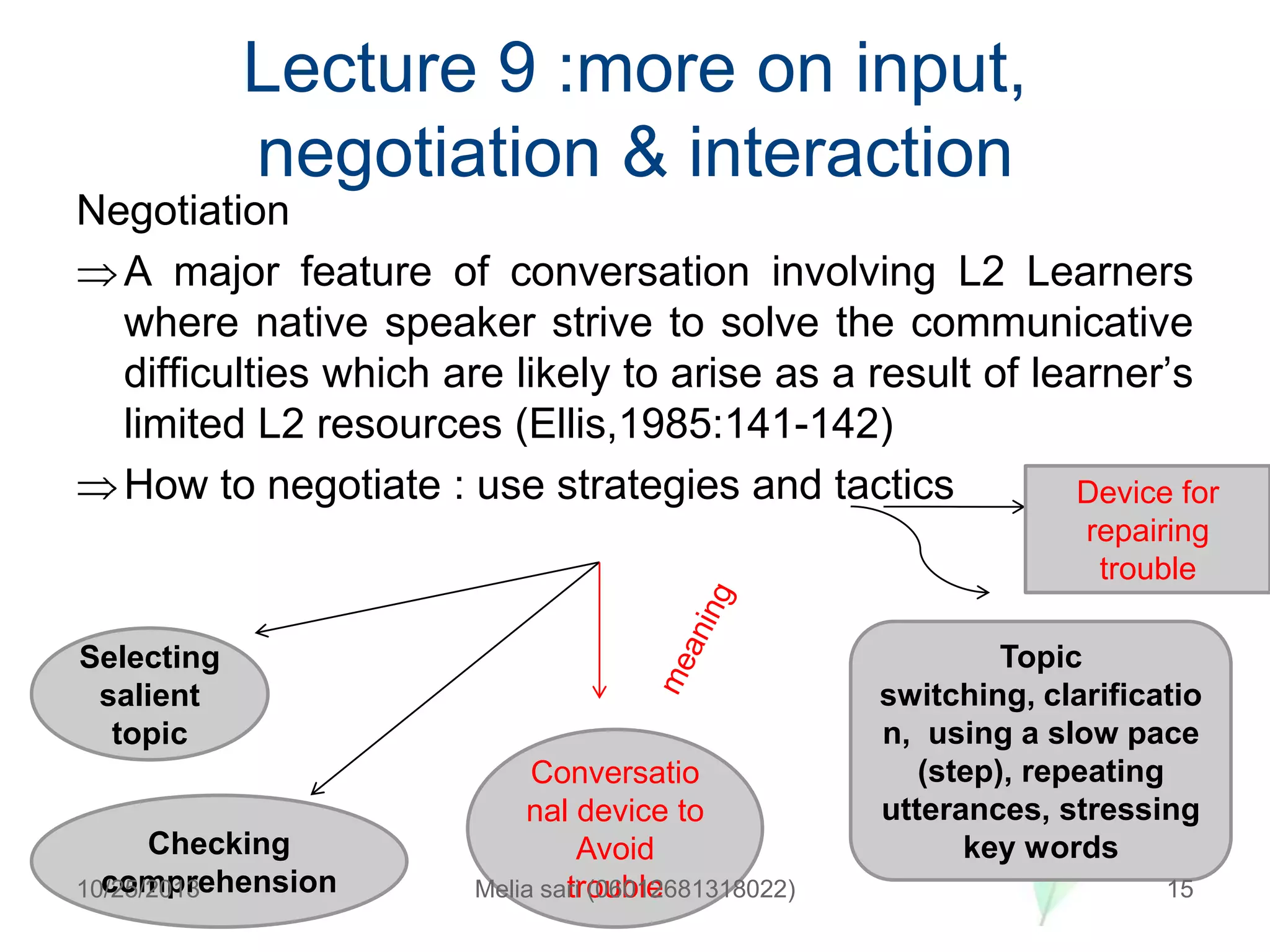
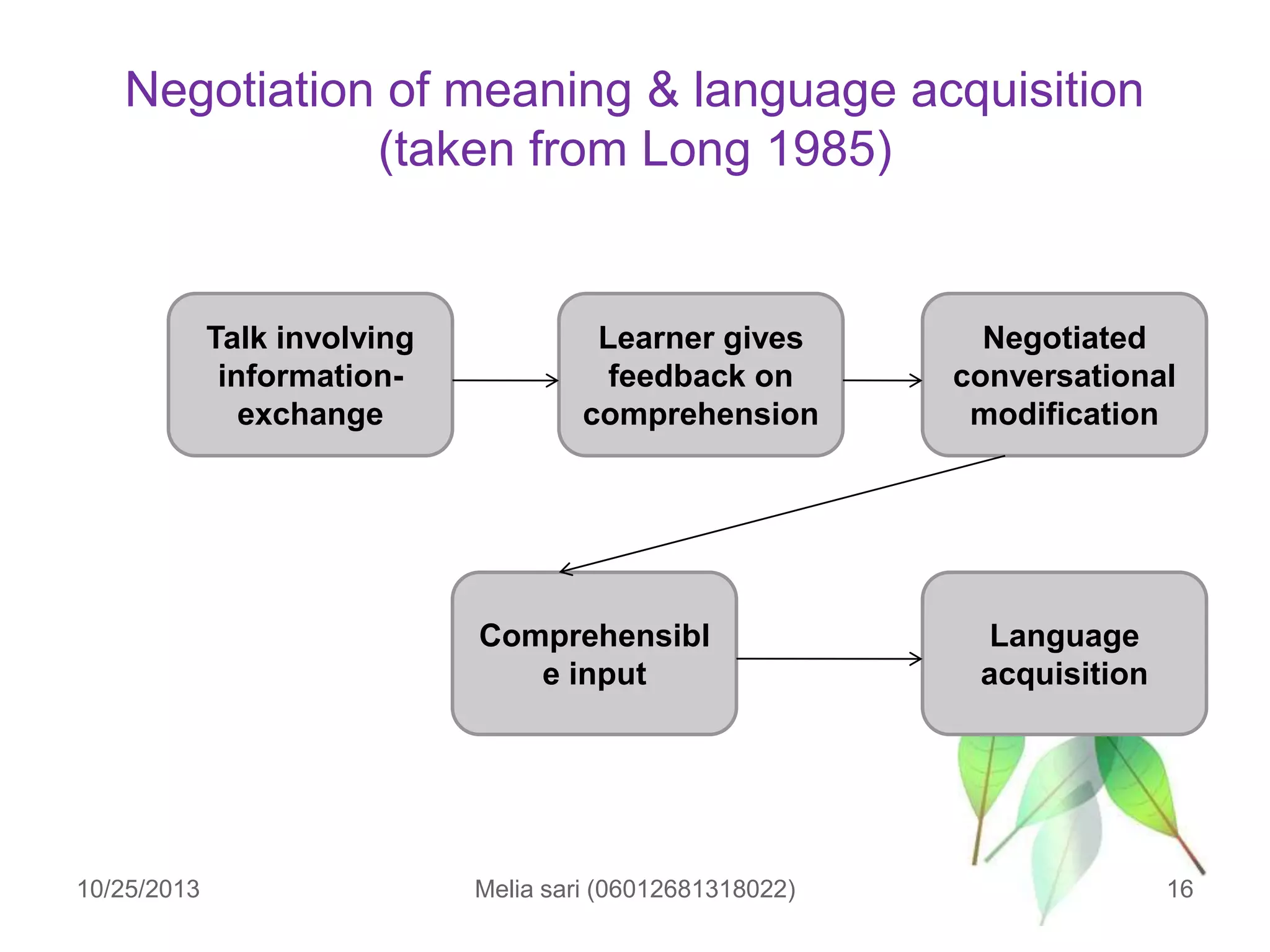
This document summarizes a lecture about describing language input and assessing its impact on second language acquisition. It discusses various types of input including written, verbal, and non-linguistic input. Key concepts covered include Krashen's input hypothesis, the role of comprehensible input, types of input outside the classroom like motherese and foreigner talk, and the role of negotiation and interaction in facilitating language acquisition.