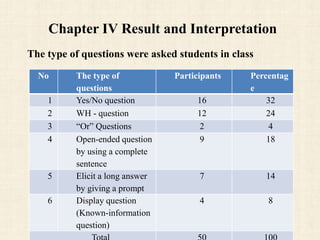
This document discusses issues related to how teachers ask questions in English classes at ethnic secondary schools in Laos. It aims to understand the types of questions teachers ask, problems students face in answering questions, and ways to address these issues. A literature review covers learning theories and question types. A study was conducted surveying 50 students and 6 English teachers about question types, causes of student problems, how students respond, and techniques to motivate responses. Key findings include students being afraid of ridicule and needing time to think. The conclusion recommends teachers ask clearer questions and allow time for students to respond without embarrassment. Addressing question techniques could help improve English teaching and learning.