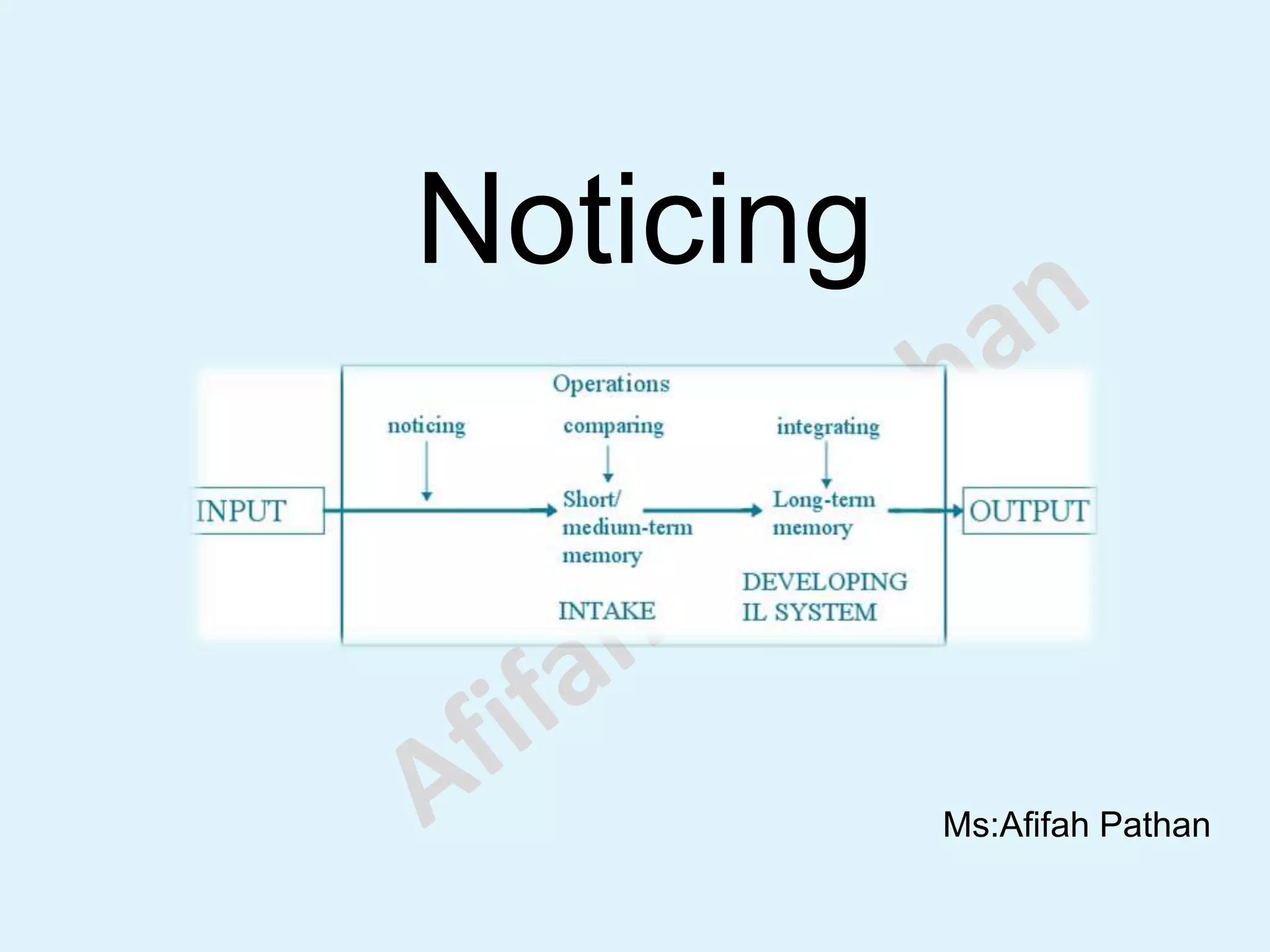
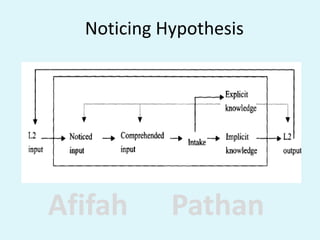
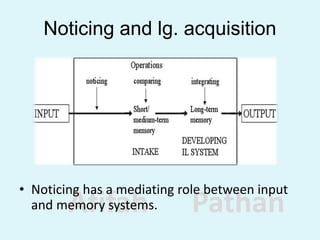
The document discusses the Noticing Hypothesis, which claims that language learning requires learners to consciously notice, or pay attention to, aspects of the language they are exposed to through input. It defines noticing and explains that noticing involves both detection and rehearsal of language features. It describes how noticing has a mediating role between input and memory in language acquisition. It also discusses how different factors like instruction, frequency, perceptual salience, skill level, and task demands can influence whether aspects of language are noticed by learners. Finally, it suggests some noticing activities that can help learners notice aspects of language in listening input.