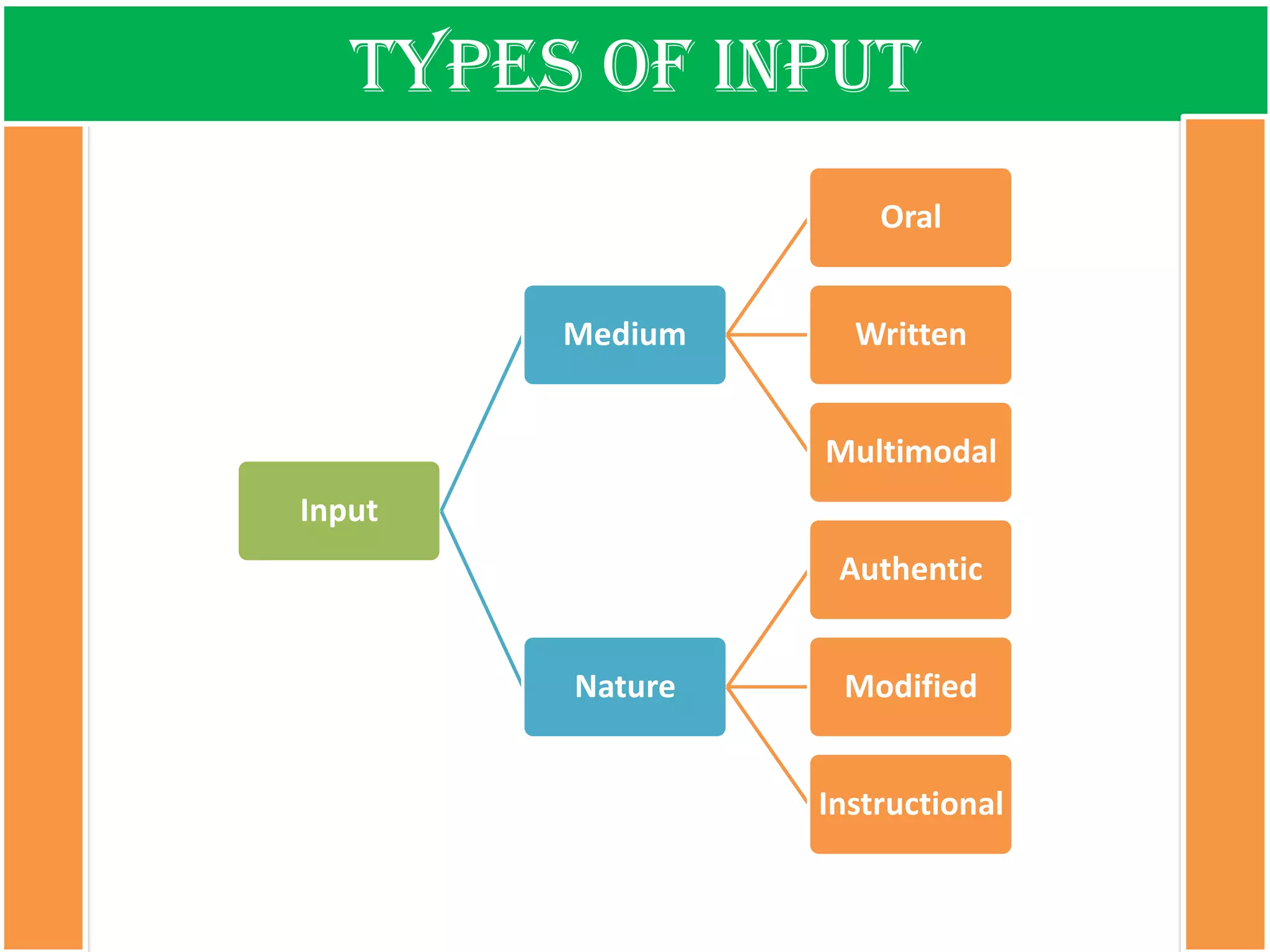
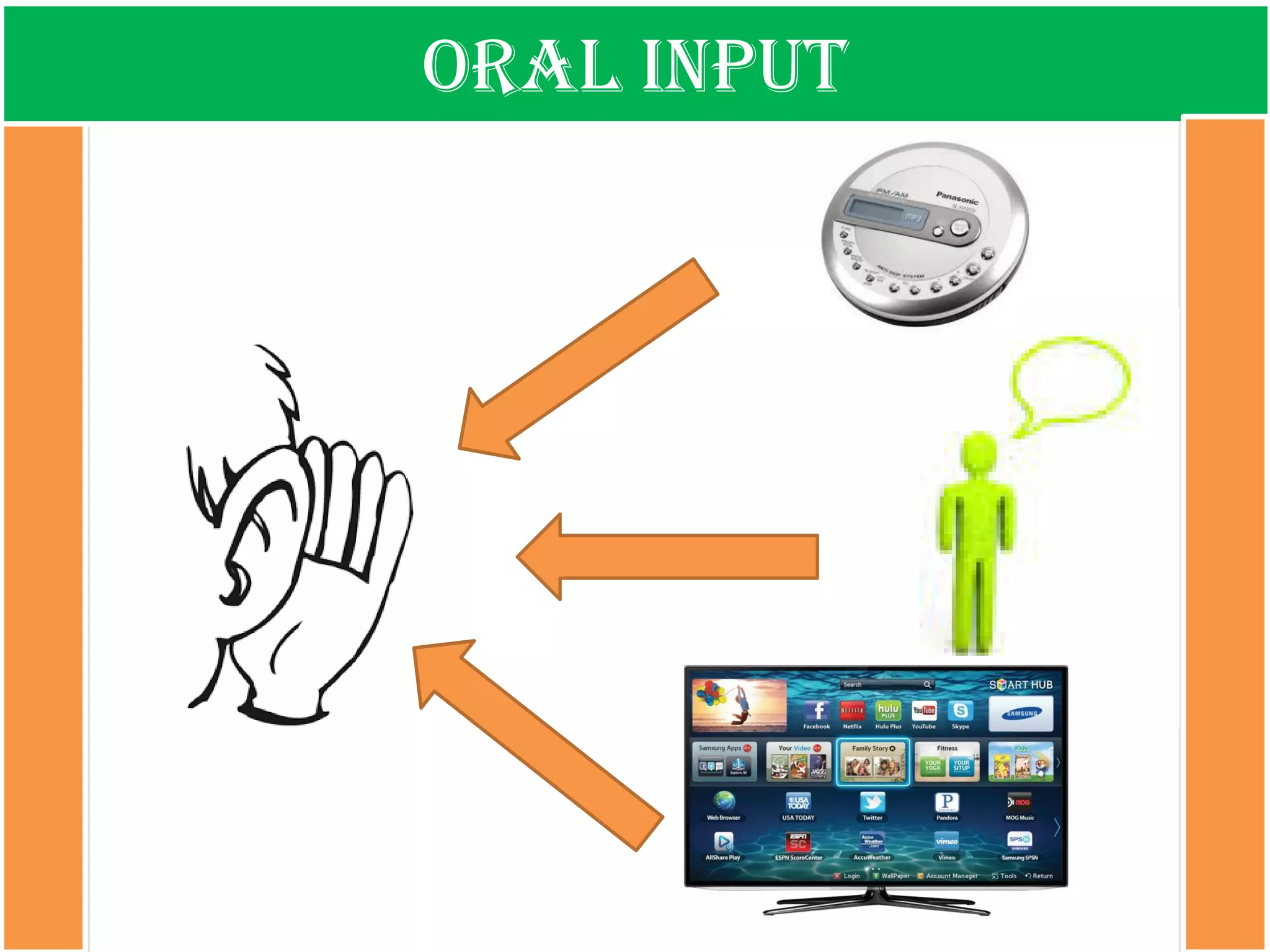
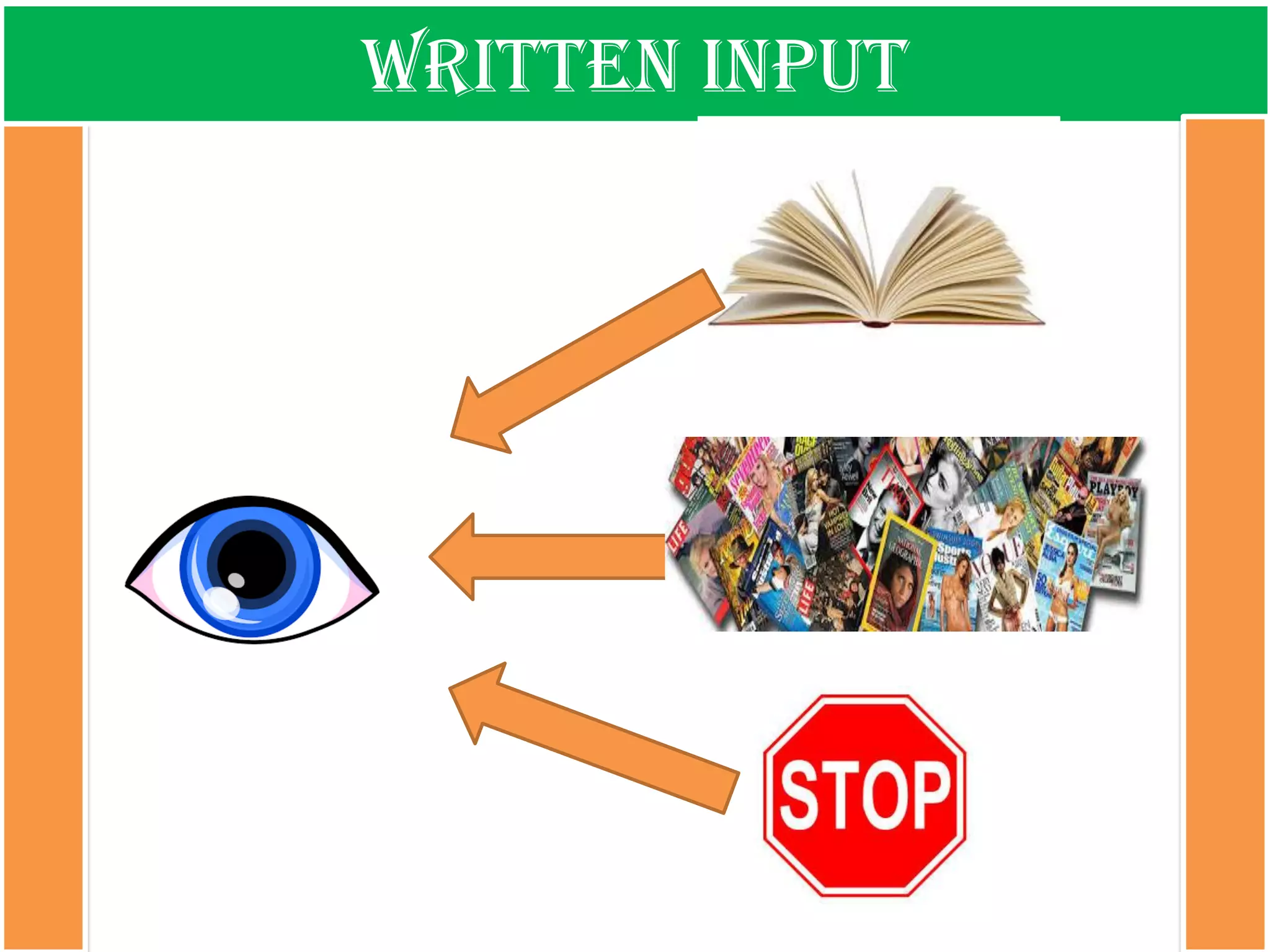
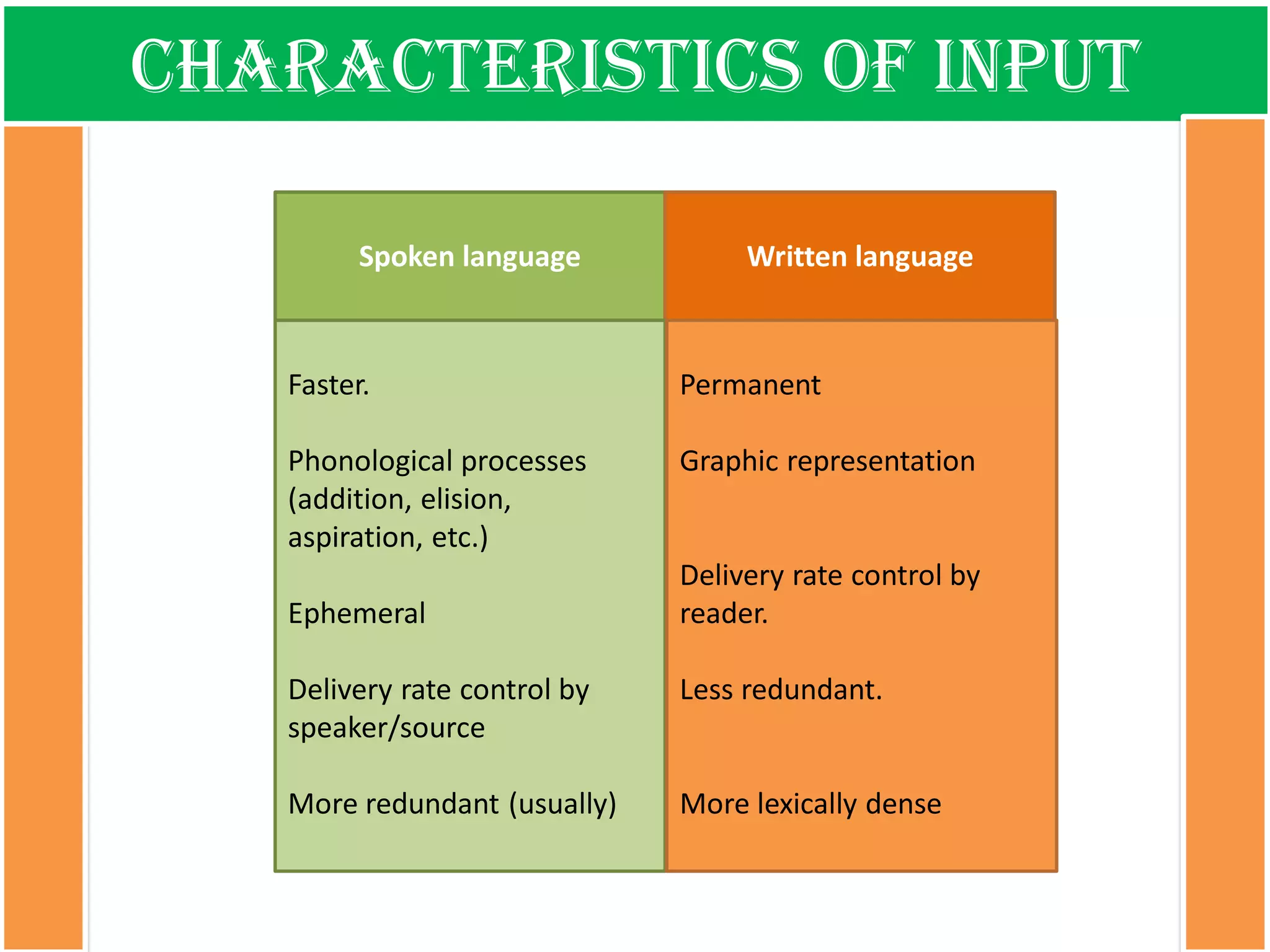
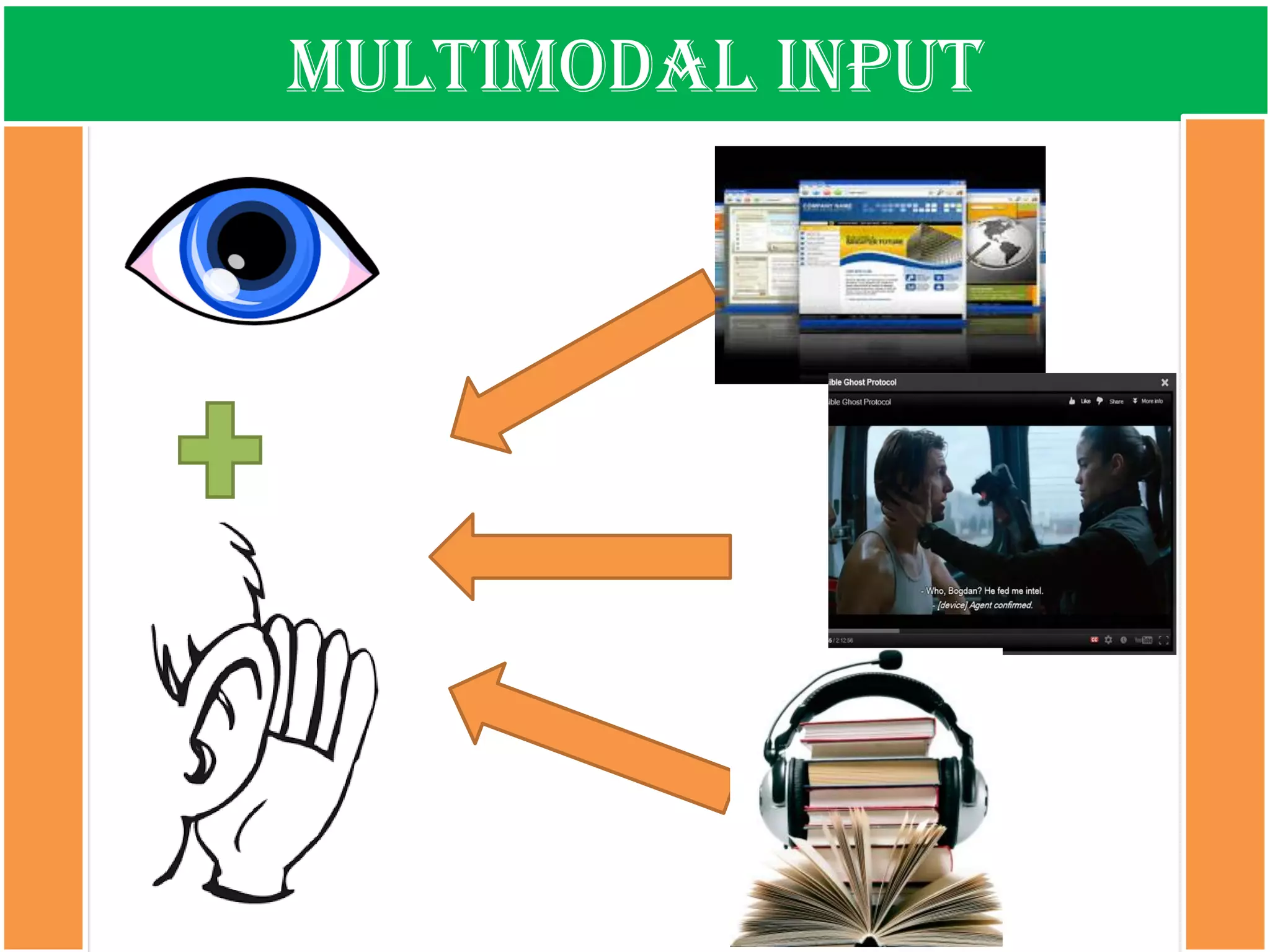
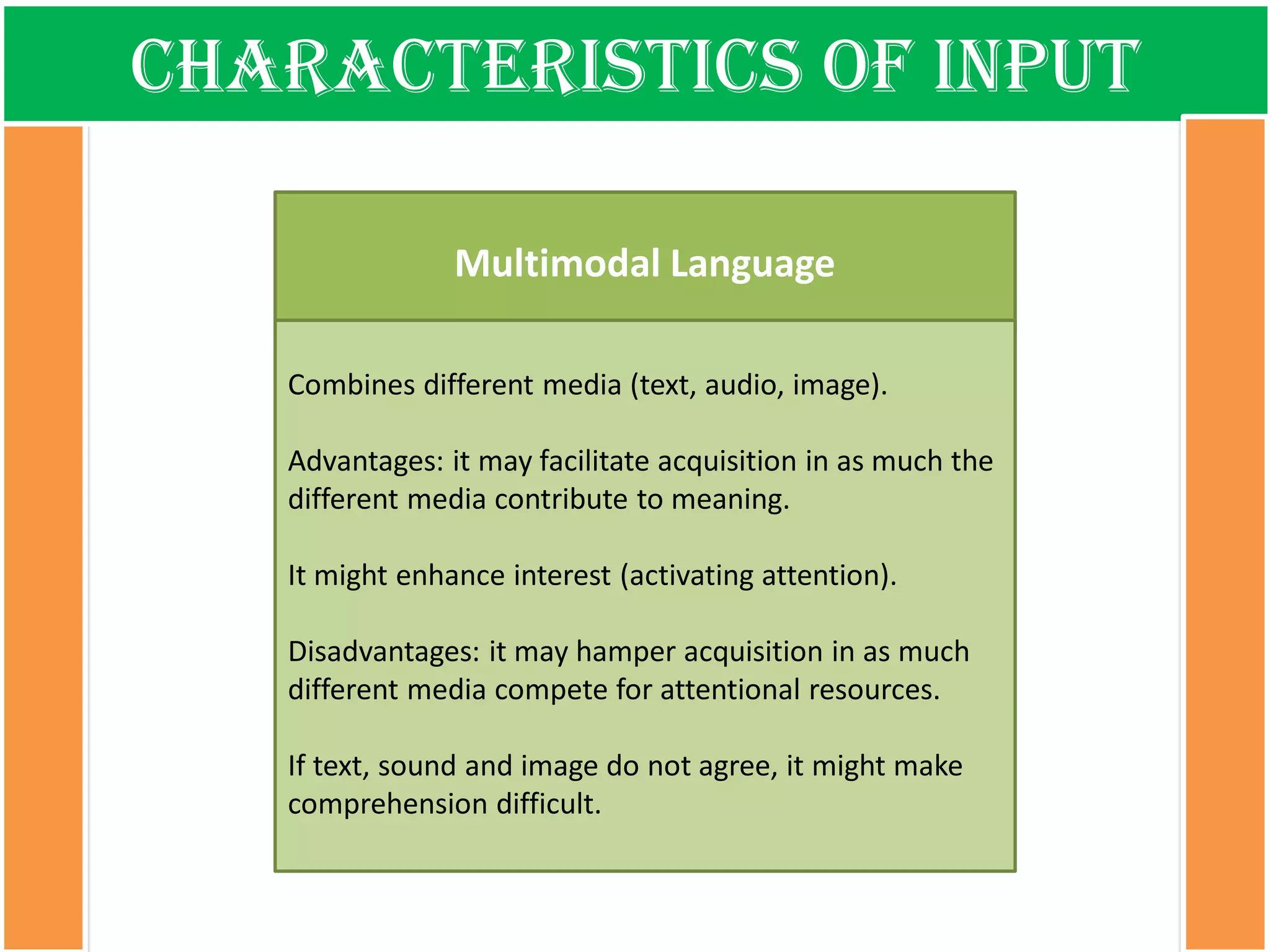
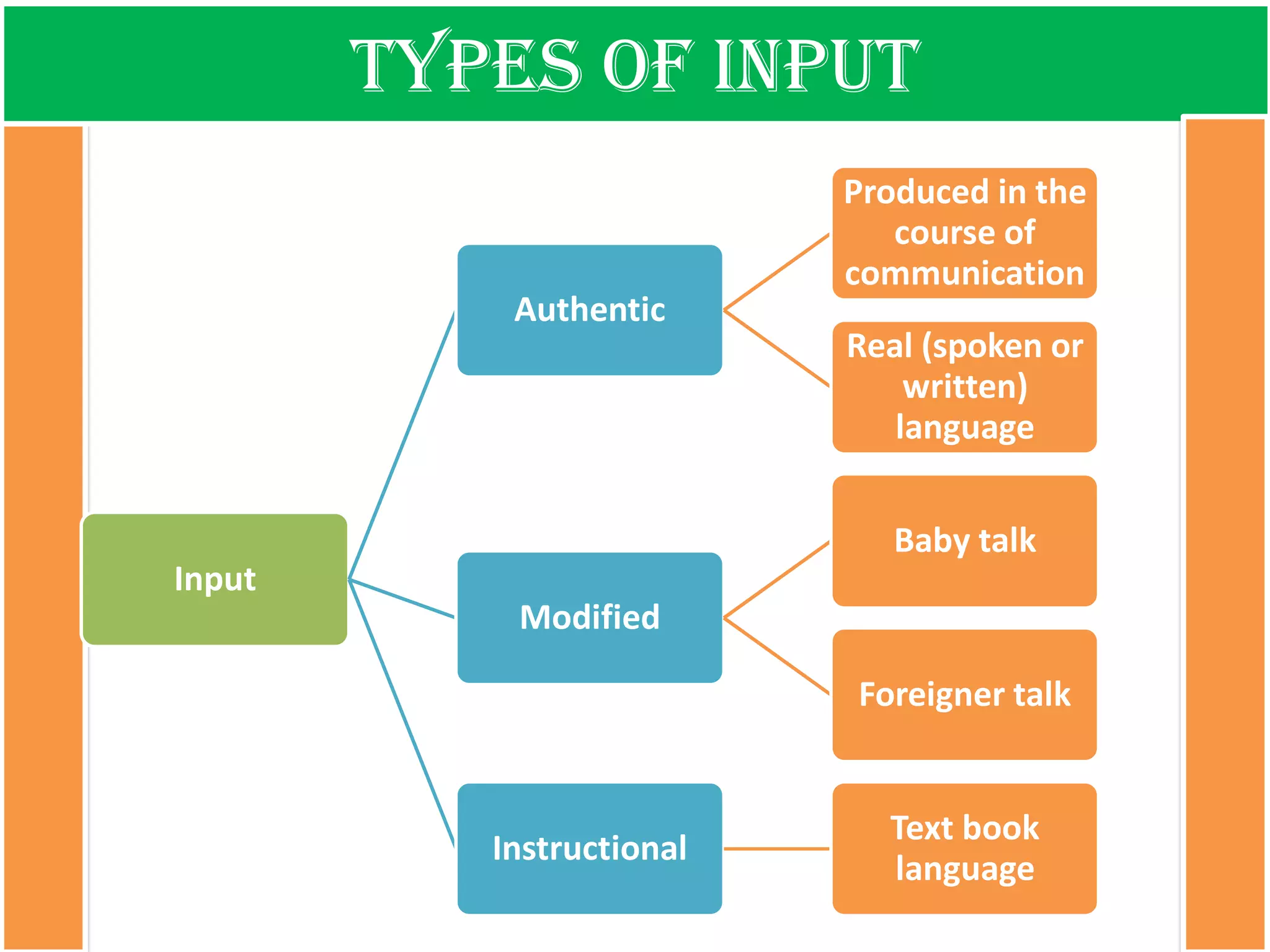
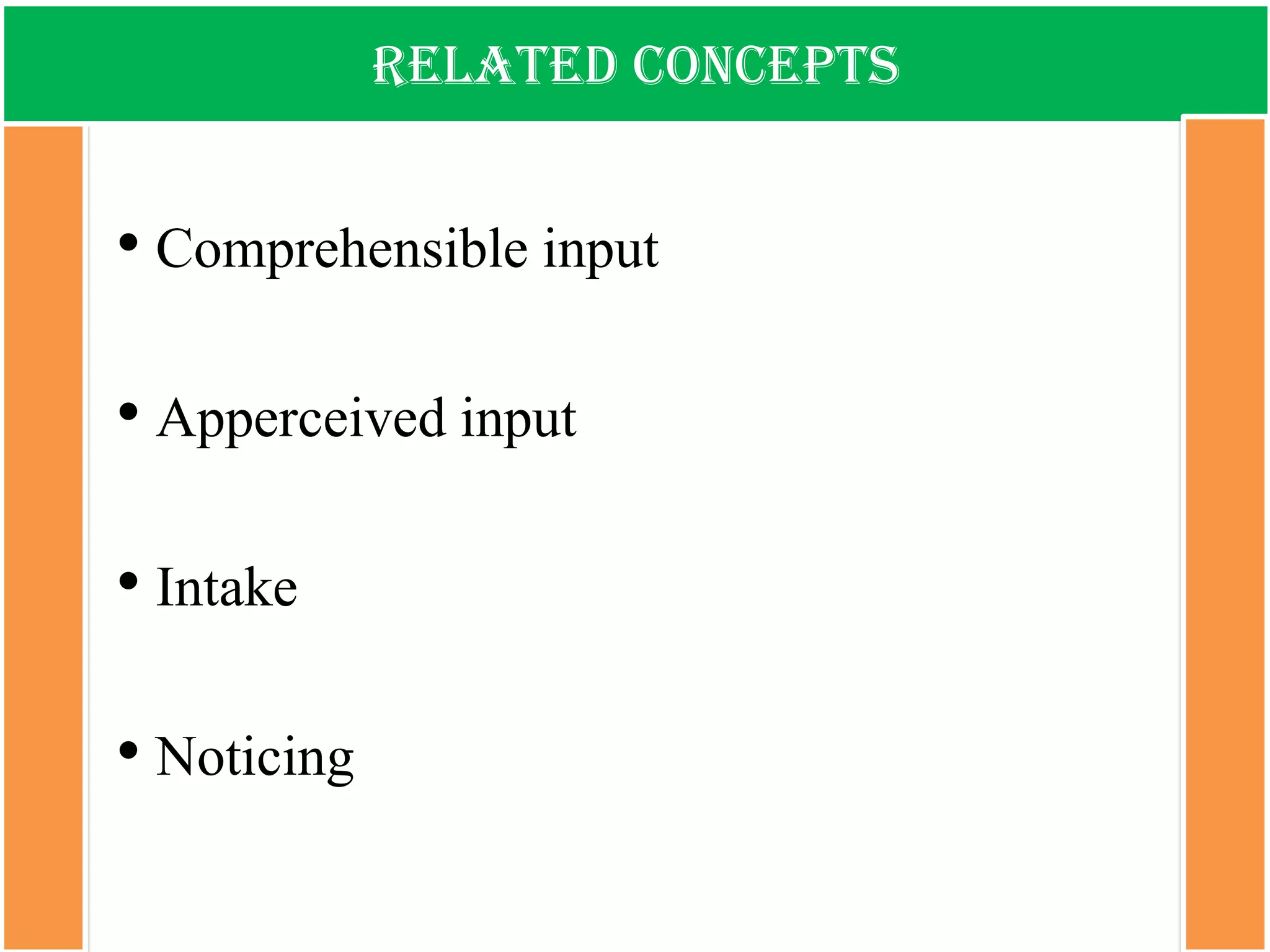
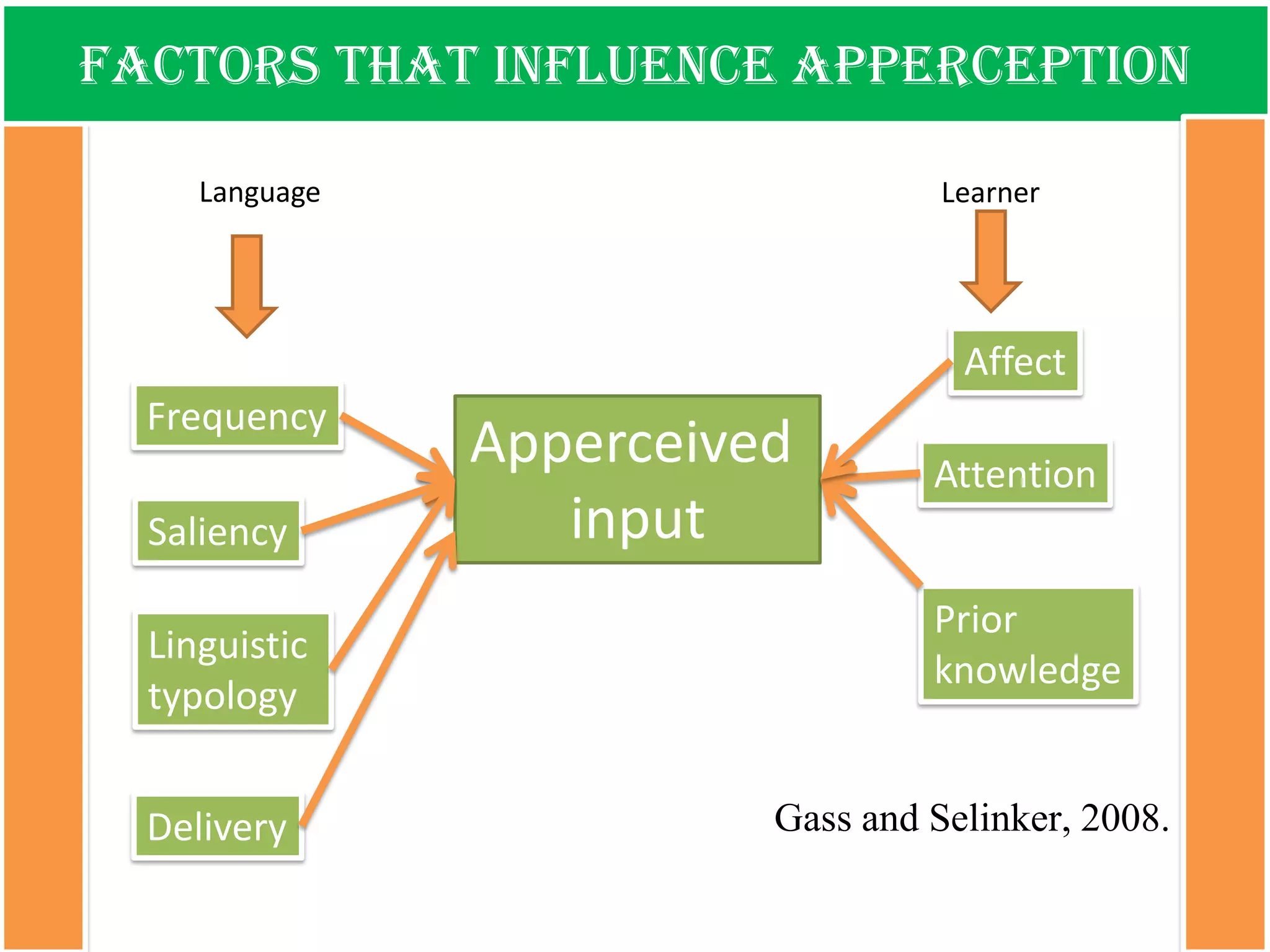
The document discusses the types of input encountered while learning a foreign language, highlighting the importance of exposure through various mediums such as oral, written, and multimodal formats. It explains the characteristics and differences between authentic and modified inputs, along with the concepts of comprehensible input, apperceived input, and intake. Finally, it stresses the necessity for attention in the learning process and provides references for further reading on second language acquisition.