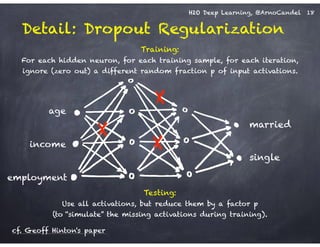
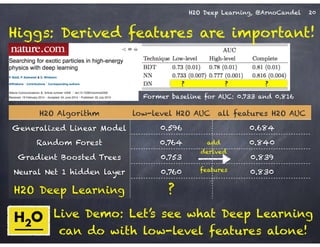
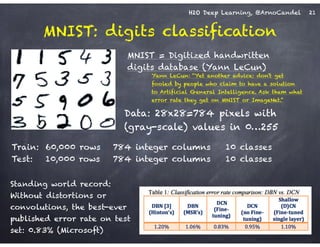
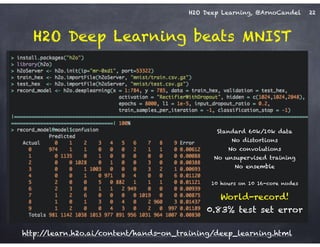
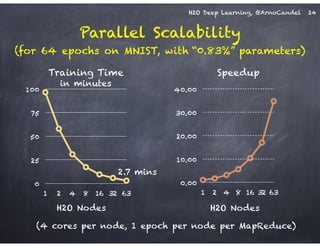
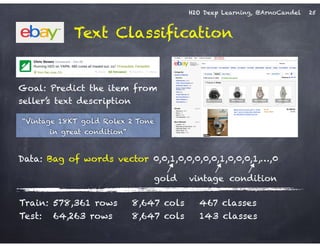
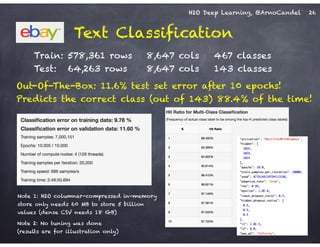
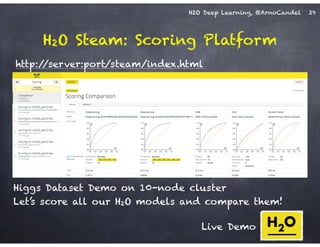
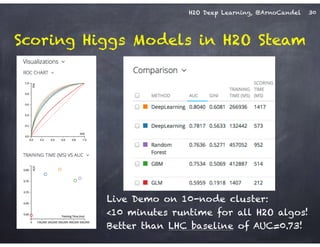
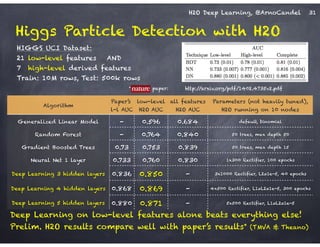
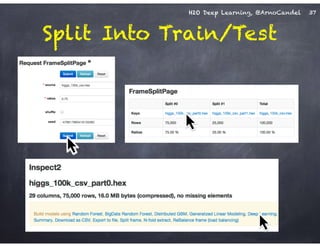
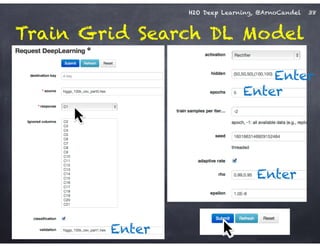
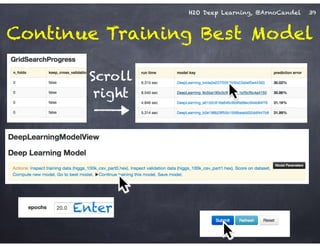
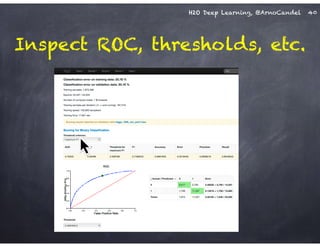
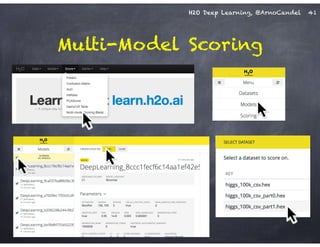
The document outlines a workshop on scalable data science and deep learning using H2O, focusing on various applications including Higgs boson classification, MNIST digit recognition, and text classification. It provides detailed insights into H2O's architecture, features, and hands-on sessions on machine learning models, techniques for data preparation, and the development of predictive analytics. Additionally, it includes live demonstrations of deep learning capabilities with performance metrics and highlights the advantages of H2O's open-source platform.





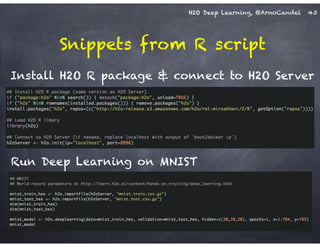
![H2O Deep Learning, @ArnoCandel 6
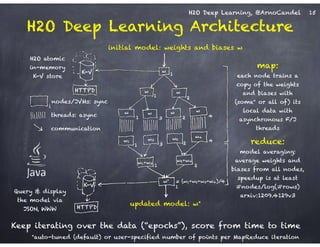
H2O Architecture - Designed for speed,
scale, accuracy & ease of use
Key technical points:
• distributed JVMs + REST API
• no Java GC issues
(data in byte[], Double)
• loss-less number compression
• Hadoop integration (v1,YARN)
• R package (CRAN)
Pre-built fully featured algos:
K-Means, NB, PCA, CoxPH,
GLM, RF, GBM, DeepLearning](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/h2odeeplearningarnocandel011715-150117011202-conversion-gate02/85/H2O-Deep-Learning-at-Next-ML-6-320.jpg)


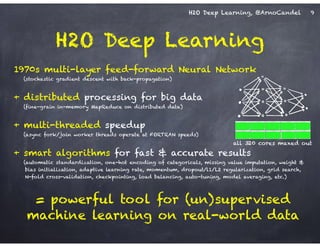


![H2O Deep Learning, @ArnoCandel
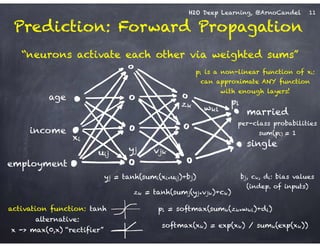
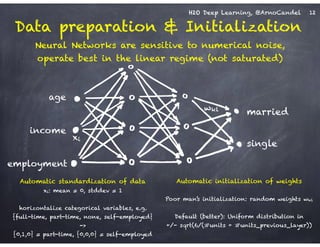
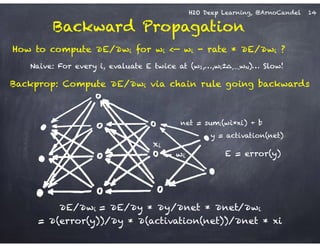
Detail: Adaptive Learning Rate
!
Compute moving average of ∆wi
2 at time t for window length rho:
!
E[∆wi
2]t = rho * E[∆wi
2]t-1 + (1-rho) * ∆wi
2
!
Compute RMS of ∆wi at time t with smoothing epsilon:
!
RMS[∆wi]t = sqrt( E[∆wi
2]t + epsilon )
Adaptive annealing / progress:
Gradient-dependent learning rate,
moving window prevents “freezing”
(unlike ADAGRAD: no window)
Adaptive acceleration / momentum:
accumulate previous weight updates,
but over a window of time
RMS[∆wi]t-1
RMS[∂E/∂wi]t
rate(wi, t) =
Do the same for ∂E/∂wi, then
obtain per-weight learning rate:
cf. ADADELTA paper
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/h2odeeplearningarnocandel011715-150117011202-conversion-gate02/85/H2O-Deep-Learning-at-Next-ML-17-320.jpg)