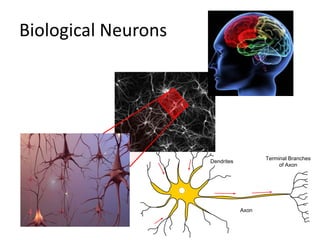
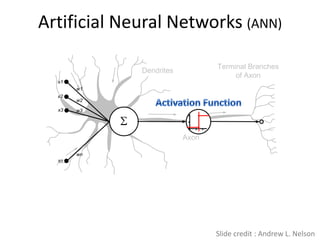
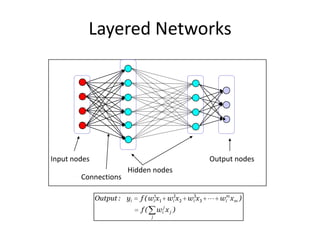
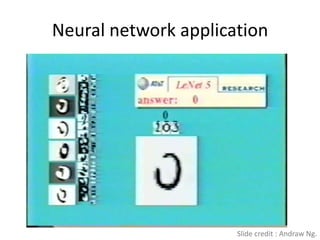
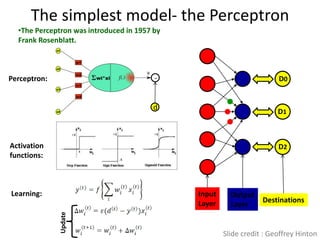
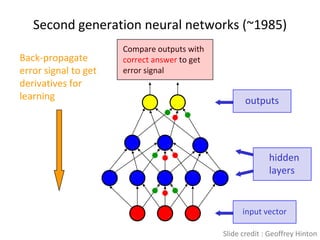
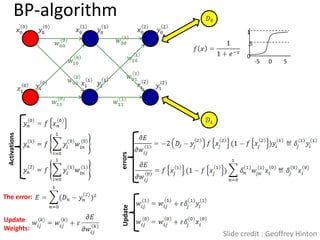
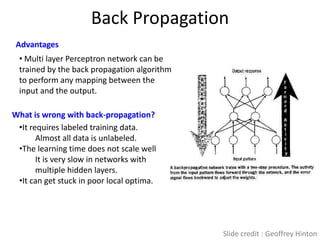
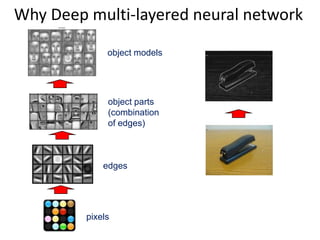
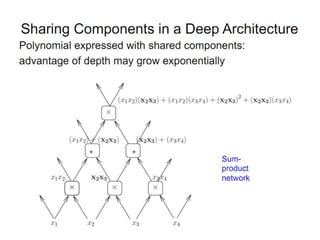
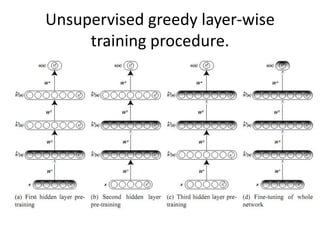
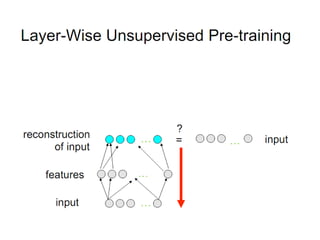
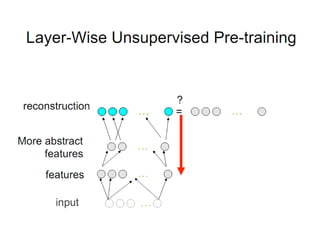
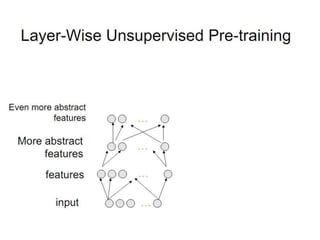
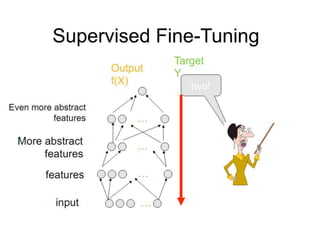
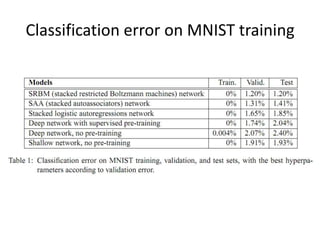
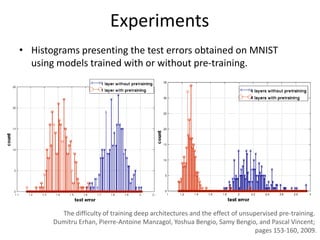
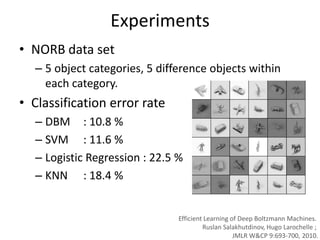
Deep learning and neural networks are inspired by biological neurons. Artificial neural networks (ANN) can have multiple layers and learn through backpropagation. Deep neural networks with multiple hidden layers did not work well until recent developments in unsupervised pre-training of layers. Experiments on MNIST digit recognition and NORB object recognition datasets showed deep belief networks and deep Boltzmann machines outperform other models. Deep learning is now widely used for applications like computer vision, natural language processing, and information retrieval.