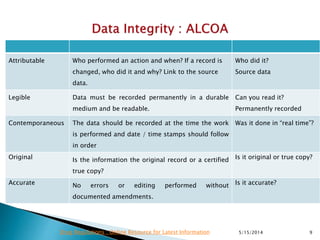
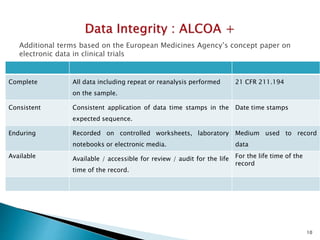
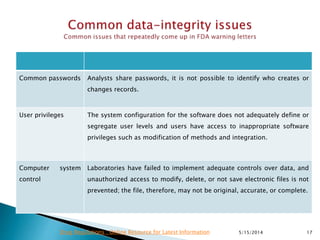
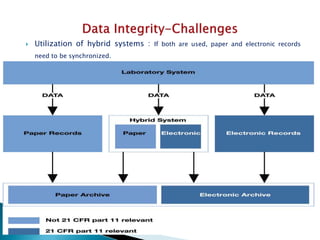
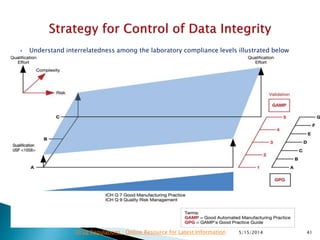
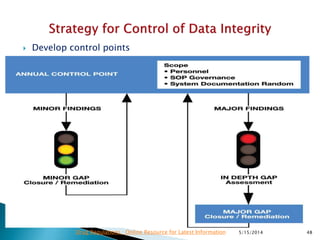
The document discusses the importance of data integrity in the pharmaceutical industry, particularly in relation to compliance with regulations such as CGMP and 21 CFR Part 11. It highlights increasing scrutiny from regulatory bodies like the FDA and emphasizes the need for secure electronic data management to prevent falsification and ensure accurate record-keeping. Additionally, it outlines best practices for maintaining data integrity, including proper documentation, user access control, and periodic audits.