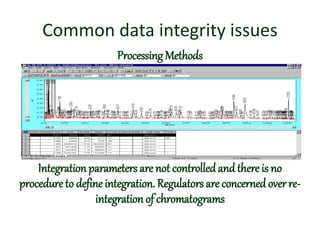
The document discusses data integrity within the pharmaceutical industry's quality control context, emphasizing its essential role in compliance with regulations and ensuring drug safety and efficacy. It outlines common concerns such as data tampering, improper recording, and the need for systematic and secure data management practices, as well as the ALCOA+ criteria for maintaining data integrity. Additionally, it highlights regulatory standards and expectations regarding the integrity of data in compliance with GMP requirements.




















![GMP regulatory requirements for data
integrity
Derived fromthe data integrity definition and the applicable 21
CFR 211 GMP regulations there are some of the following points:
Equipment must be qualifiedand fit for purpose [§211.160(b),
§211.63]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labdataintegrityupload-170318085355/85/Lab-data-integrity-23-320.jpg)
![GMP regulatory requirements for data
integrity
Software must be validated [§211.63]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labdataintegrityupload-170318085355/85/Lab-data-integrity-24-320.jpg)
![GMP regulatory requirements for data
integrity
Any calculations used must be verified [§211.68(b)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labdataintegrityupload-170318085355/85/Lab-data-integrity-25-320.jpg)
![GMP regulatory requirements for data
integrity
Data generatedduring analysis must be backed up [§211.68(b)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labdataintegrityupload-170318085355/85/Lab-data-integrity-26-320.jpg)
![GMP regulatory requirements for data
integrity
Reagents and reference solutions are prepared correctly with
appropriaterecords [§211.194(c)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labdataintegrityupload-170318085355/85/Lab-data-integrity-27-320.jpg)
![GMP regulatory requirements for data
integrity
Methods used must be documented and approved [§211.160(a)]
Methods must be verified under actual conditions of use
[§211.194(a)(2)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labdataintegrityupload-170318085355/85/Lab-data-integrity-28-320.jpg)
![GMP regulatory requirements for data
integrity
Data generatedand transformed must meet the criterion of
scientific soundness [§211.160(a)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labdataintegrityupload-170318085355/85/Lab-data-integrity-29-320.jpg)
![GMP regulatory requirements for data
integrity
Test data must be accurate, complete and procedures should
be followed [§211.194(a)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labdataintegrityupload-170318085355/85/Lab-data-integrity-30-320.jpg)
![GMP regulatory requirements for data
integrity
Data and the reportable value must be checkedby a second
individual to ensure accuracy, completeness and conformance
with procedures [§211.194(a)(8)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labdataintegrityupload-170318085355/85/Lab-data-integrity-31-320.jpg)
