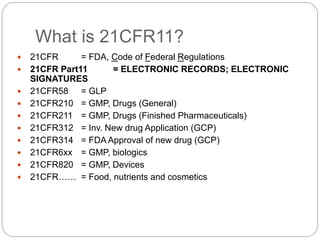
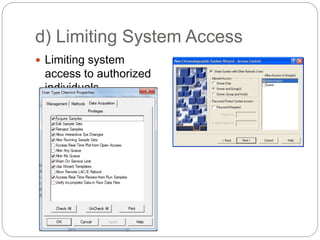
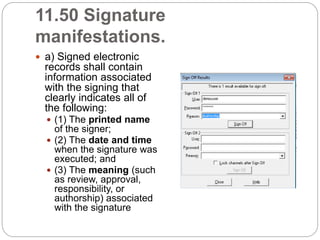
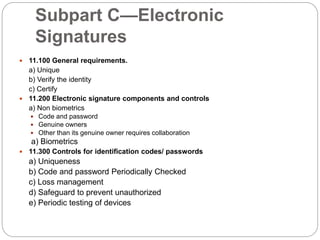
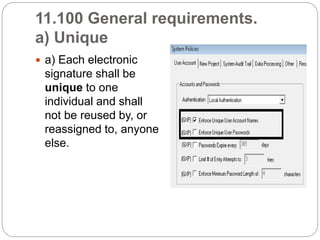
21 CFR Part 11 outlines FDA regulations for electronic records and electronic signatures. It requires that electronic records be trustworthy, reliable, and equivalent to paper records. It also requires that electronic signatures be equivalent to handwritten signatures. The document then outlines the key subparts and sections of 21 CFR Part 11, including requirements for controls on closed and open systems, electronic signature components and controls, and validation of electronic records and signatures.