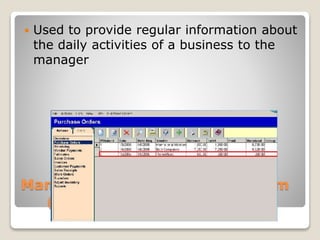
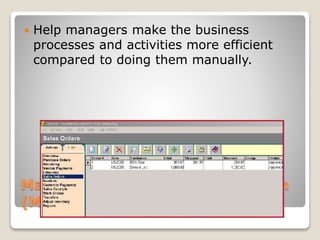
Cyber crime involves using computers and the internet to commit unlawful acts where the computer is either a tool or target. Cyber security protects networks, computers, programs and data from attacks, damage or unauthorized access. There are two categories of cyber crime - where the computer is the target, such as hacking, and where it is used as a weapon to commit real-world crimes like credit card fraud. Information systems were developed to help businesses run more efficiently compared to manual systems by providing regular information to managers through management information systems, keeping track of transactions through transaction processing systems, giving managers information to make decisions using decision support systems, helping top management plan strategies with executive information systems, and storing expert knowledge to make logical suggestions for users in expert


















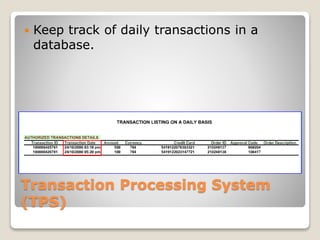
![Transaction Processing System
(TPS)
Used to record business transactions.
Information and Communication Technology [Form 5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cybersecurity-170225045133/85/Cyber-security-23-320.jpg)

![Decision Support System
(DSS)
Provide managers with information to
make the best decisions.
Information and Communication Technology [Form 5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cybersecurity-170225045133/85/Cyber-security-26-320.jpg)








