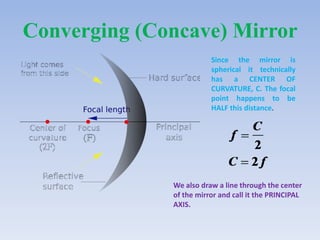
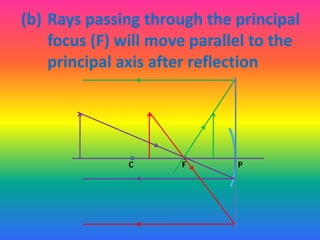
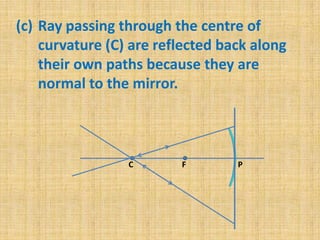
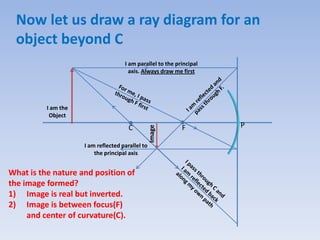
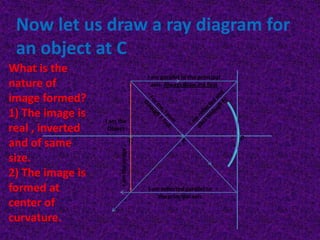
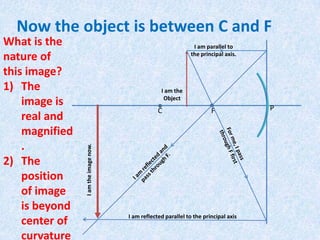
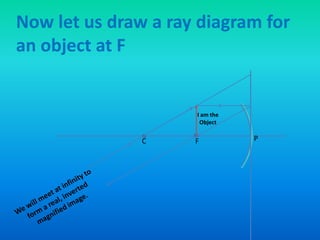
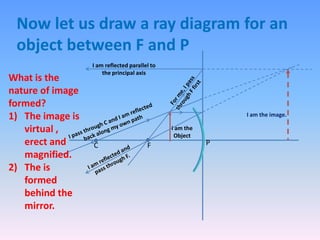
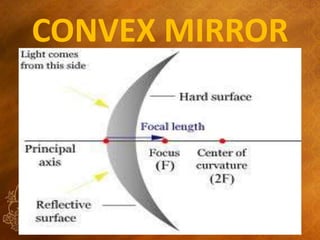
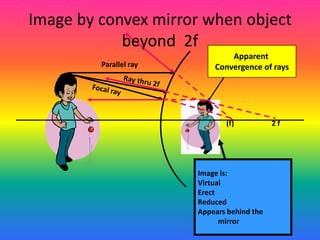
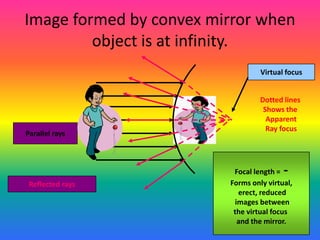
This document discusses virtual and real images formed by mirrors. Virtual images cannot be projected onto a screen and are always on the opposite side of the mirror from the object. Real images can be projected onto a screen and are on the same side of the mirror as the object. Concave mirrors form real, inverted images between the focal point and center of curvature for objects beyond the center of curvature. Ray diagrams are used to determine the nature and position of images formed by concave mirrors depending on the object's position relative to the focal point and center of curvature. The mirror equation can also be used to calculate the position of images.