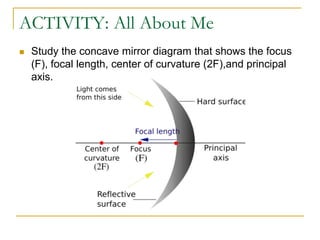
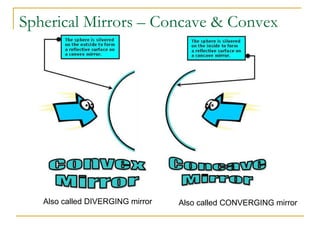
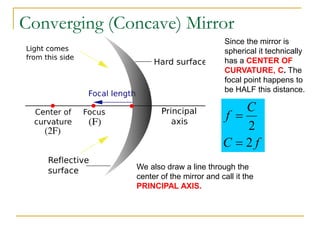
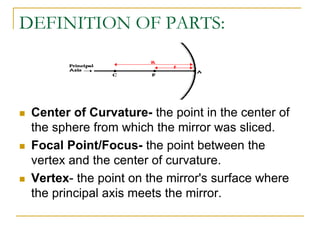
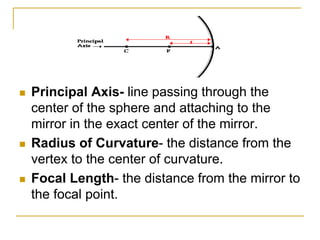
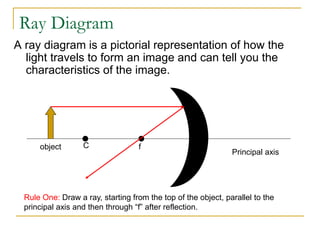
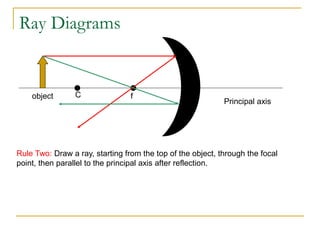
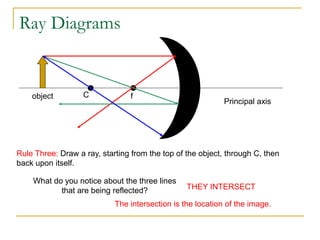
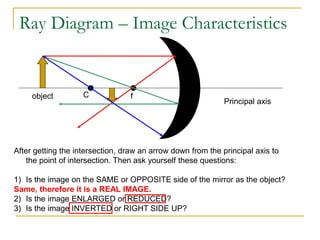
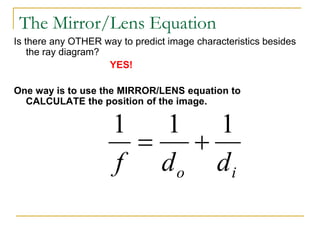
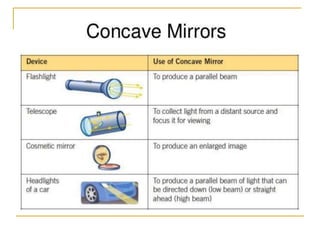
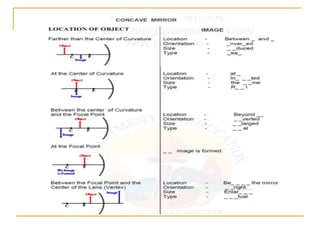
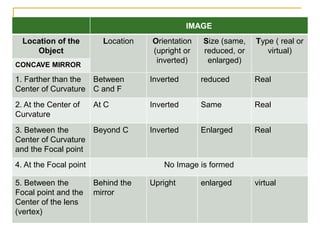
The document provides guidance on safety practices during the COVID-19 pandemic, including maintaining physical distance, good hygiene, wearing face masks and limiting exposure. It also discusses the properties of concave mirrors and how light rays behave when reflecting off of one. Key points covered include that concave mirrors can form real or virtual images that are upright or inverted, and can be magnified, minified or the same size as the object. Ray diagrams are demonstrated as a way to determine the characteristics of an image formed by a concave mirror.