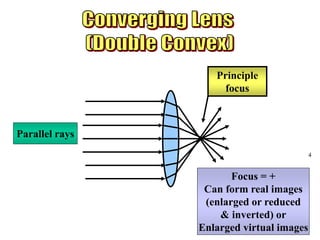
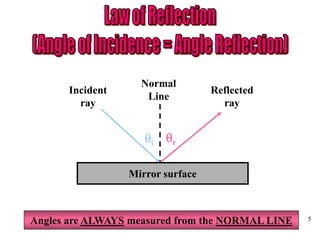
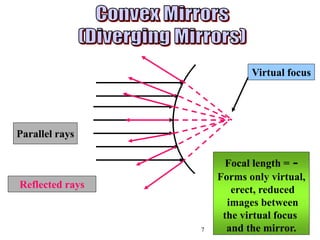
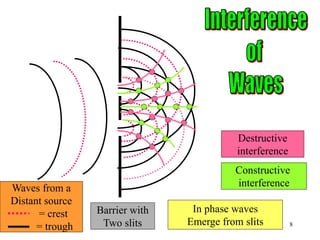
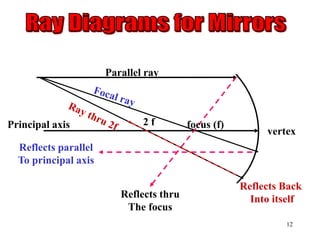
The document discusses the behavior of light as it travels through different mediums, specifically glass and air, including concepts like refraction, focus types, and image formation. It covers the principles of light reflection, the photoelectric effect, and the properties of visible and invisible light. Diagrams and mathematical relationships are referenced throughout to illustrate the principles described.