Embed presentation
Downloaded 67 times



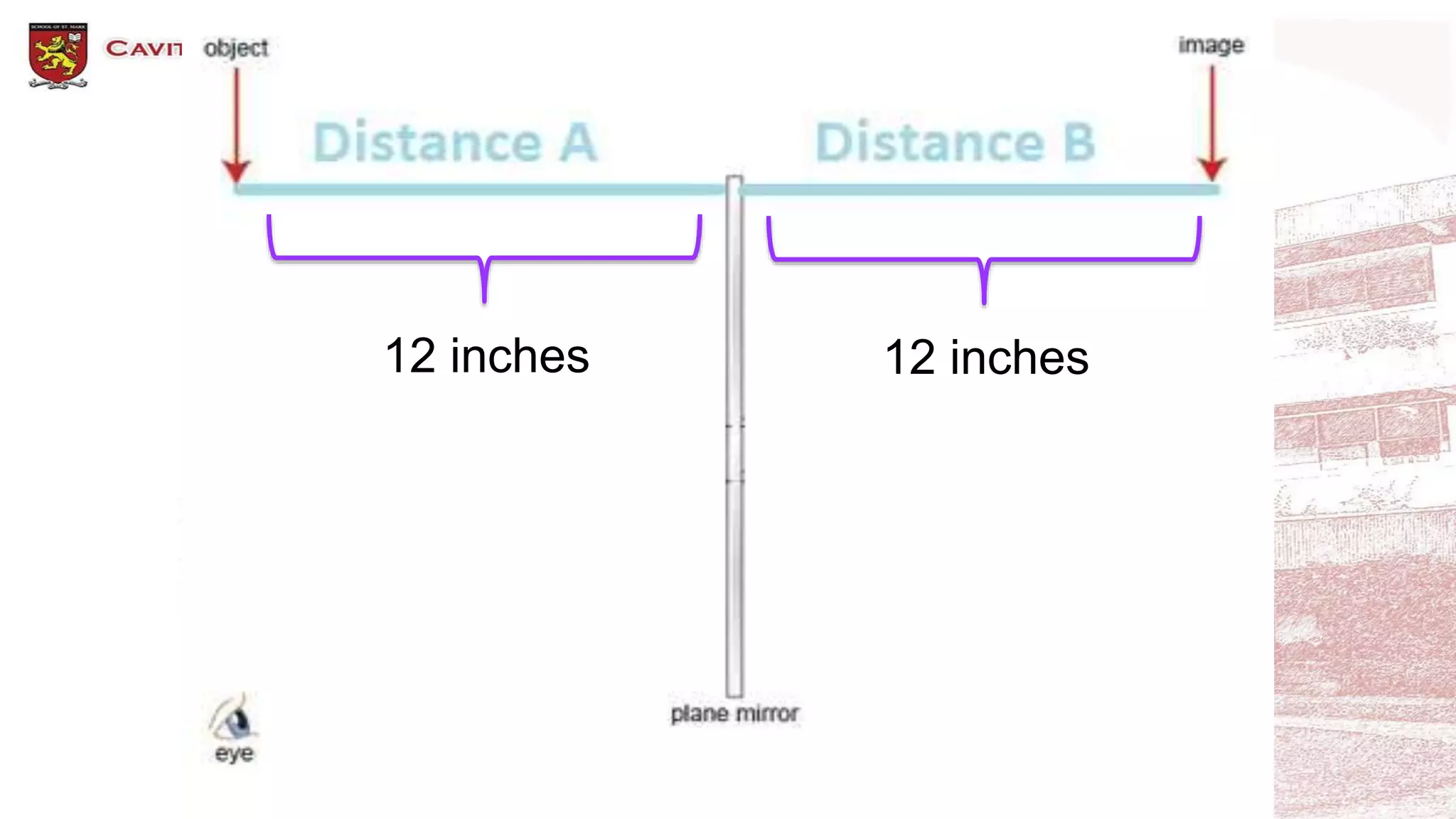
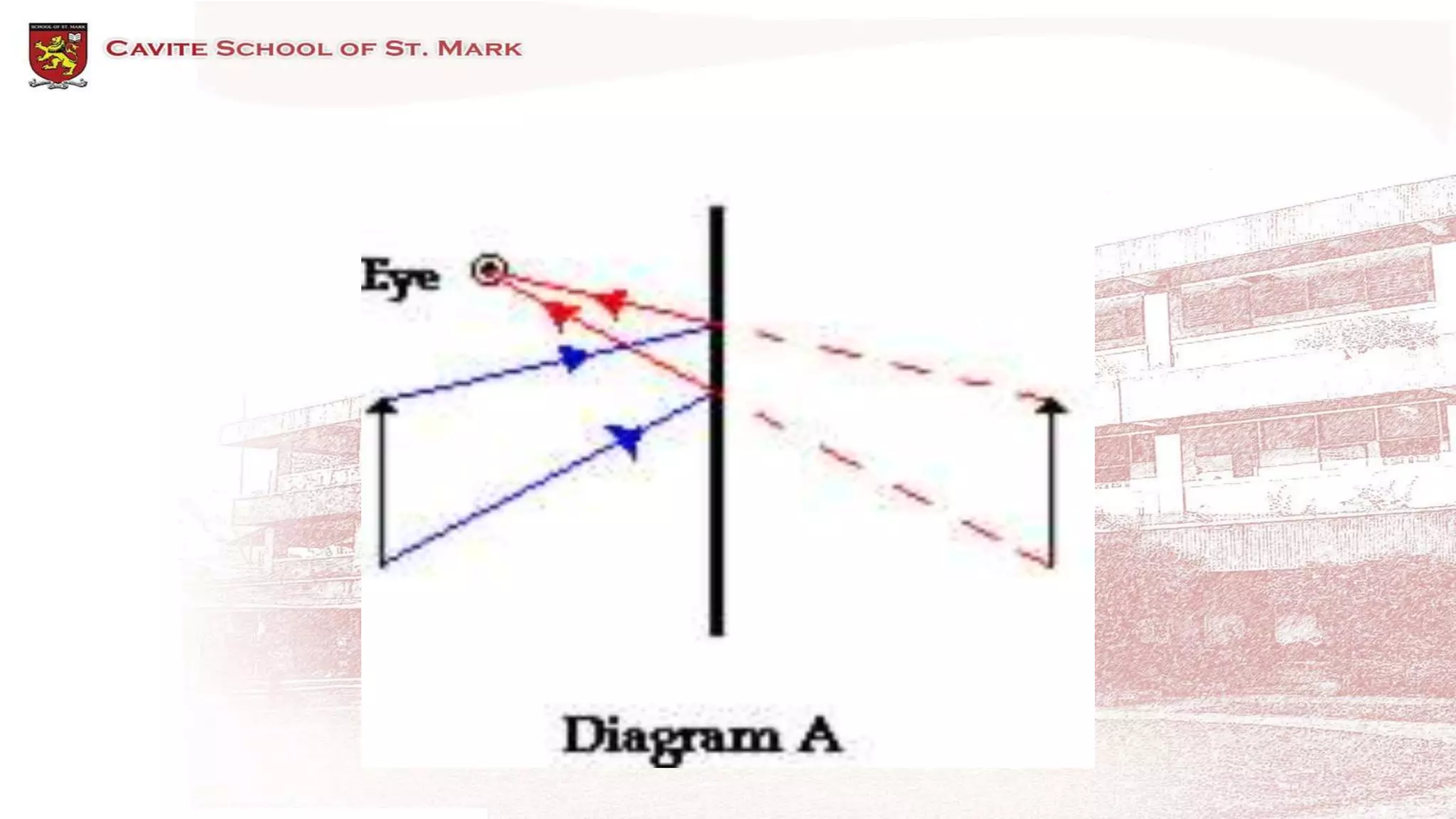
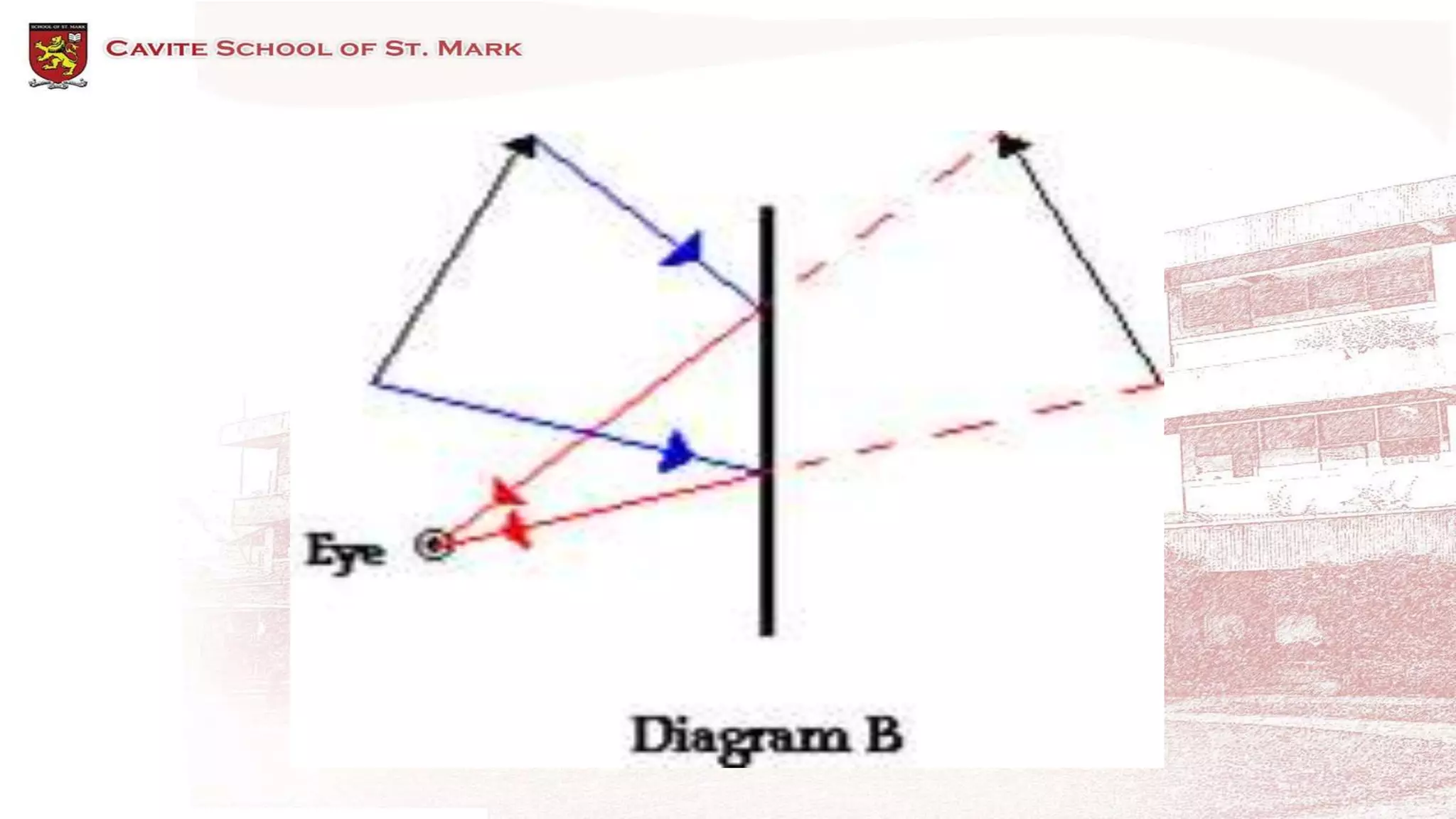




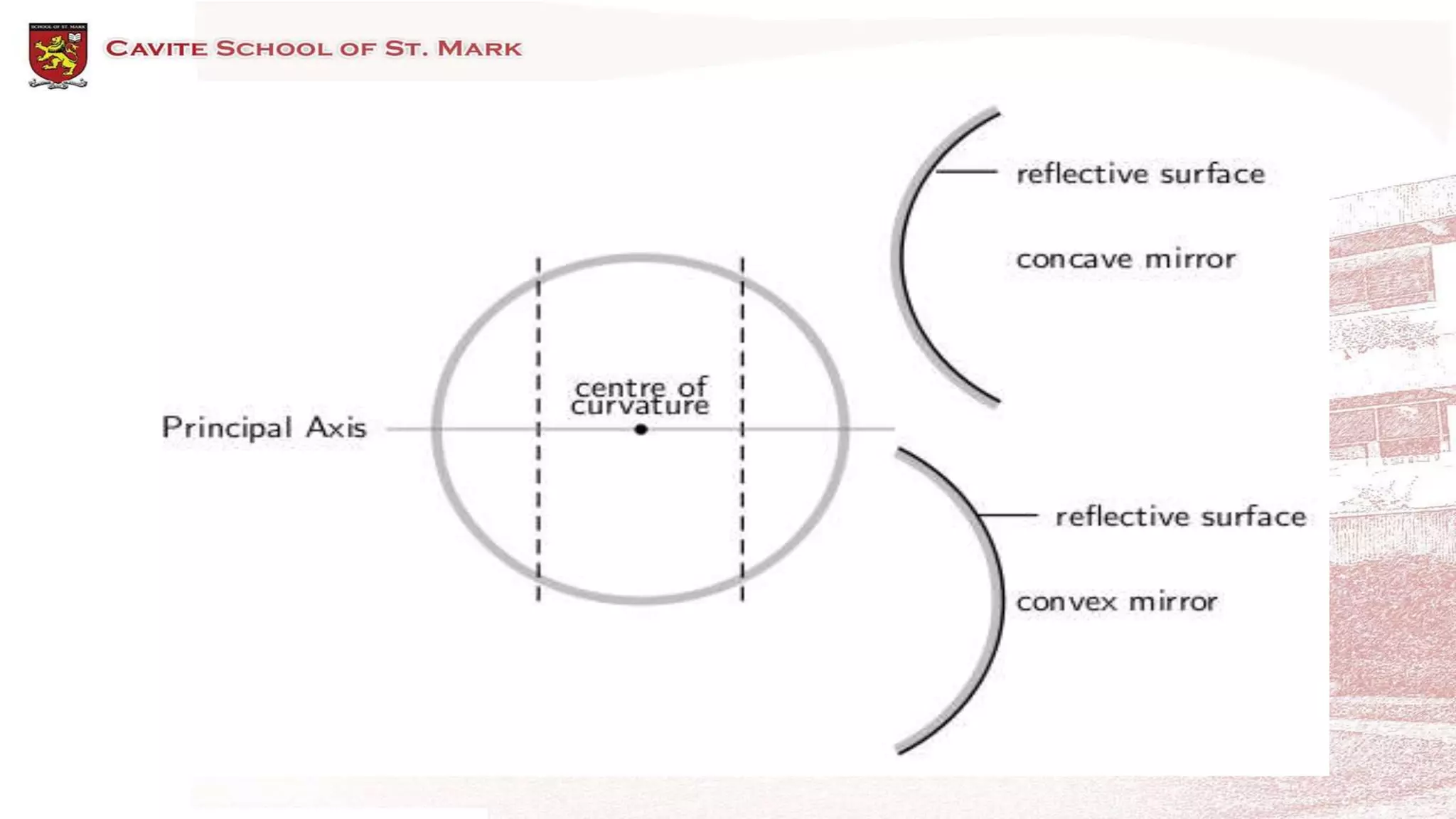
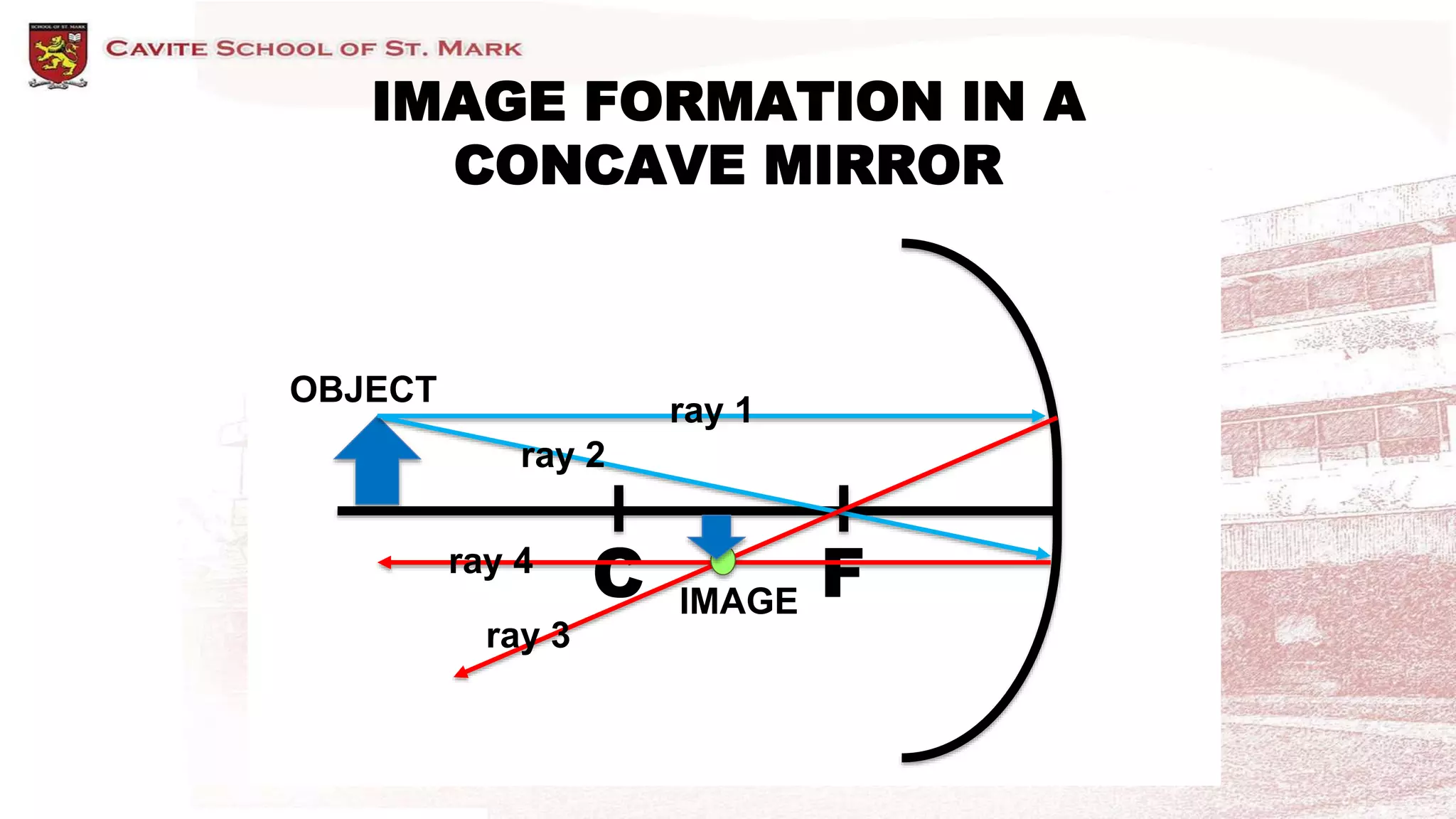
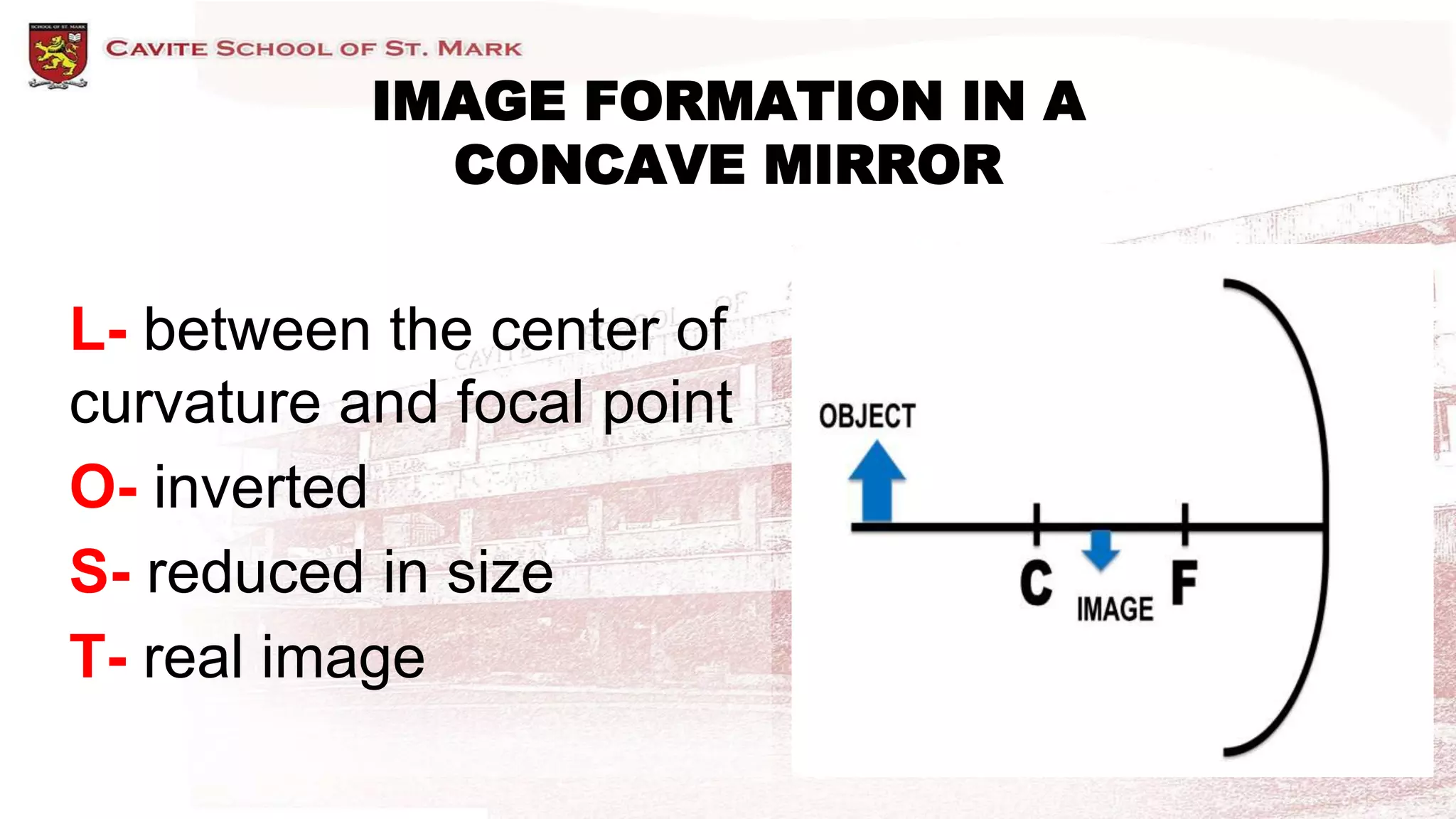
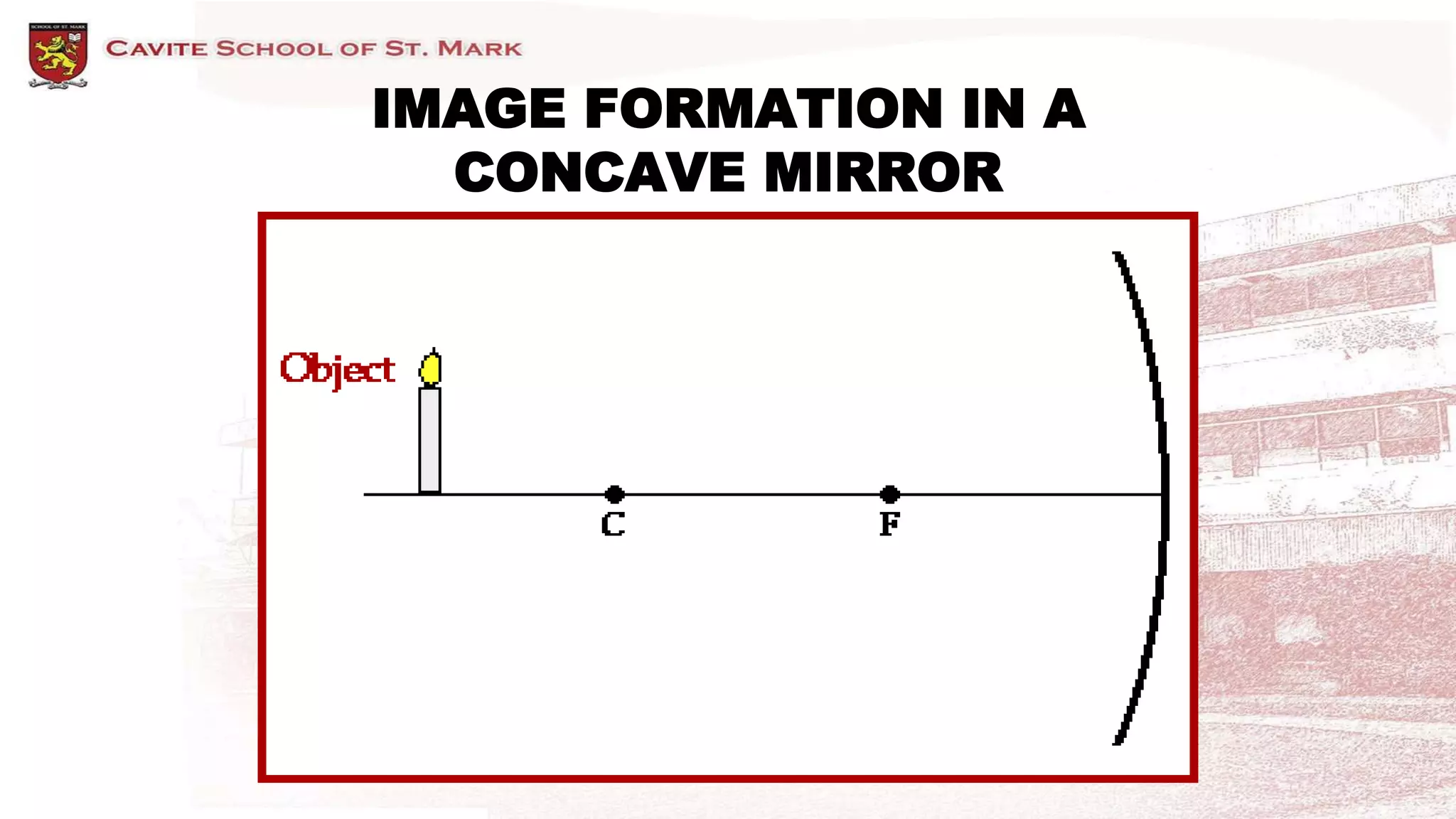
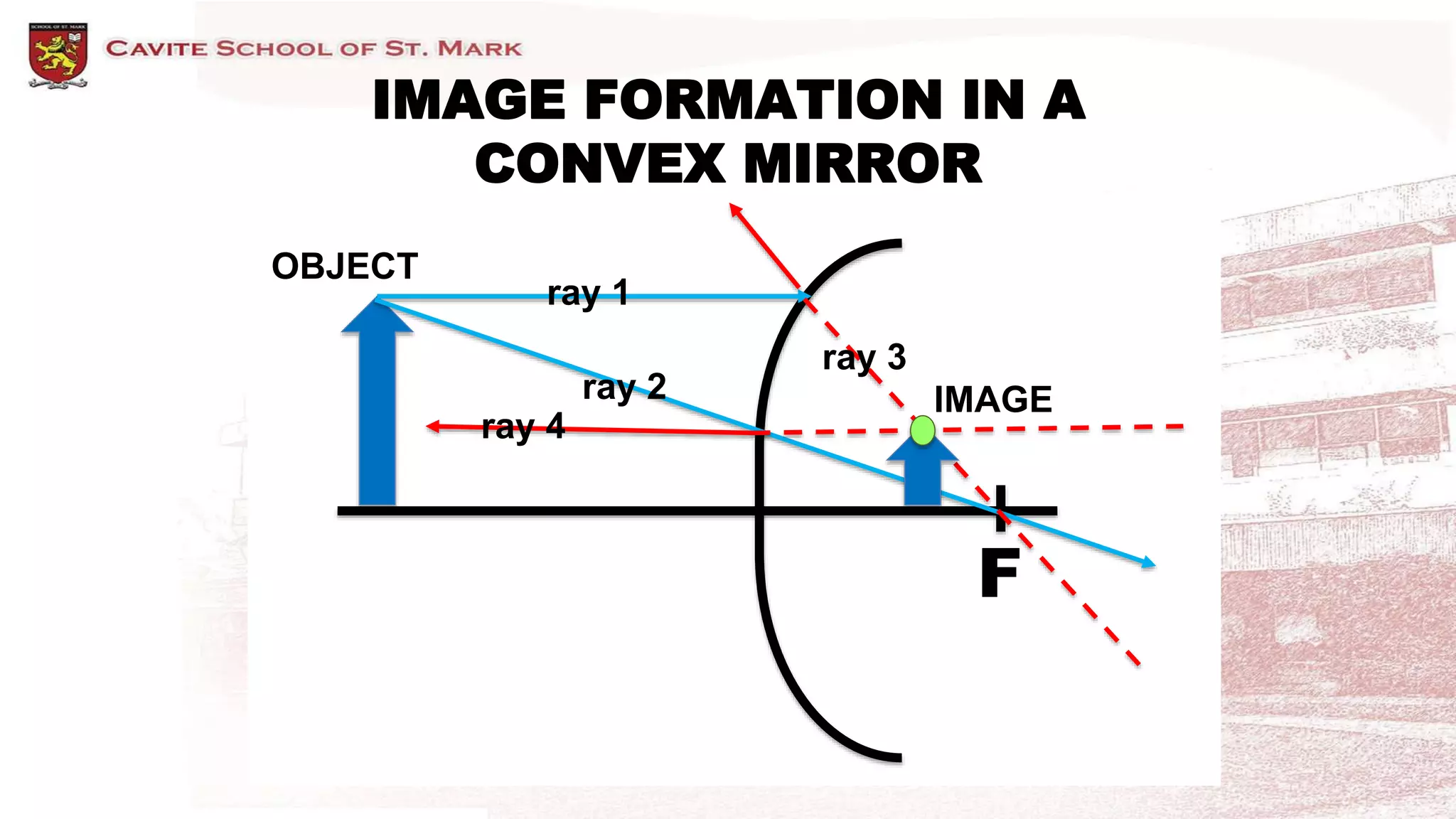
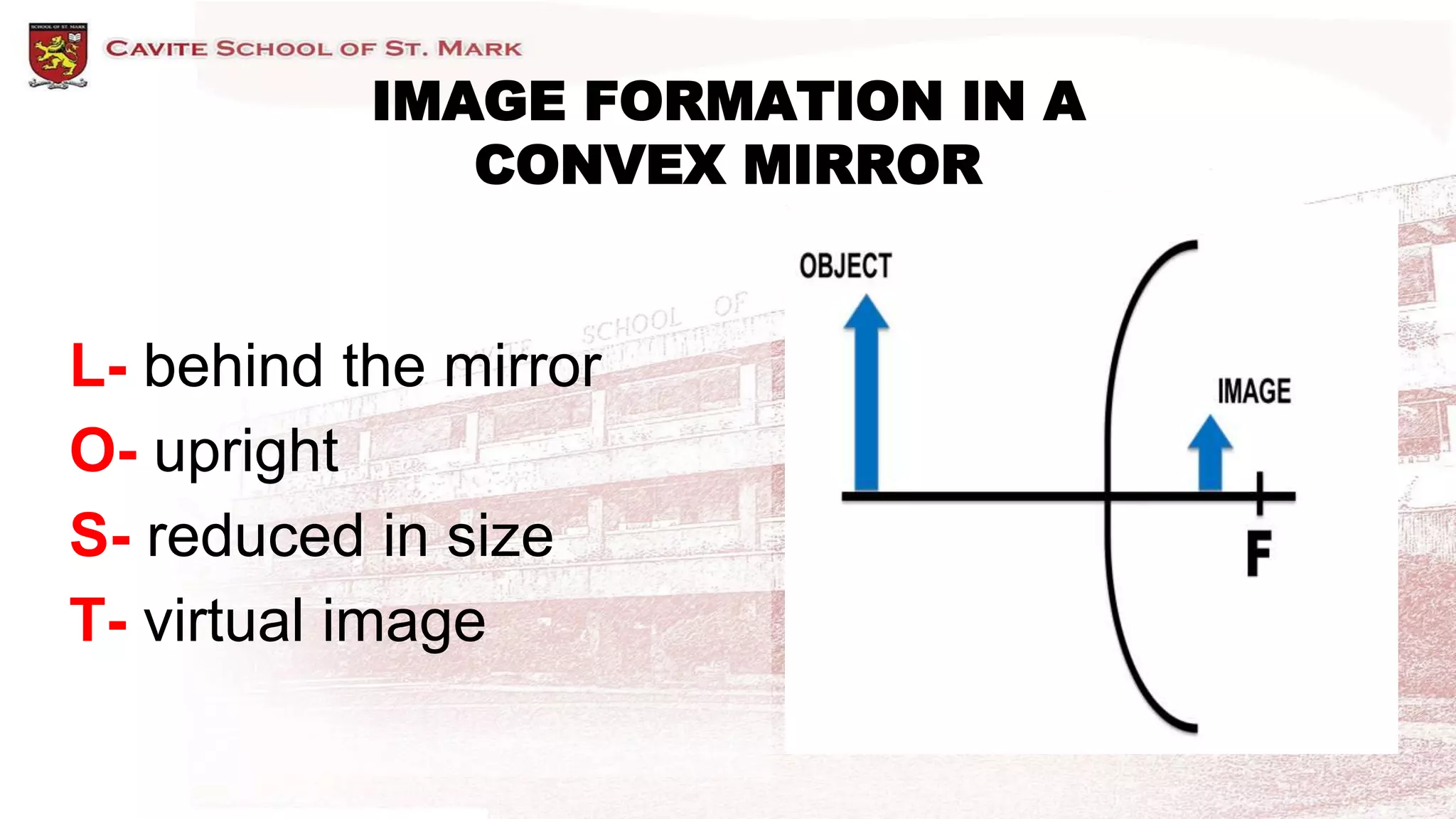

This document discusses different types of mirrors and how they form images. It describes plane mirrors, which produce images of the same size as the object, and curved mirrors, including concave mirrors that can produce real or virtual images depending on the object's position, and convex mirrors that only produce smaller virtual images. Ray diagrams are introduced as a way to determine the characteristics of images formed by mirrors and lenses. Specific examples of image formation using ray diagrams are provided for concave and convex mirrors.
















