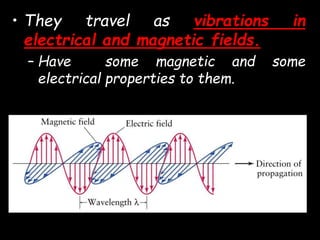
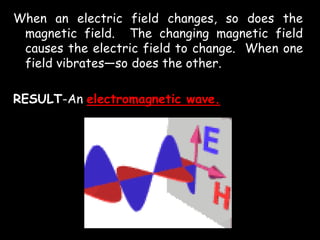
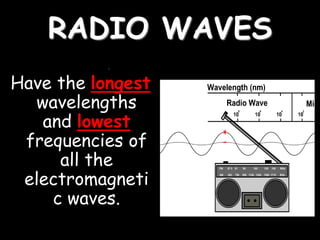
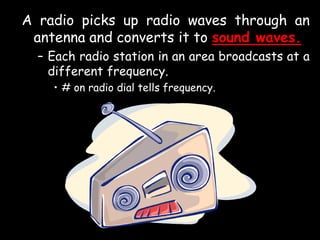
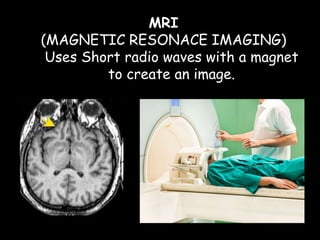
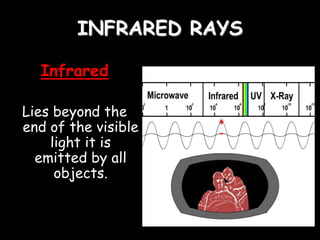
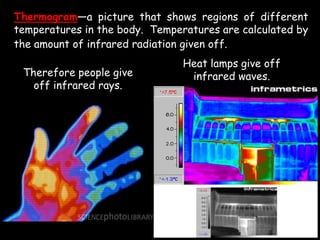
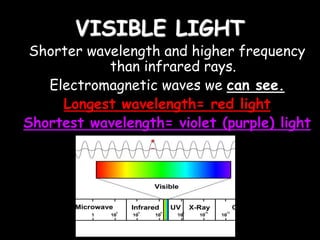
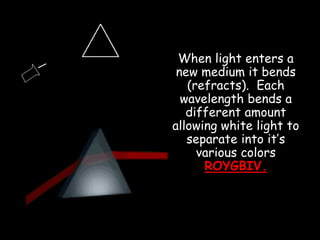
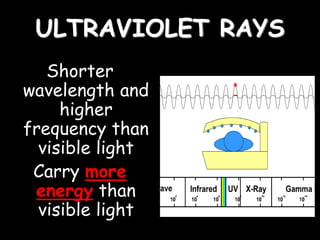
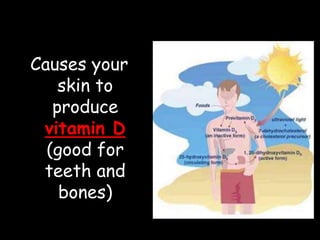
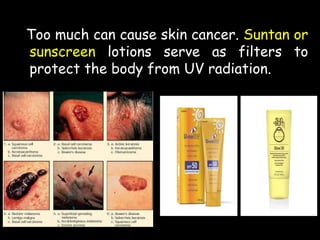
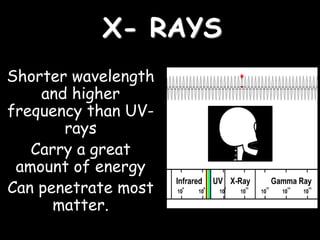
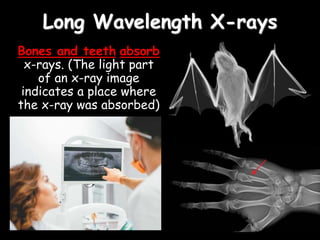
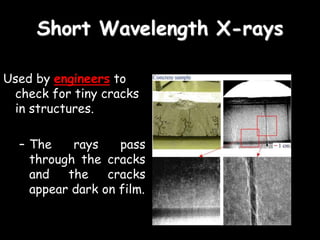
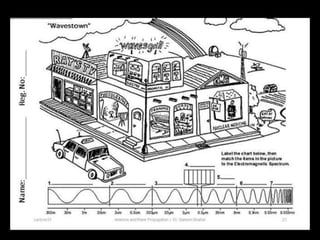
Radio waves are used for GPS, wireless communications, and medical imaging. Microwaves are used in microwave ovens, radar, and satellite communications. Infrared is used in thermal imaging, remote controls, and night vision. Visible light is what we see, while ultraviolet sterilizes water and produces vitamin D. X-rays are used for medical imaging, and gamma rays are used for cancer treatment and in nuclear weapons. All electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light and have different wavelengths and frequencies that determine their energy and ability to penetrate matter.