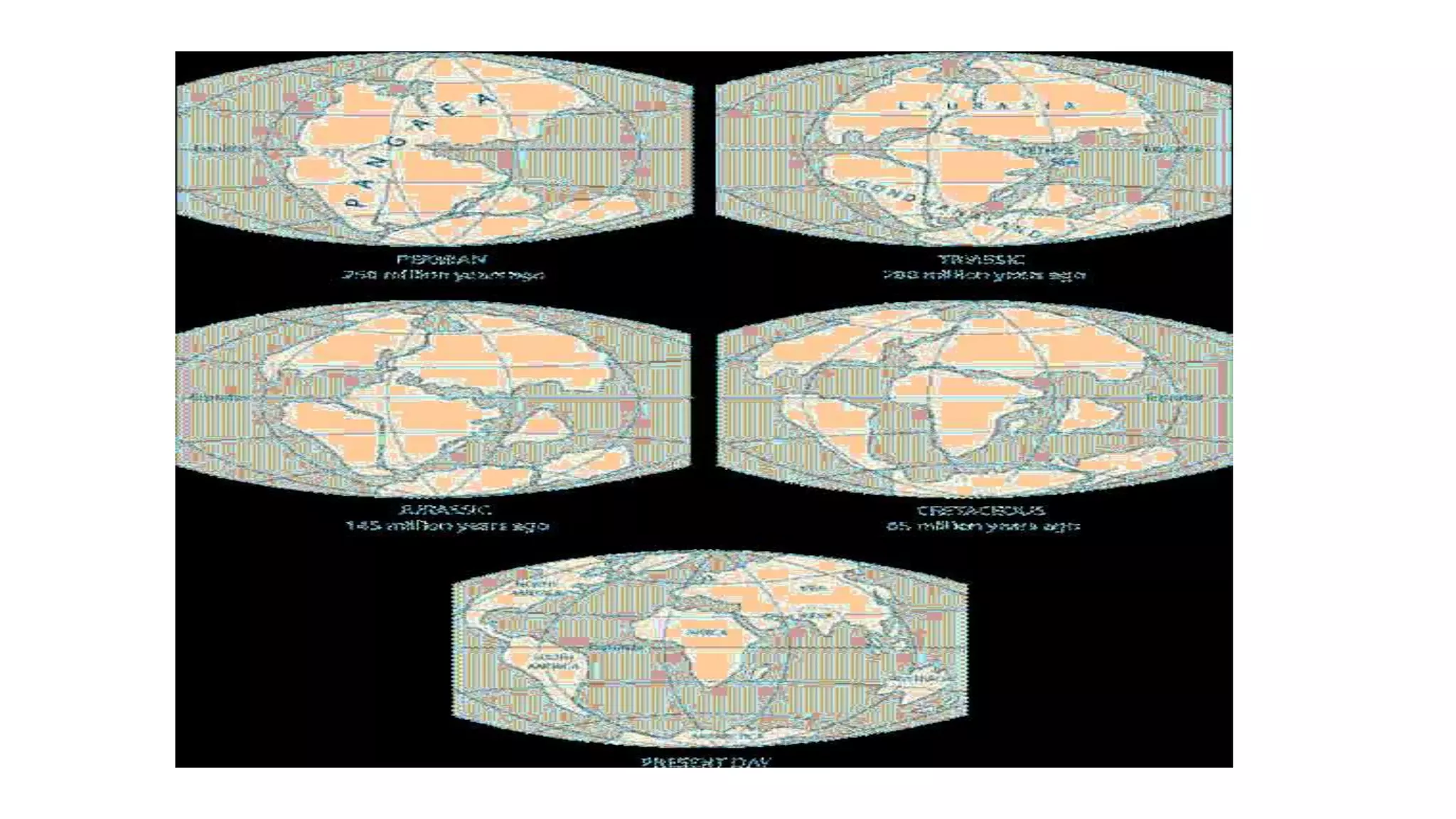
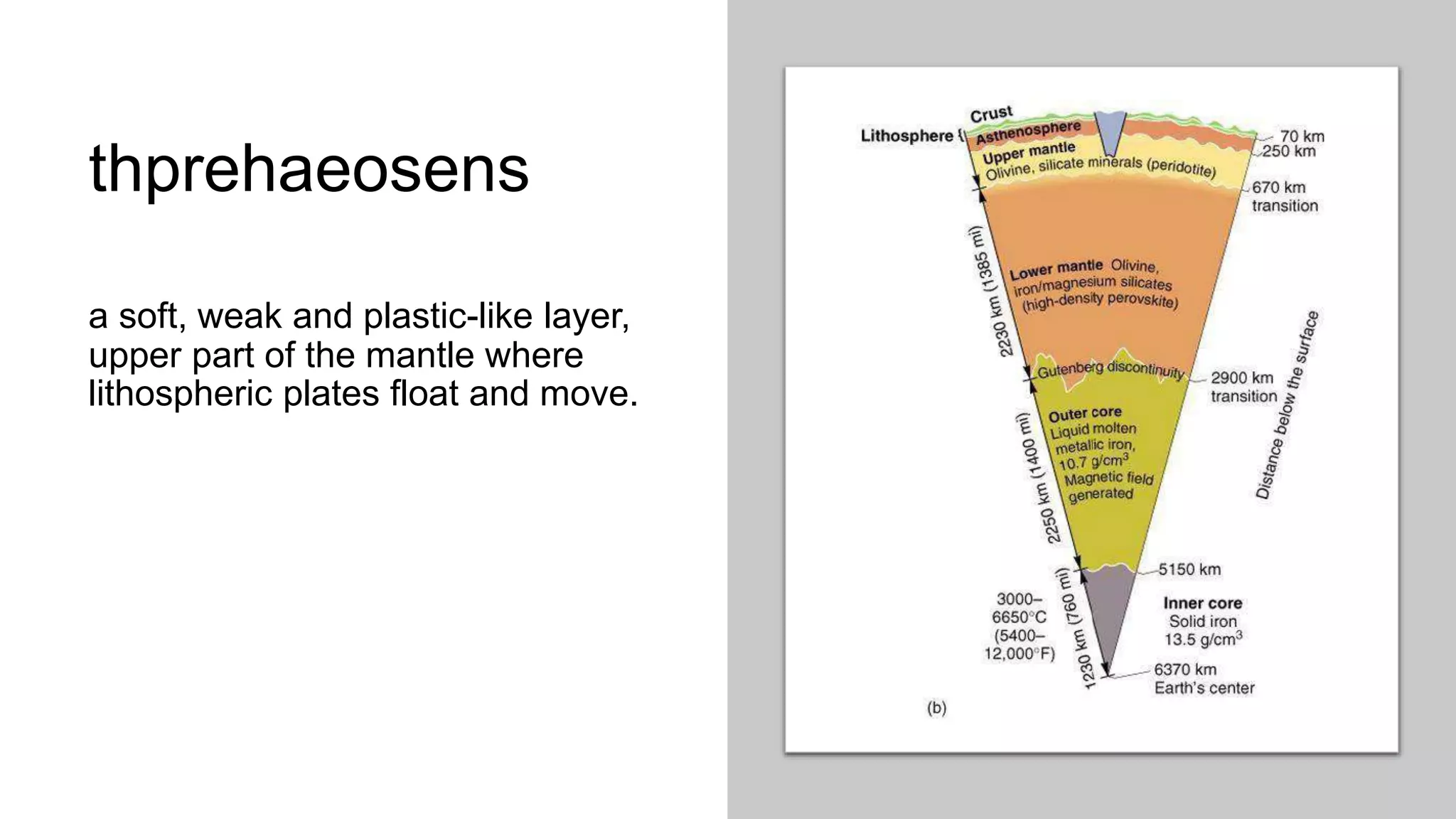
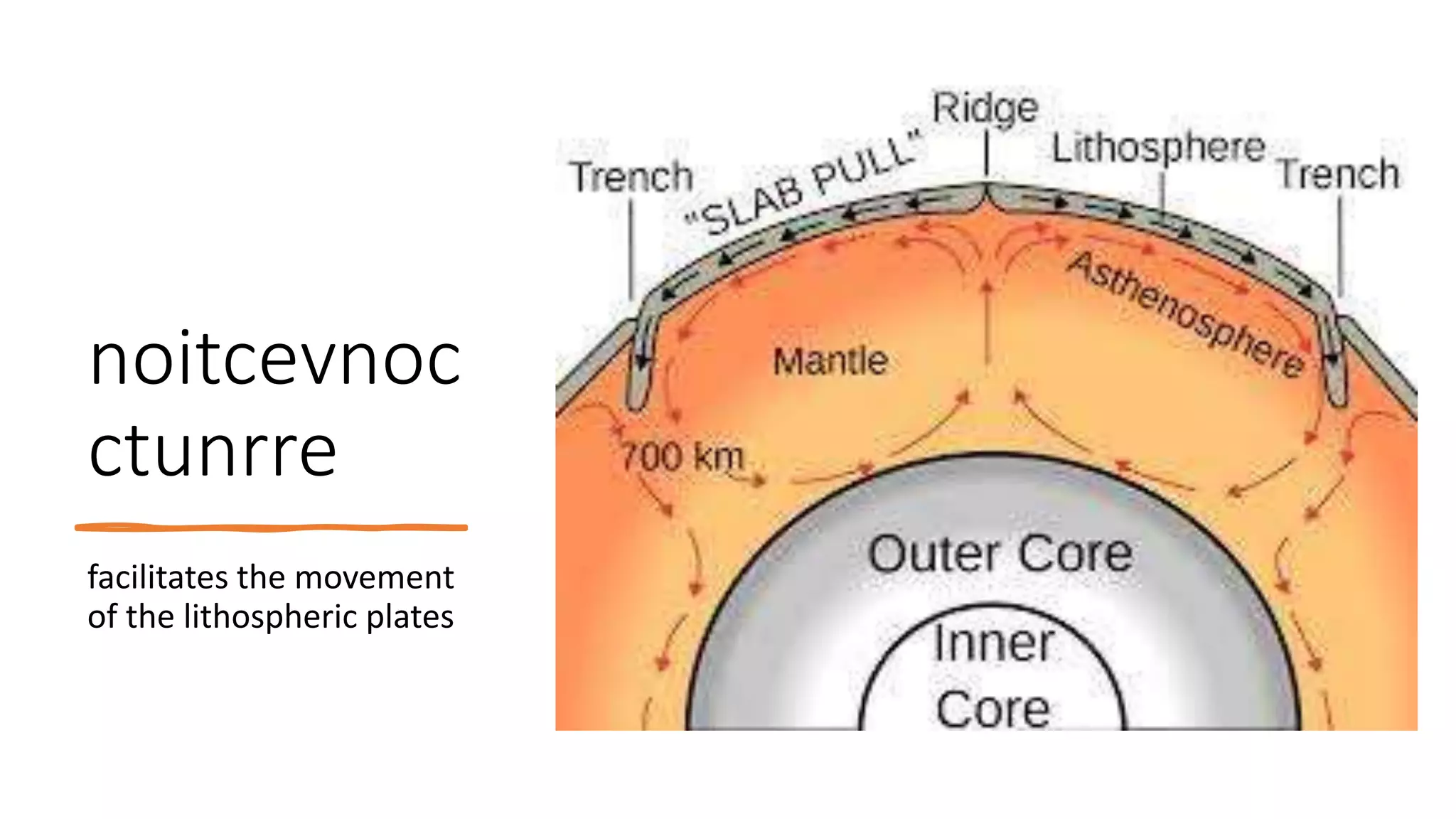
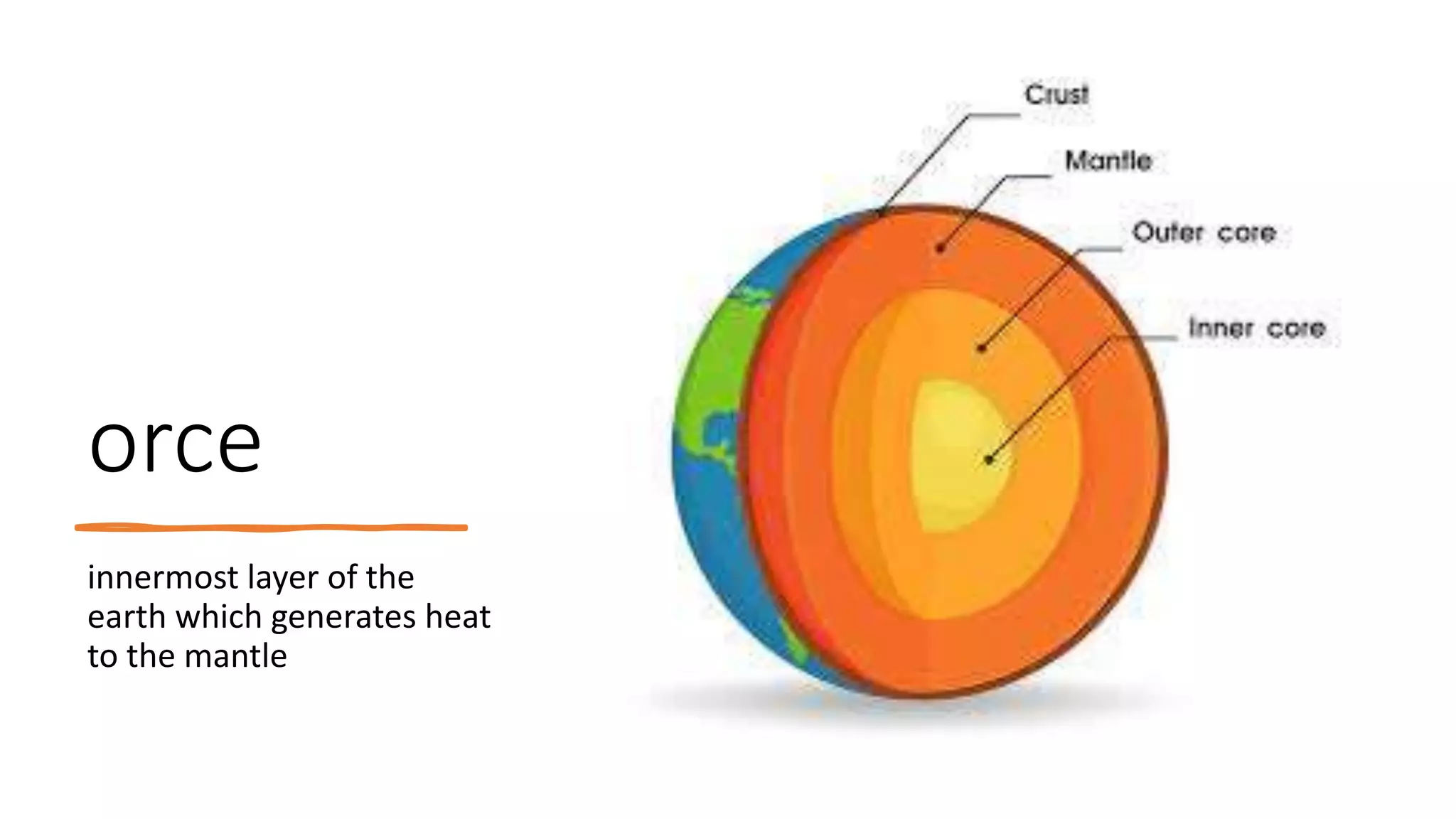
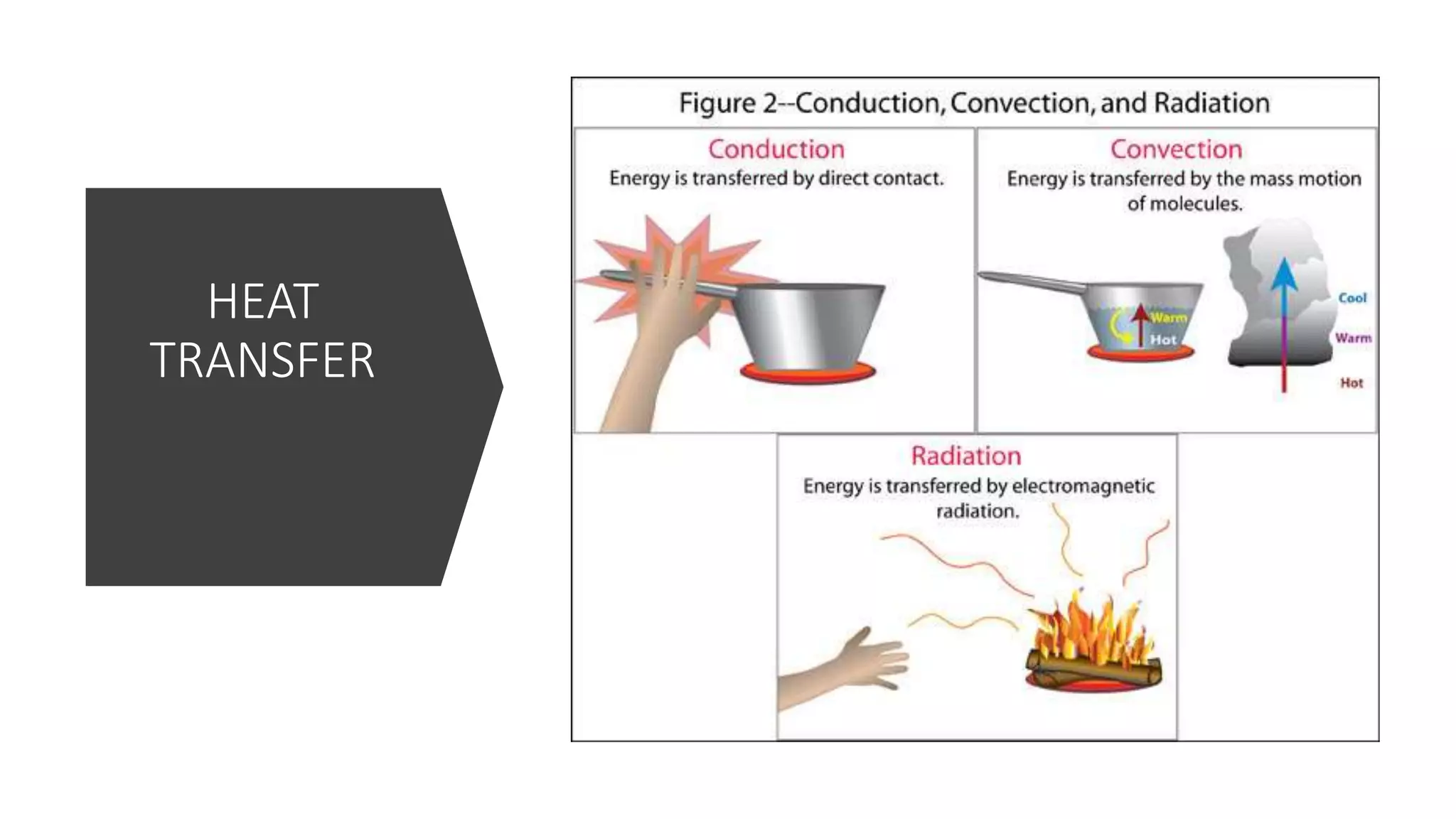
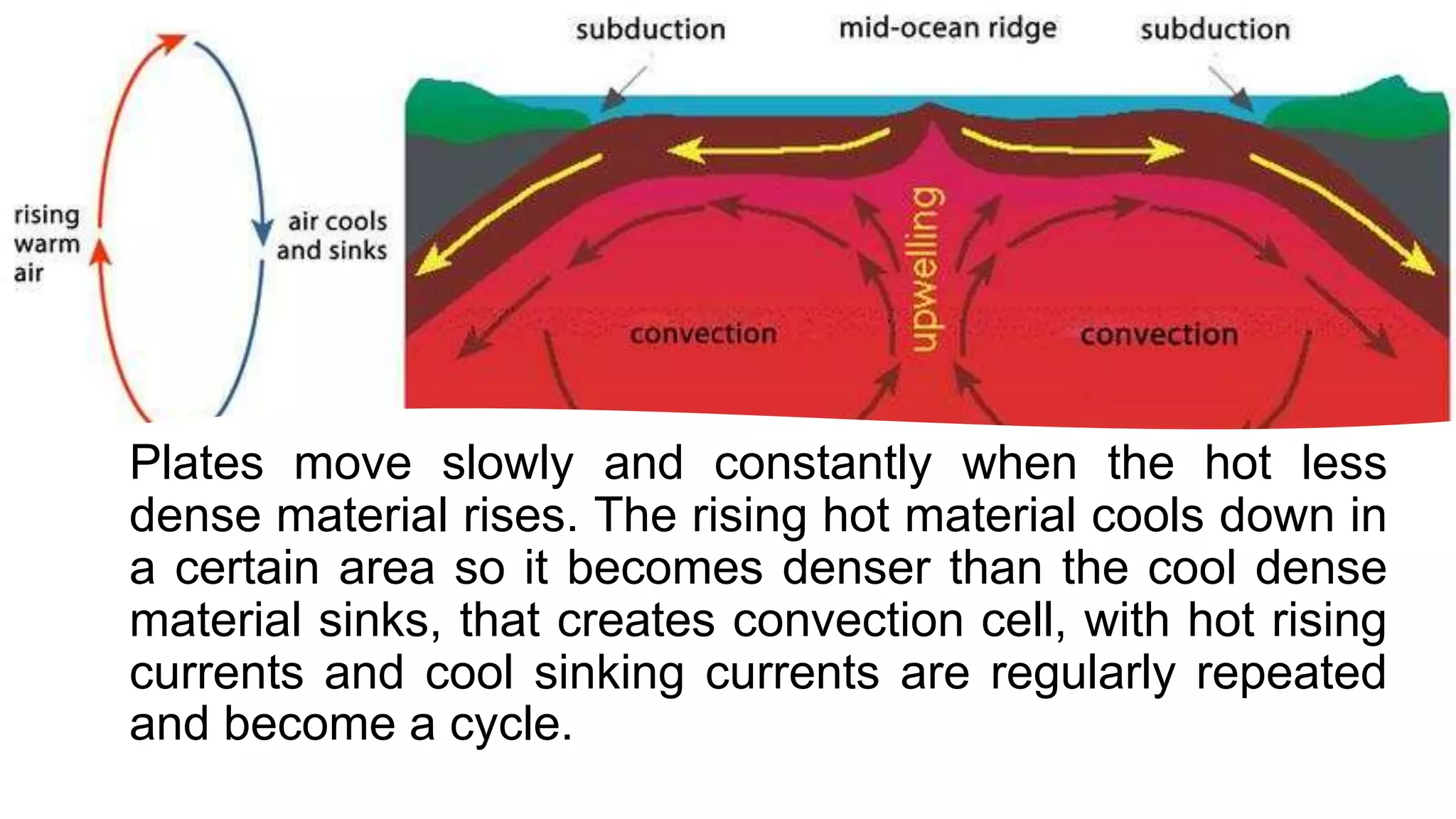
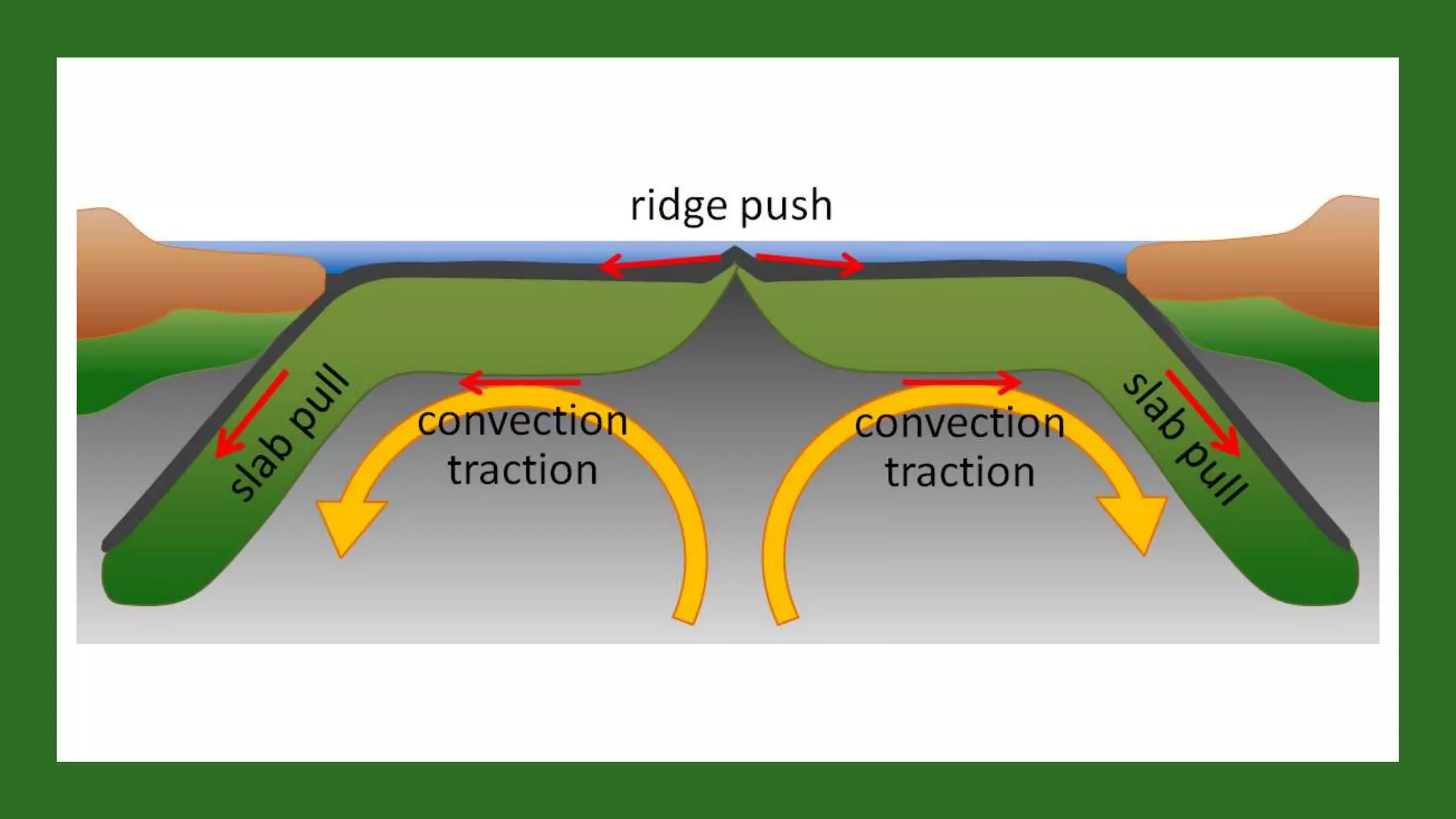
The document discusses theories of the Earth's movement including continental drift and seafloor spreading. It explains that mantle convection causes lithospheric plates to move via convection currents. Hot mantle material rises and cools, sinking elsewhere, moving the plates over geologic timescales through processes like ridge push and slab pull. Plate tectonics integrates these ideas to explain volcanoes, earthquakes, and mountain building at plate boundaries.