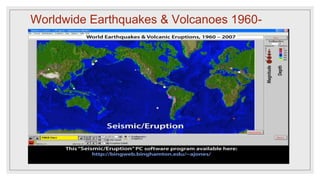
Active volcanoes, earthquake epicenters, and major mountain belts are mostly found along plate boundaries. As the plates move, geological events occur where the plates meet. Most volcanoes are located along boundaries like the Ring of Fire in the Pacific Ocean. Earthquake epicenters are also commonly found near plate boundaries where tectonic plates collide, diverge, or move past each other. Likewise, major mountain ranges tend to form at plate boundaries due to compression as the plates converge. The distribution of these geological features relates to plate tectonic theory, which explains that their formation is caused by the movement and interactions of tectonic plates.