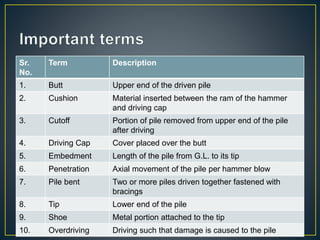
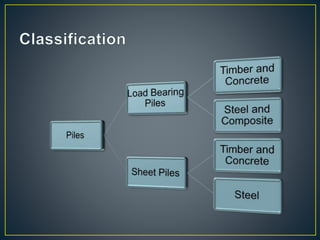
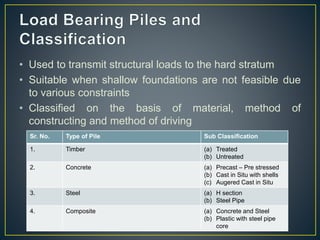
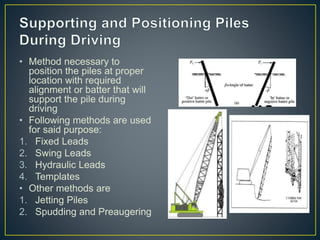
This document provides an overview of pile foundations and construction techniques. It begins with definitions of key pile terminology. Piles are then classified based on material (timber, concrete, steel, composite) and construction method. Details are given on driving and installing different pile types, including considerations for soil conditions, hammer selection, and positioning equipment. Additional foundation techniques like diaphragm walls are also introduced. Test pile programs are recommended to select the appropriate pile design and installation method for site conditions.