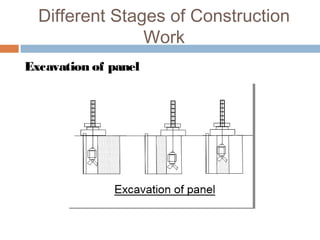
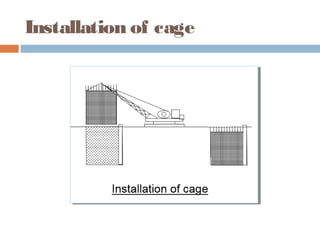
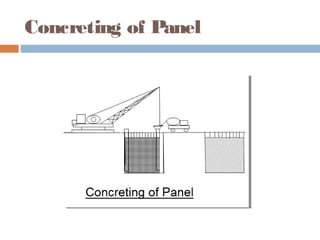
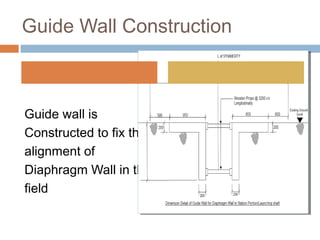
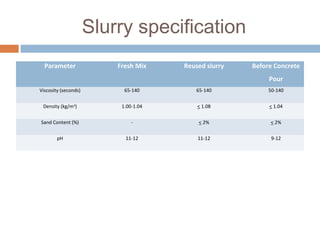
A diaphragm wall is a reinforced concrete wall constructed underground using a slurry trench technique. A slurry trench involves excavating in a trench filled with a thick, viscous fluid called slurry that balances pressure to prevent trench collapse. Reinforcing cages are lowered into the trench and concrete is poured by tremie to displace the slurry. Diaphragm walls can be built close to existing structures, to great depths, and provide strong, watertight basement walls. However, they require specialized equipment and have high costs.