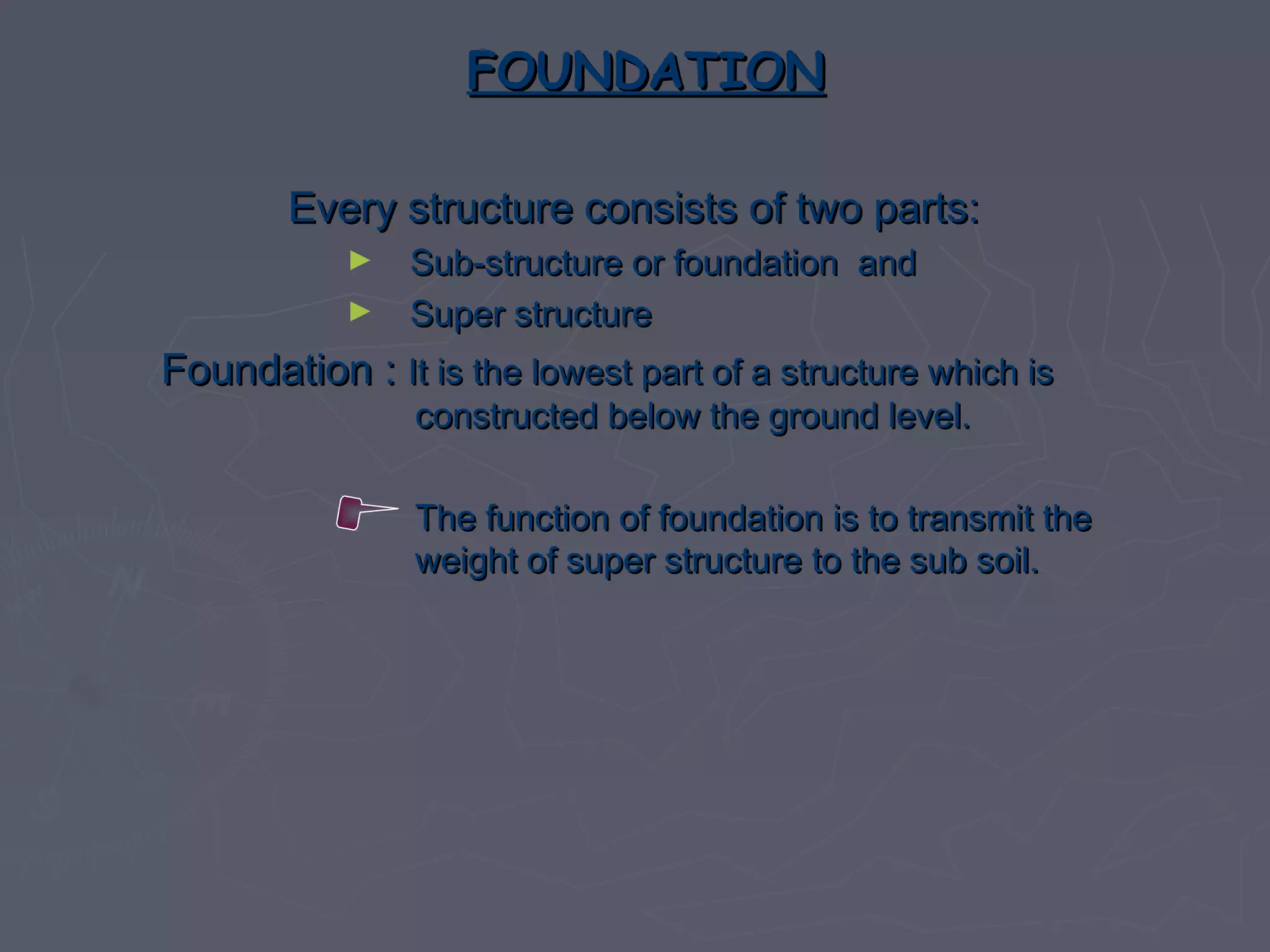
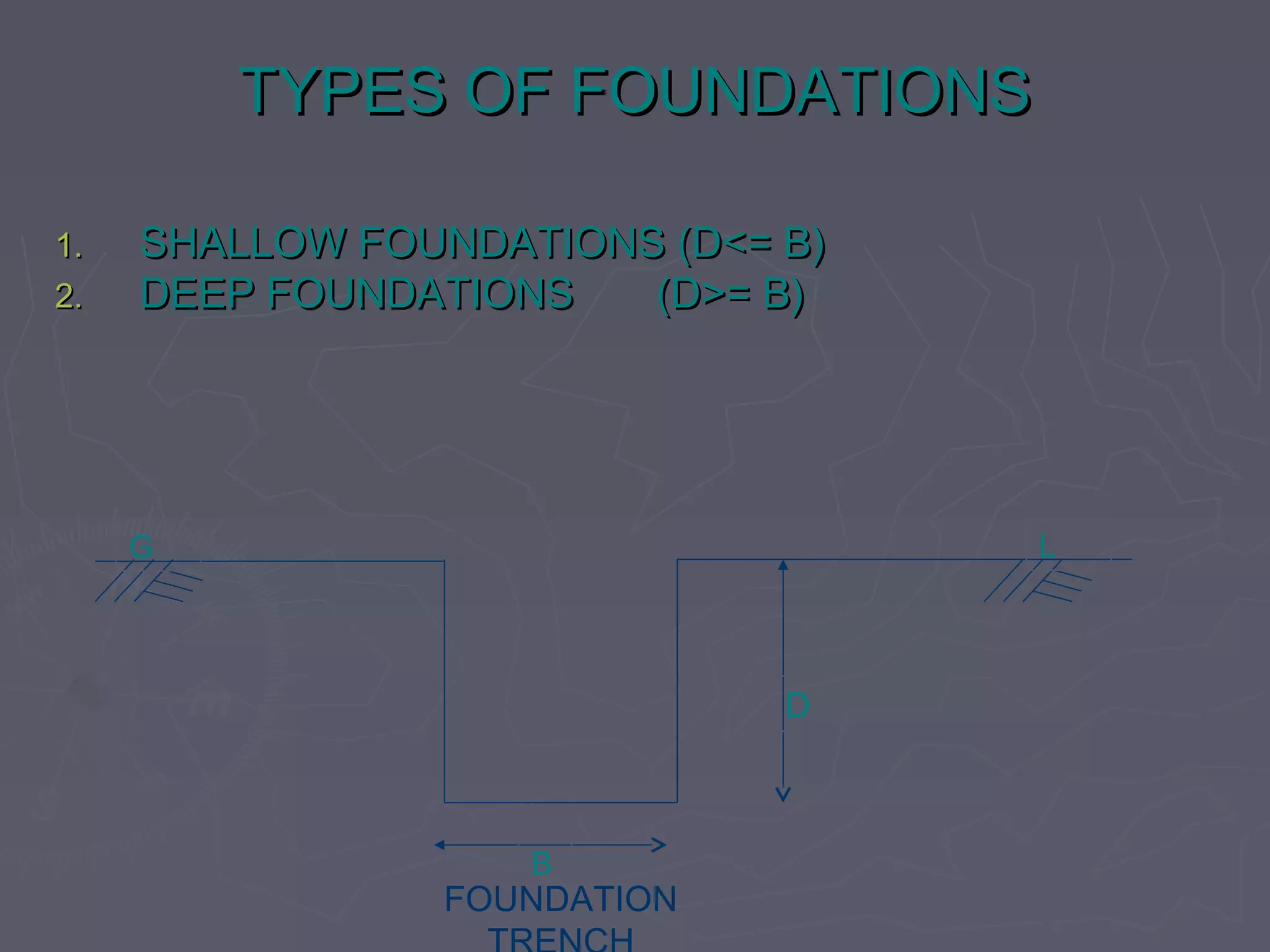
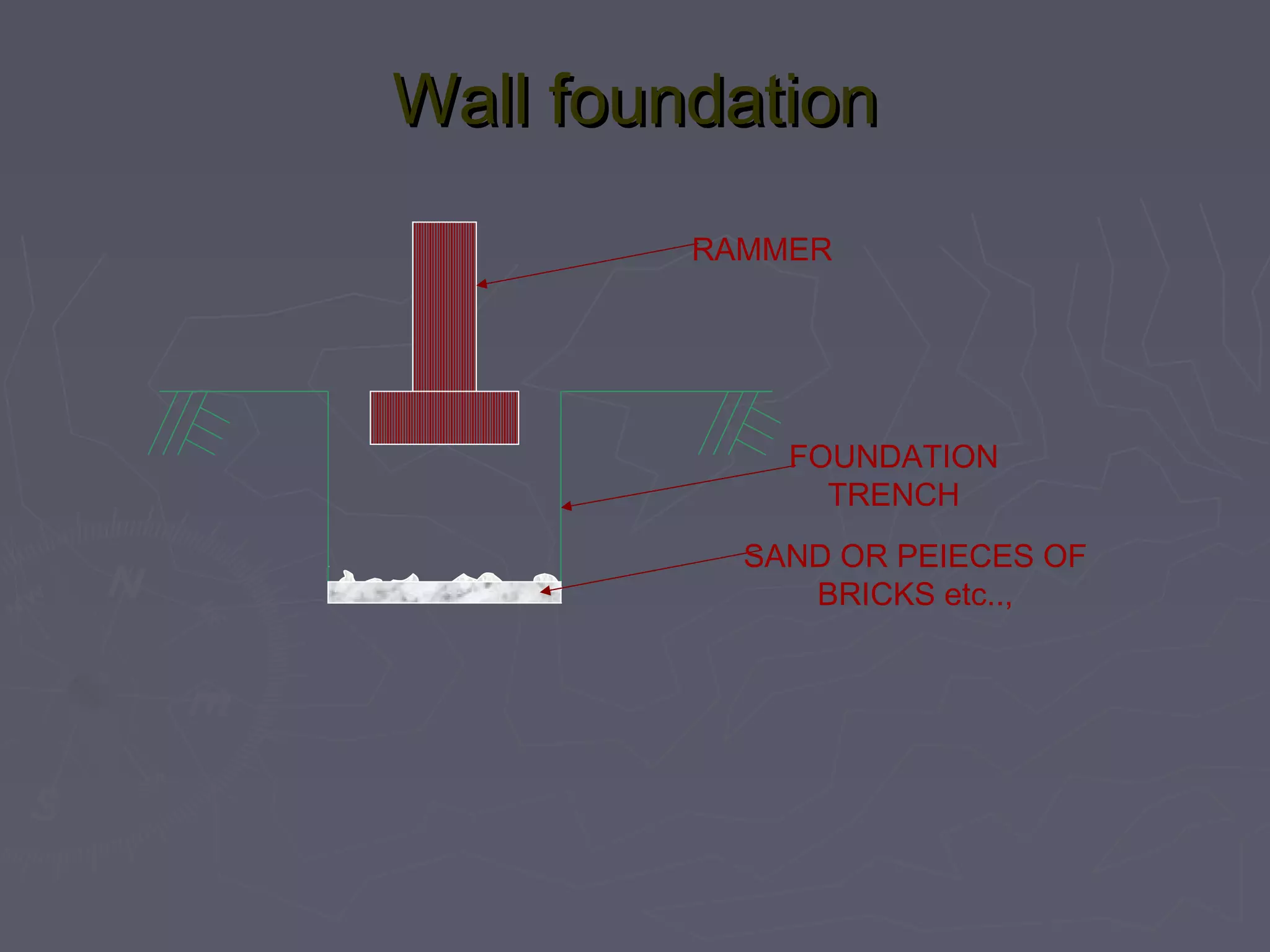
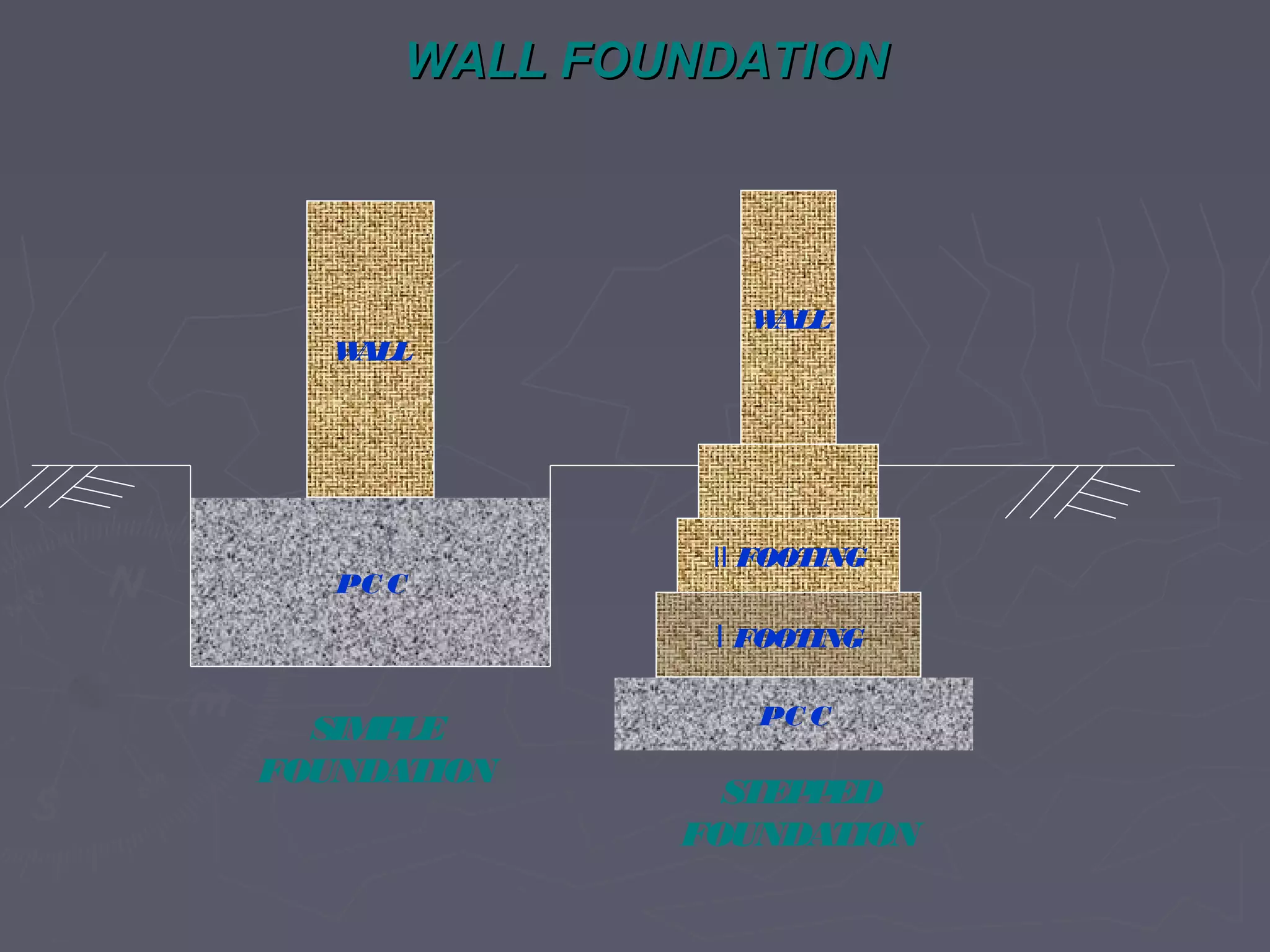
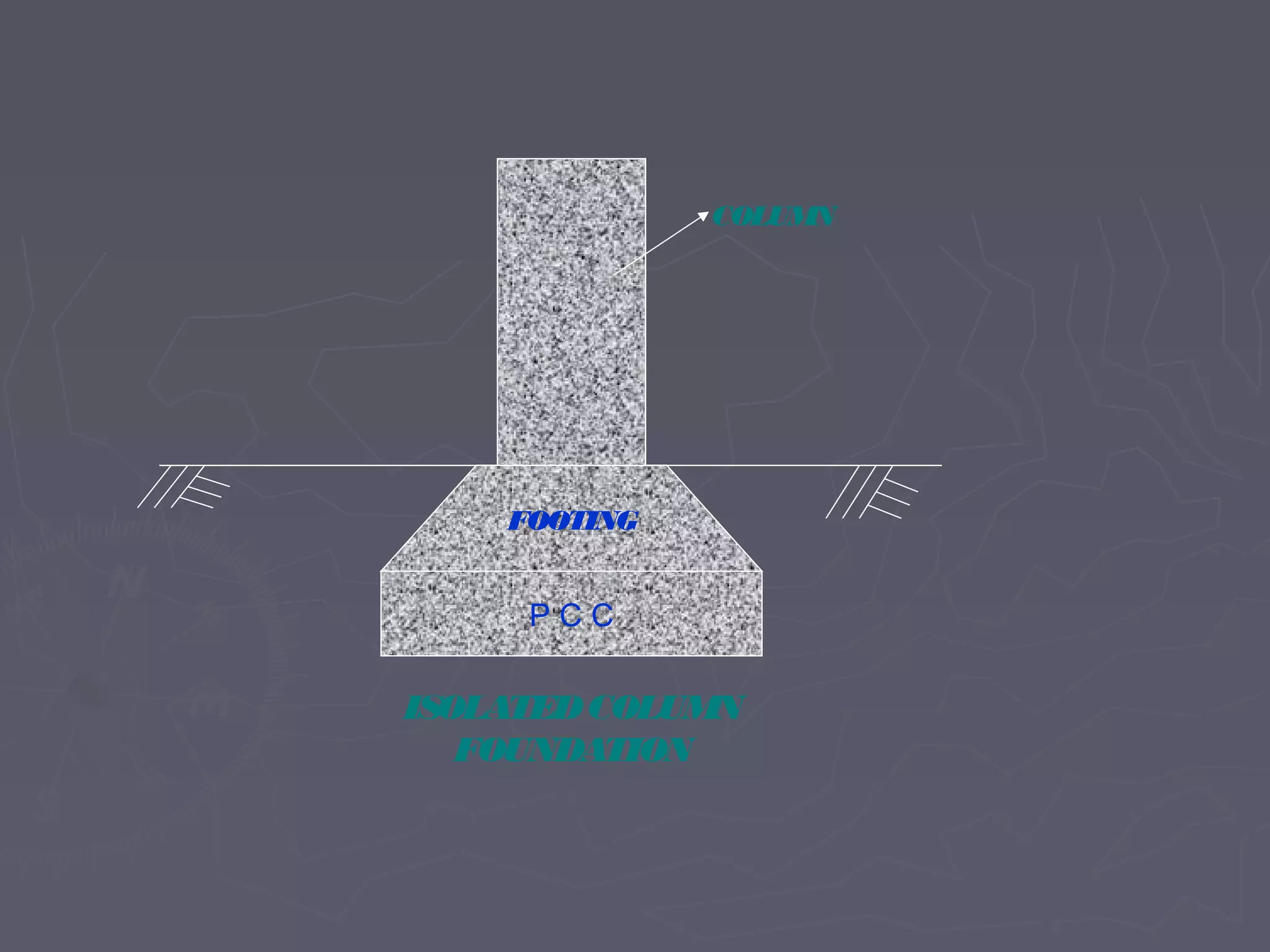
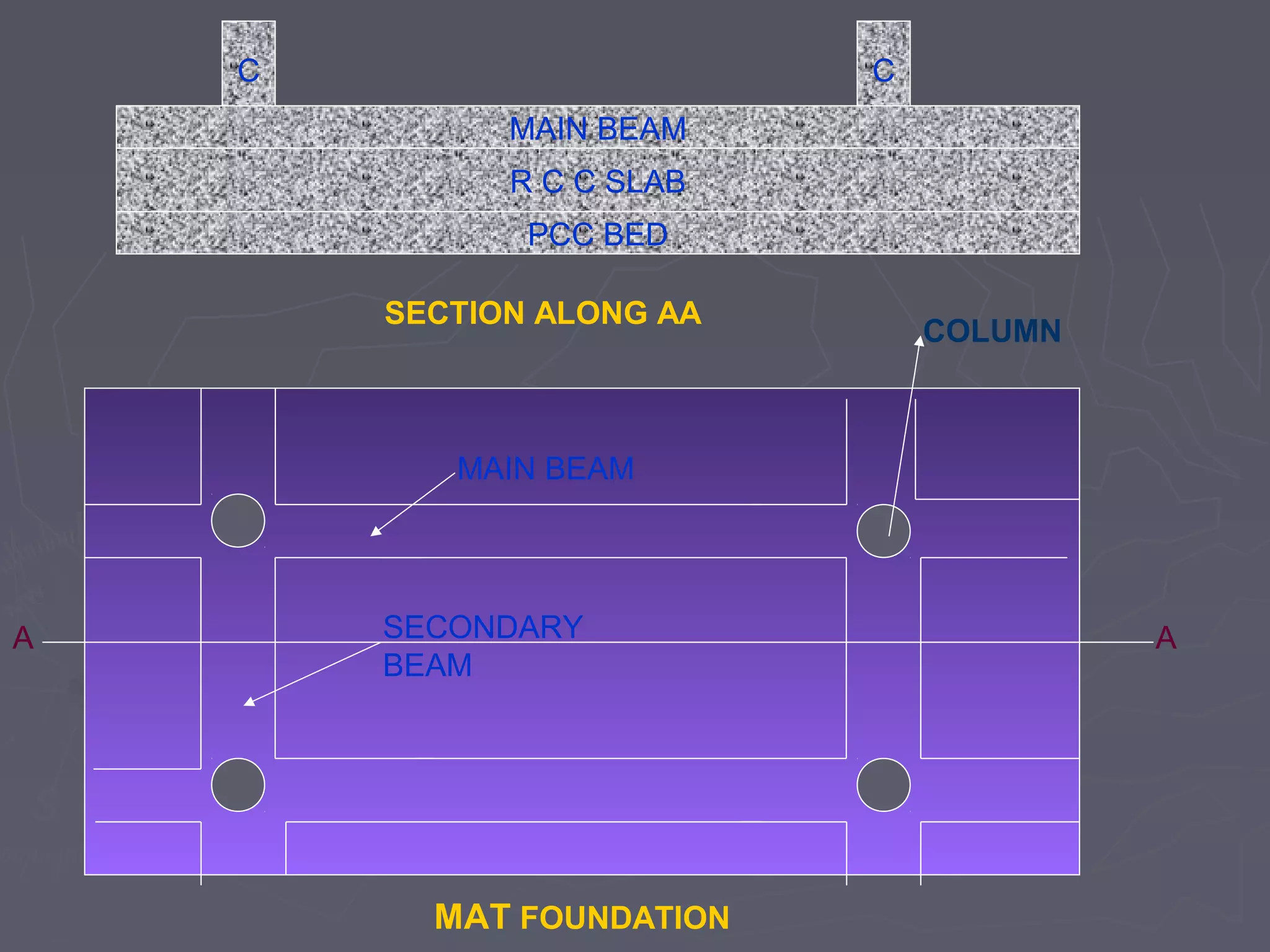
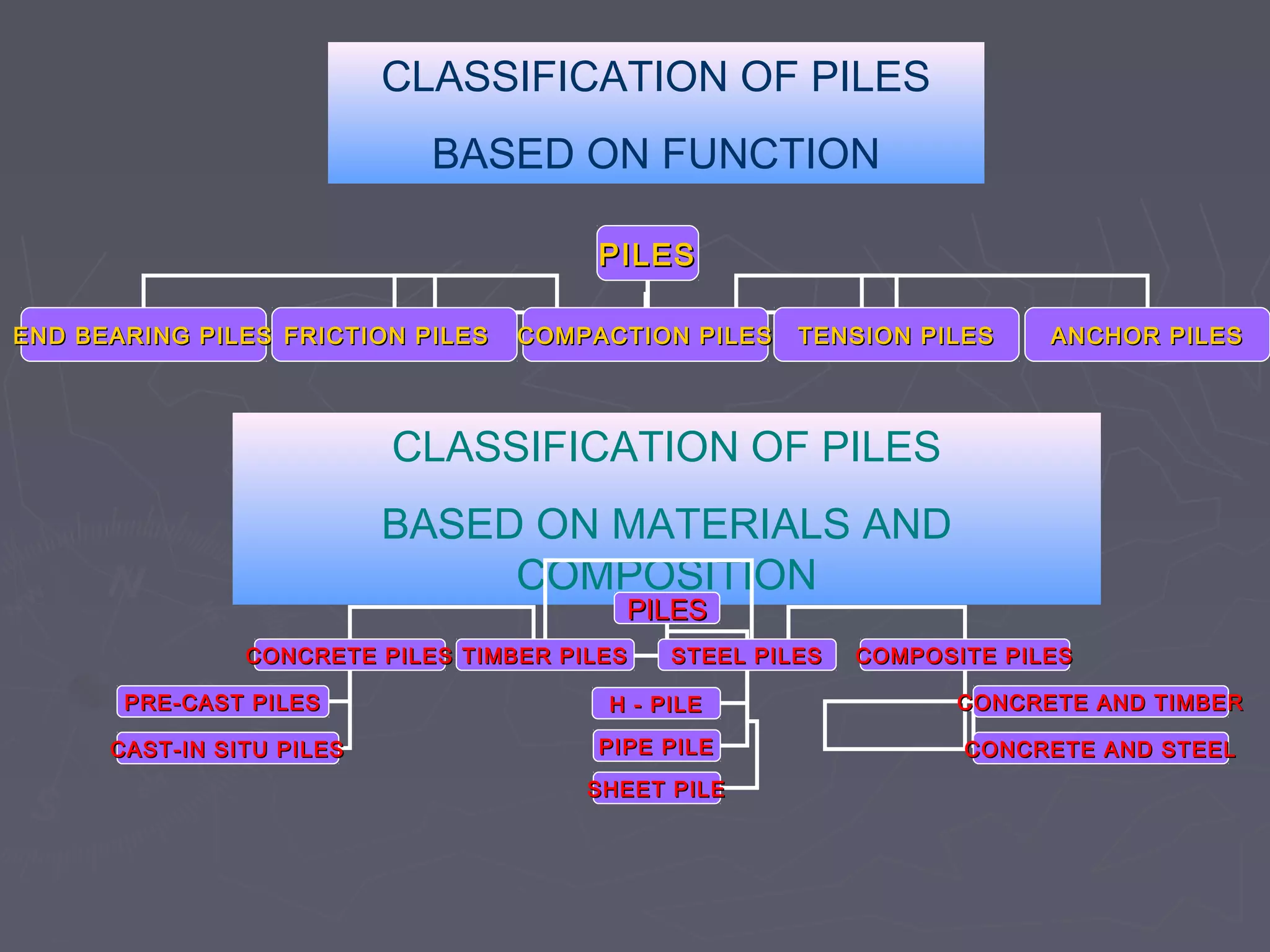
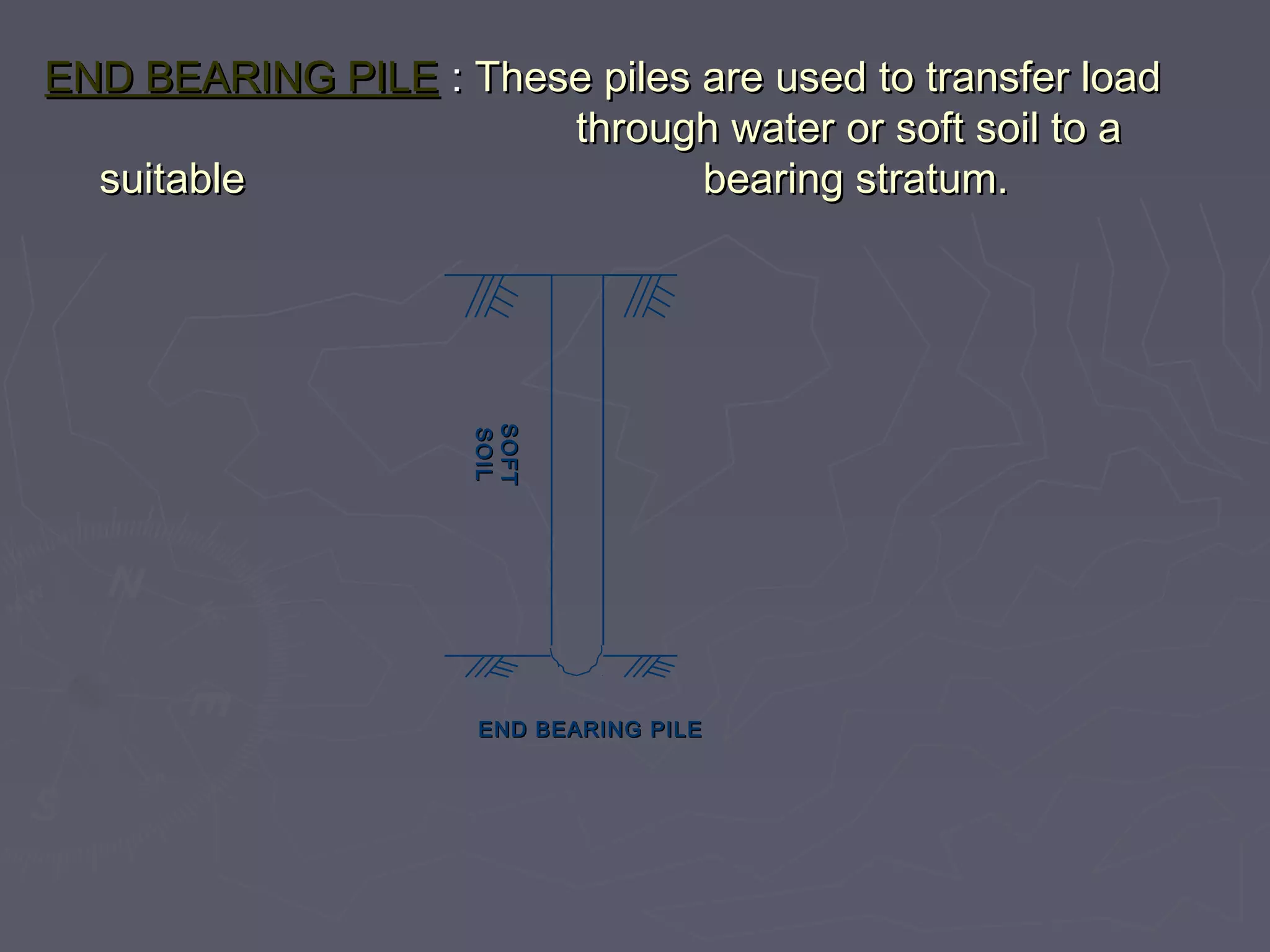
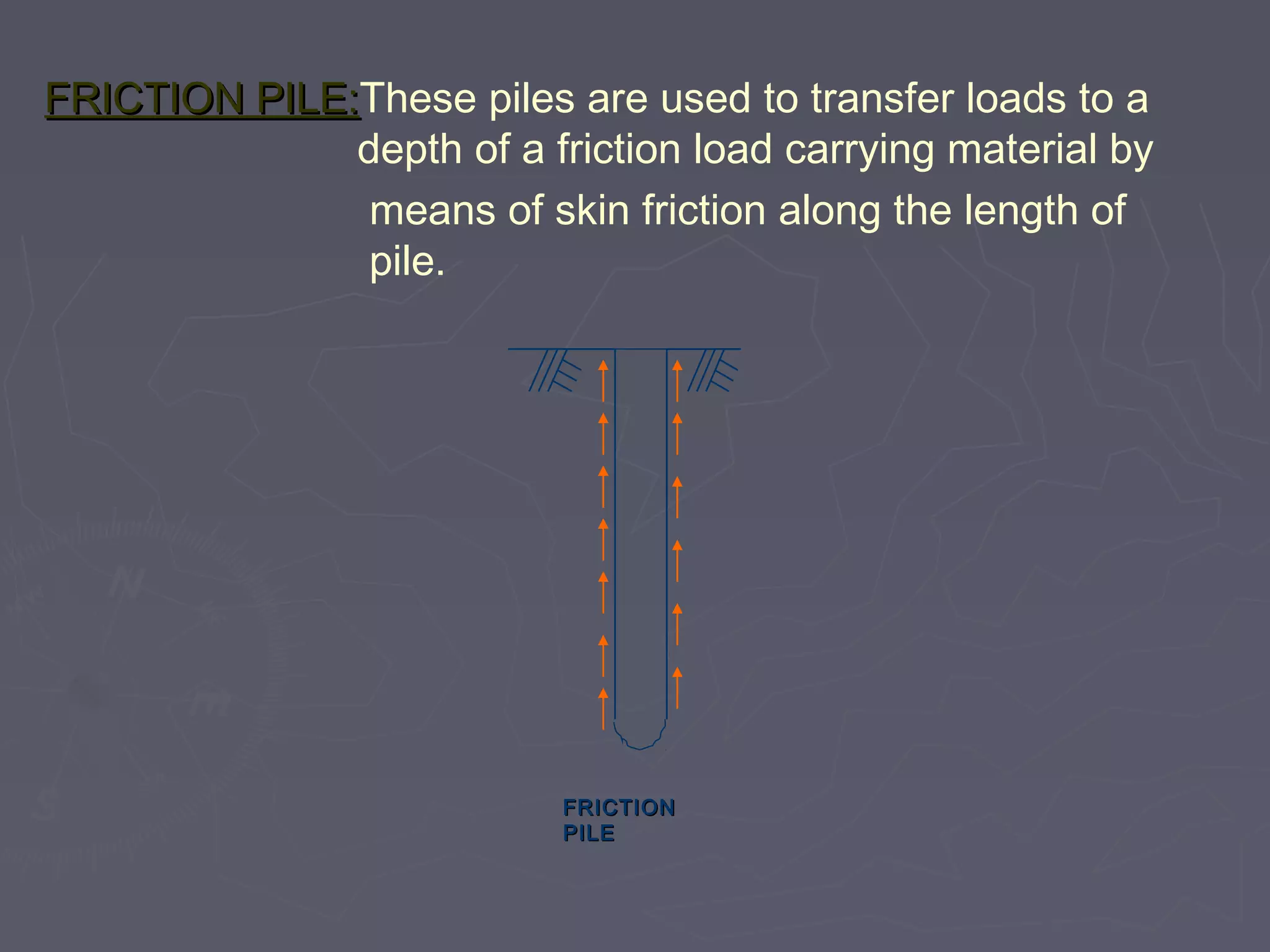
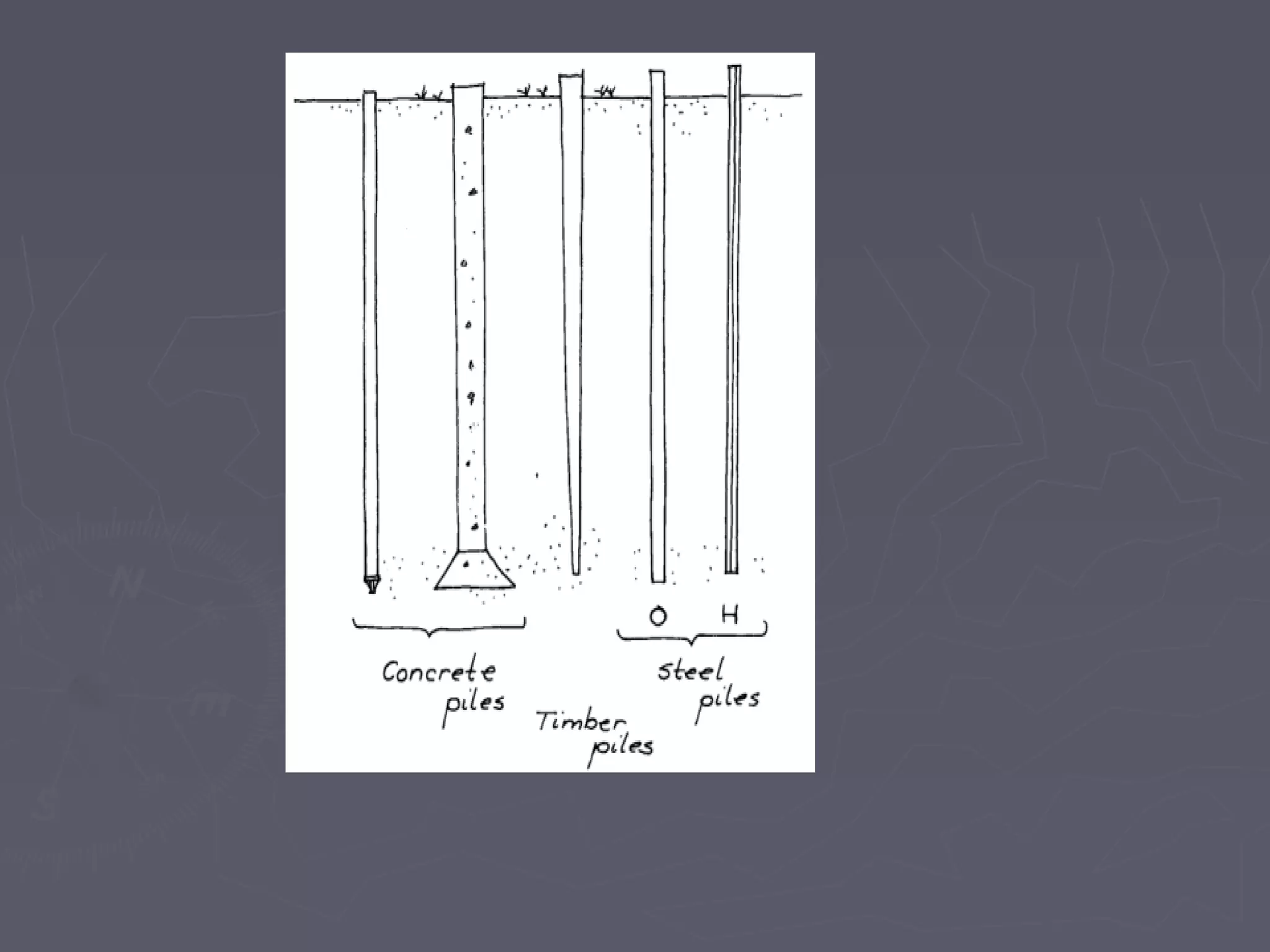
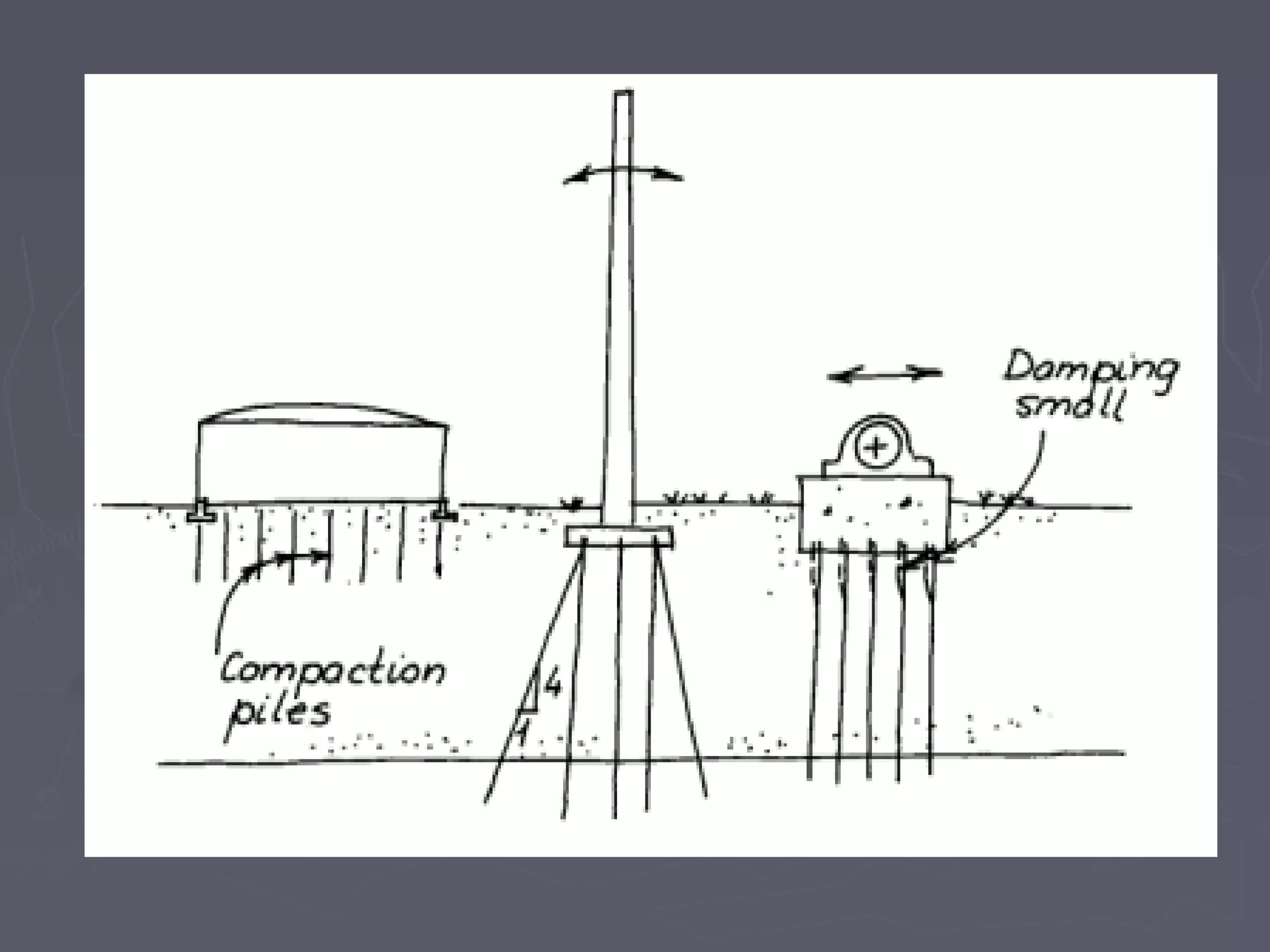
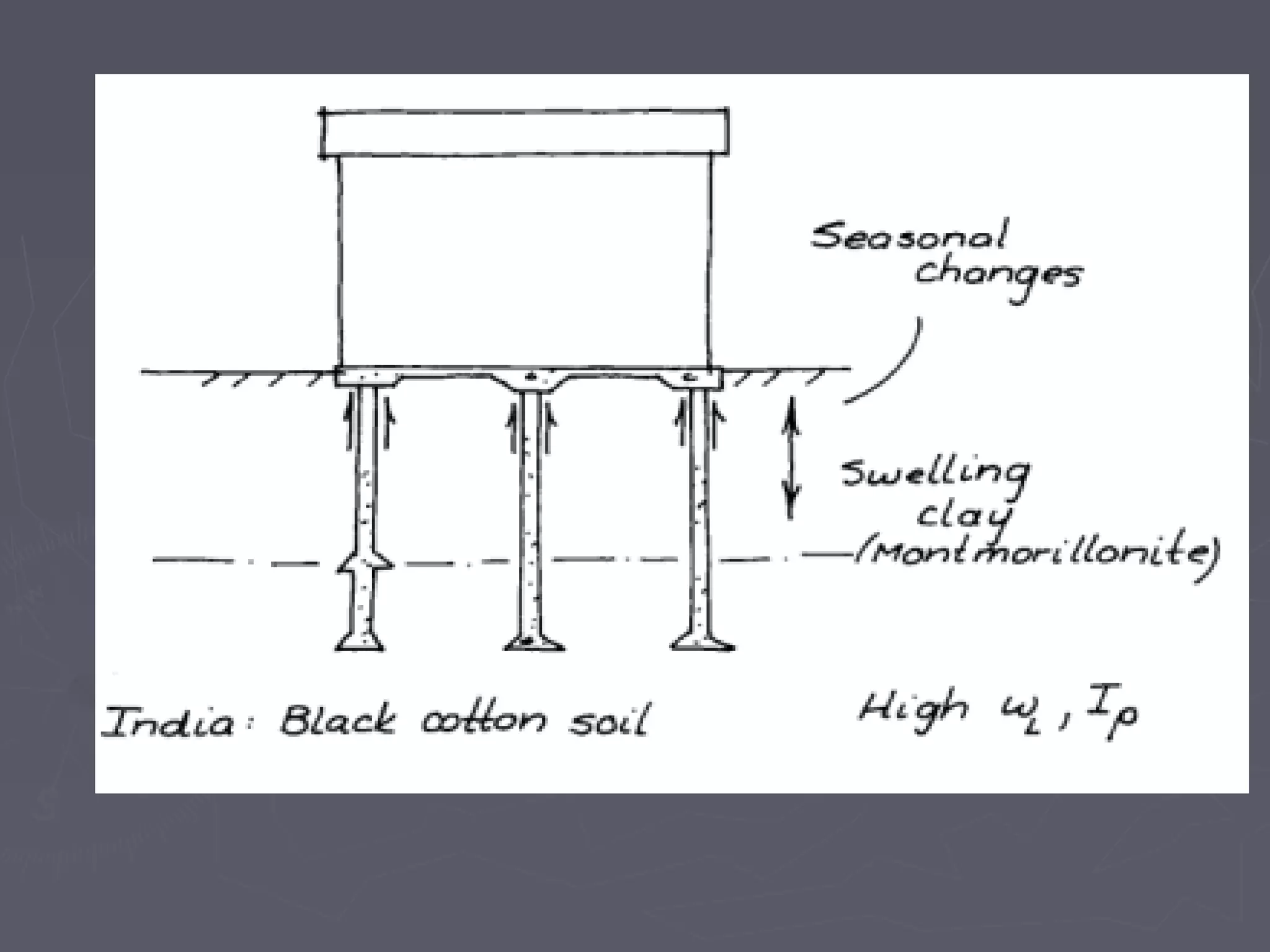
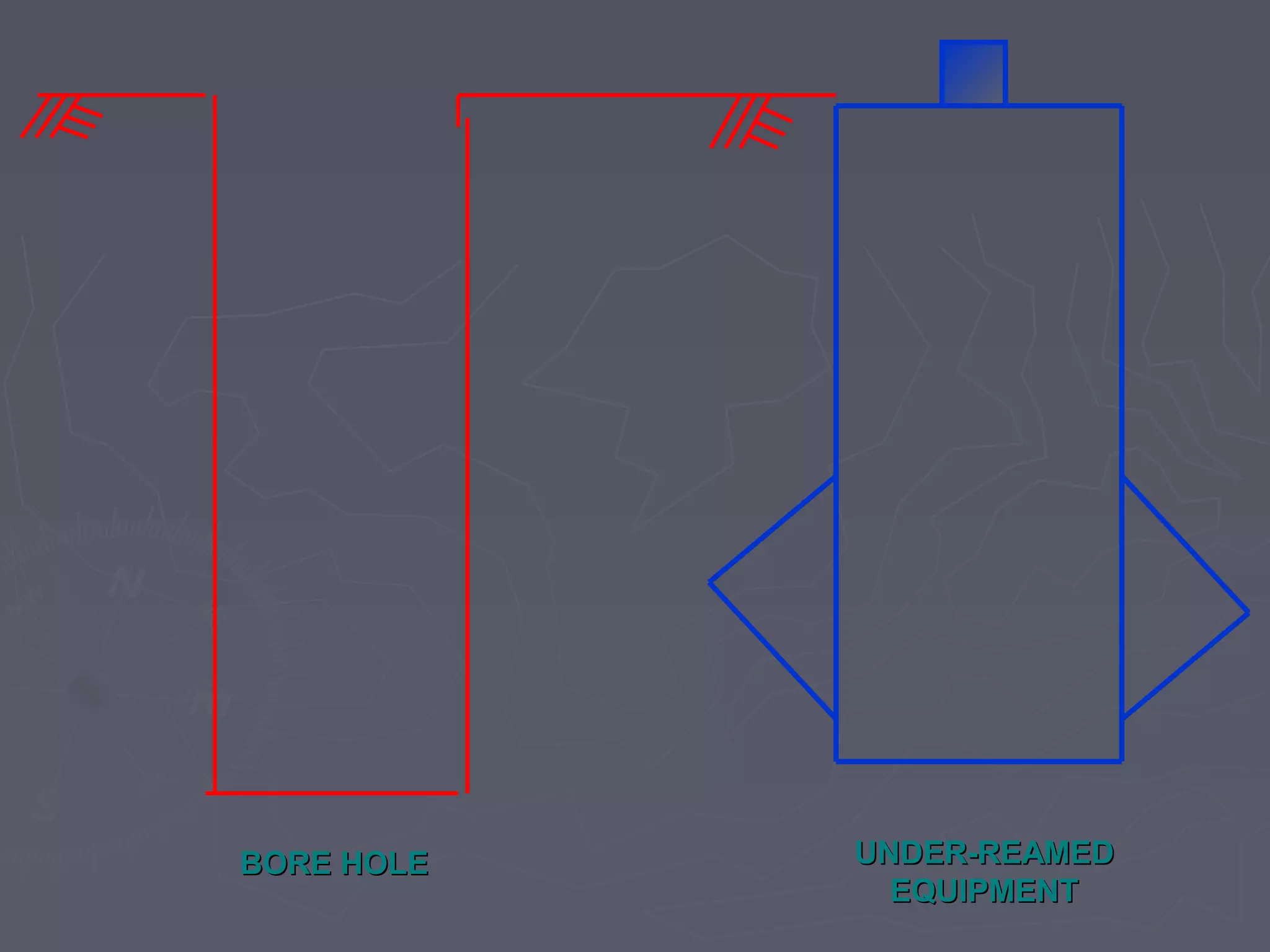
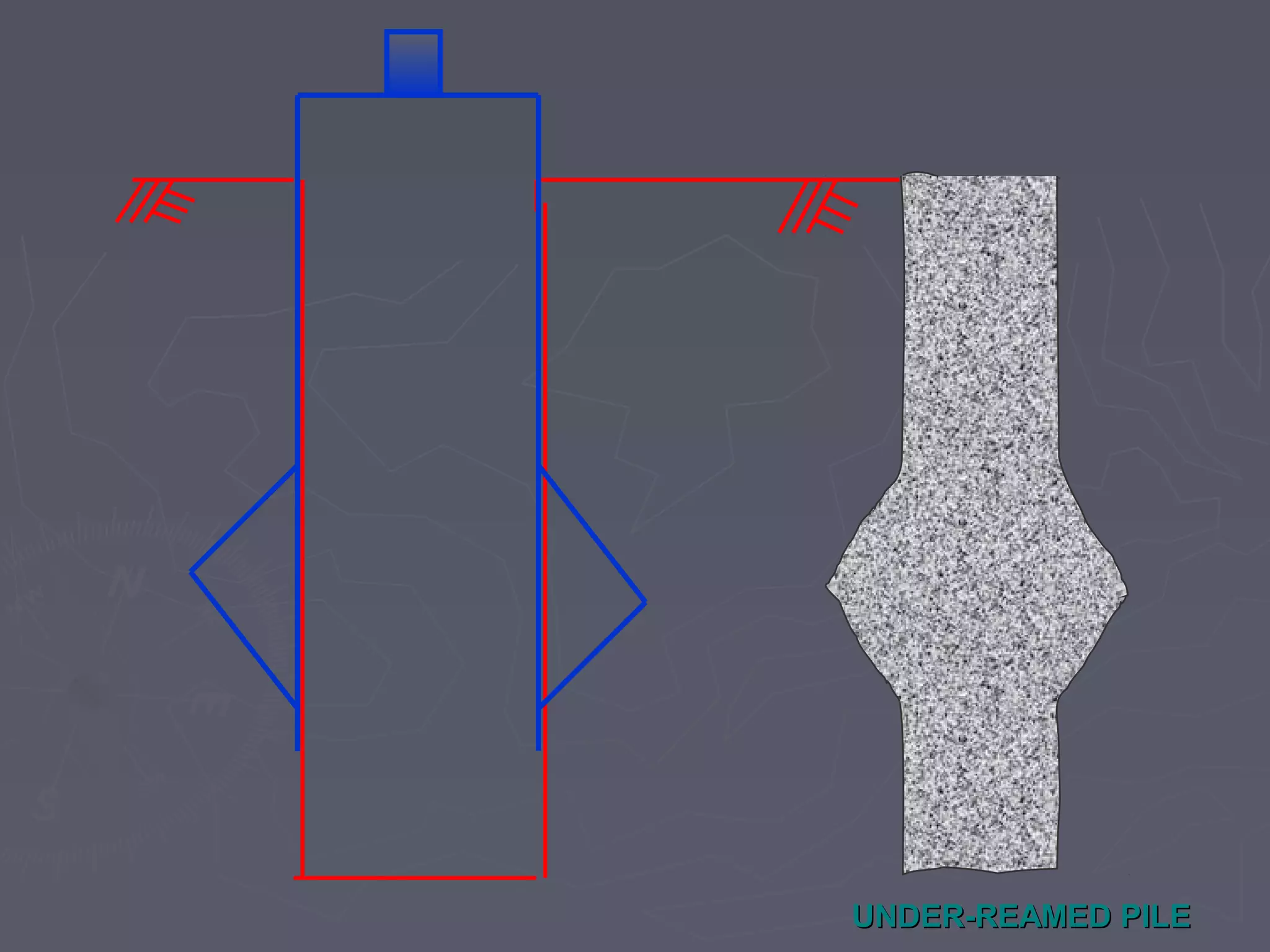
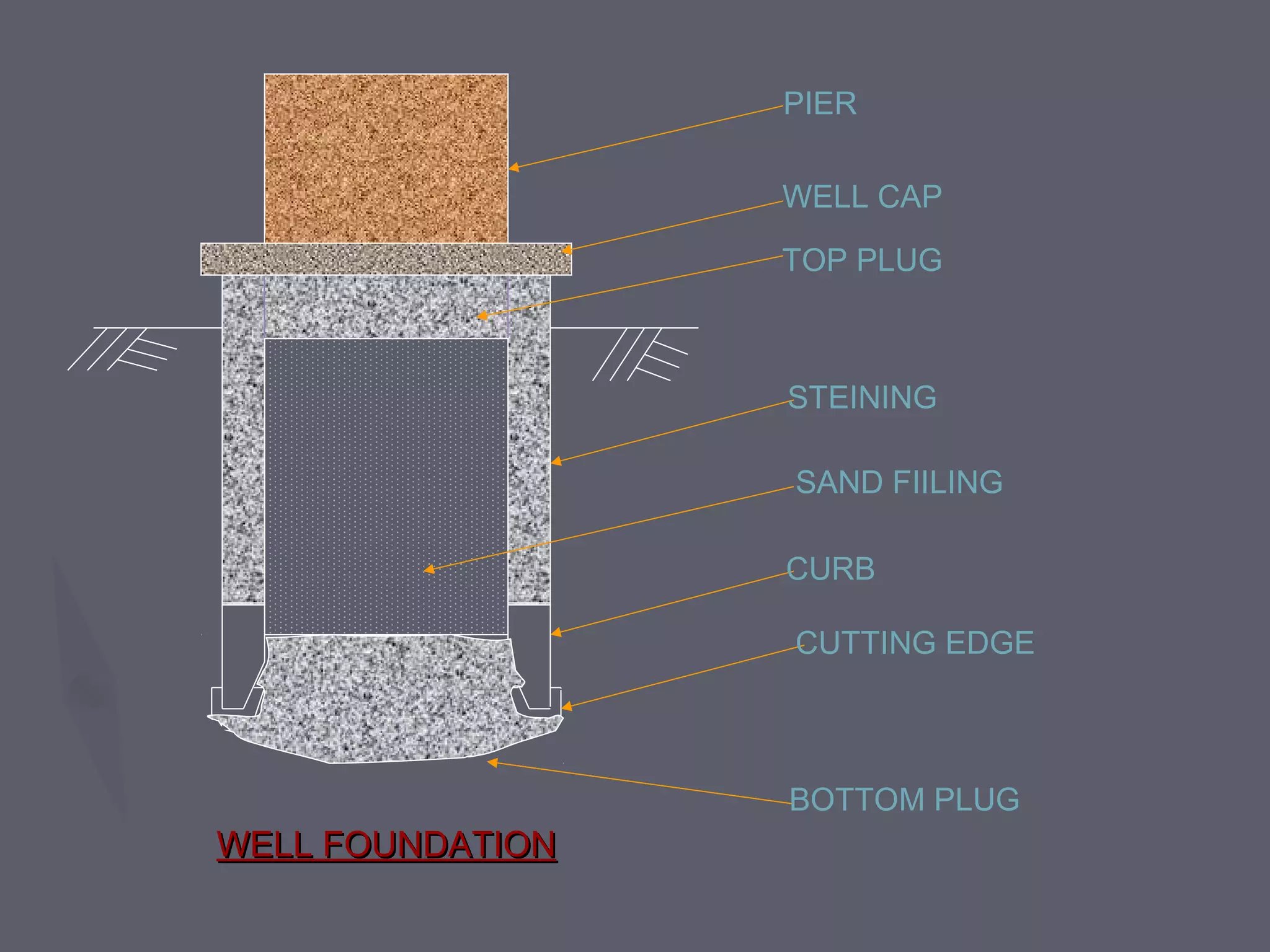
This document discusses different types of foundations used to support structures. It begins by stating the objectives are to understand foundation construction, types of foundations, and which are suitable for different soil types. It then defines foundations as the lowest part of a structure below ground that transmits the weight to the subsoil. The main types discussed are shallow foundations, which include wall, column, combined, and mat foundations, and deep foundations, such as pile, under-reamed pile, and well foundations. Specific foundation types like isolated column, combined, mat, pile, under-reamed pile and well foundations are then described in more detail.