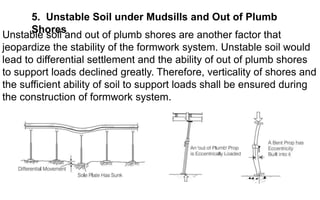
The document discusses various aspects of shuttering in concrete construction, detailing its role as a temporary formwork and the potential causes of formwork failure, including improper stripping, inadequate bracing, and unstable soil. It also outlines types of failures, enabling and triggering events that can lead to these issues, and emphasizes the importance of competent design and inspection of formwork. Recommendations for ensuring safe and effective formwork practices during concrete pours and the order of removing shuttering are provided.