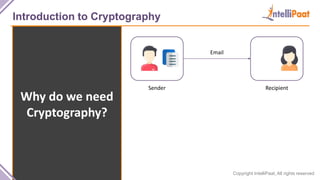
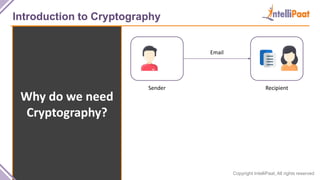
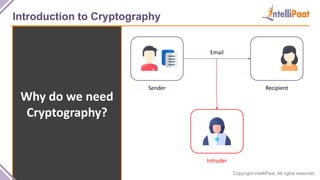
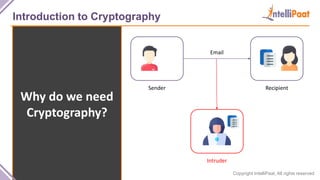
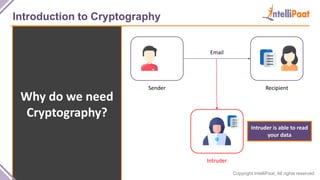
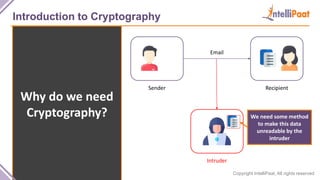
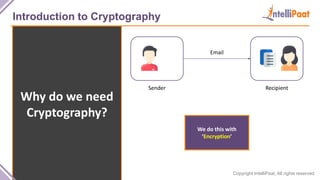
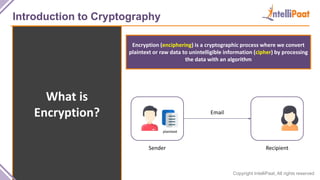
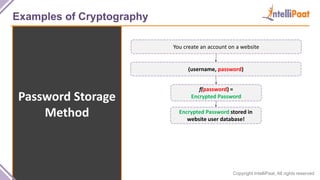
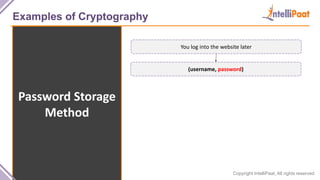
The document discusses various topics related to cryptography including:
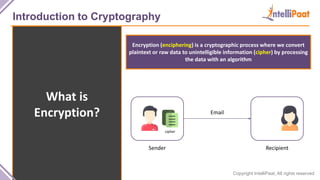
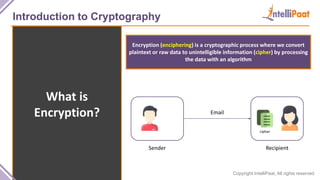
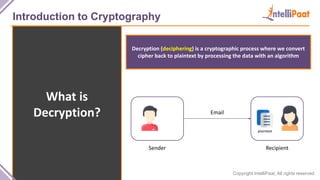
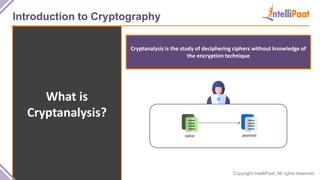
- Introduction to cryptography including definitions of encryption, decryption and cryptanalysis.
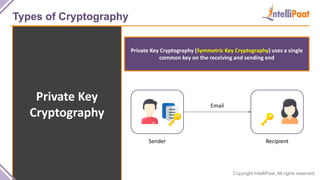
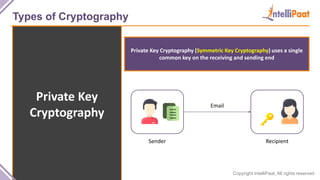
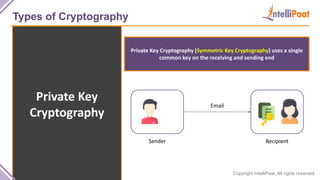
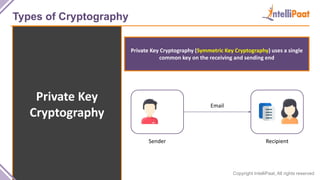
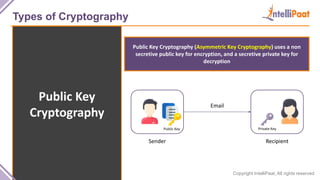
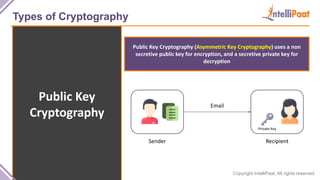
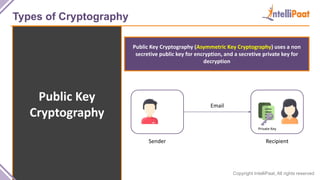
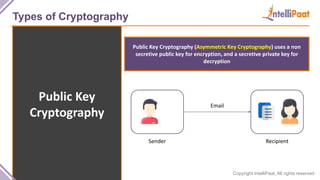
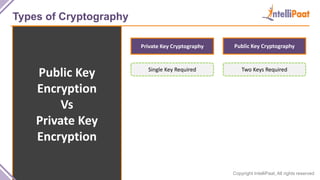
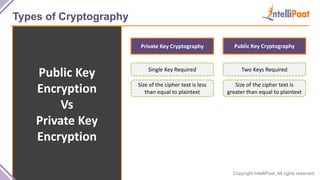
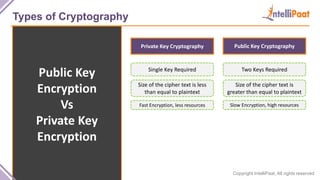
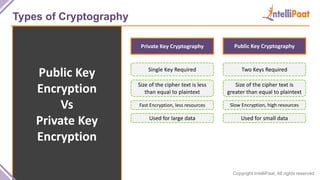
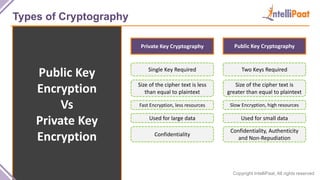
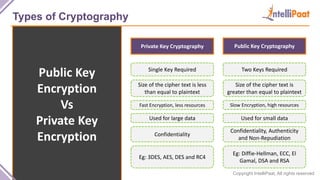
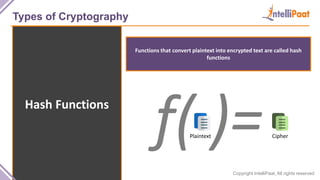
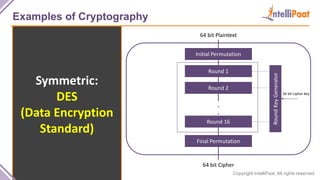
- Types of cryptography including private key cryptography, public key cryptography and hash functions. Comparisons are made between private and public key cryptography.
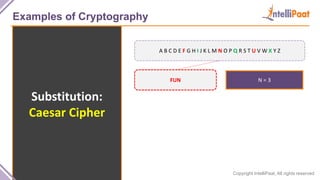
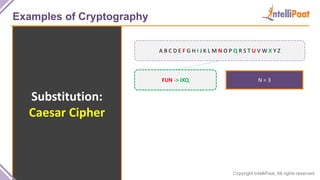
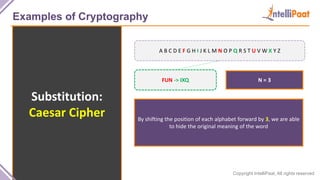
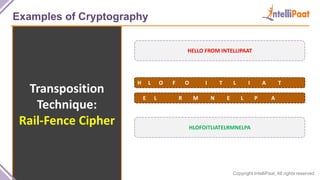
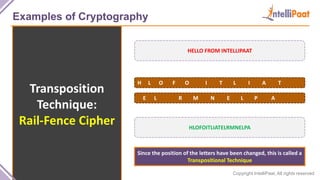
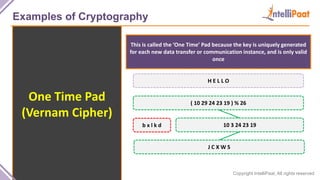
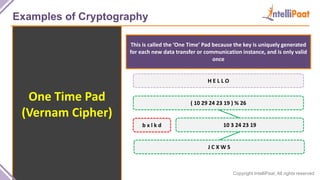
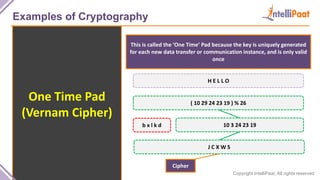
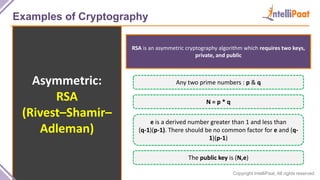
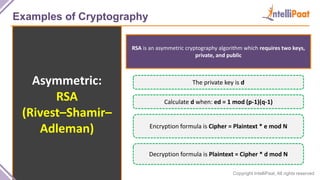
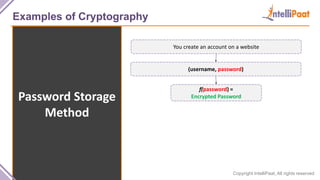
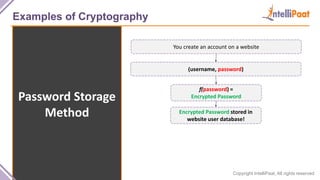
- Examples of cryptography techniques like Caesar cipher, rail fence cipher, steganography, and the one time pad cipher.
- The overall document provides an overview of cryptography concepts, types and examples to explain the field of cryptography.