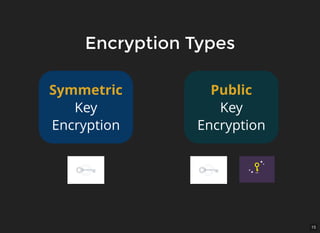
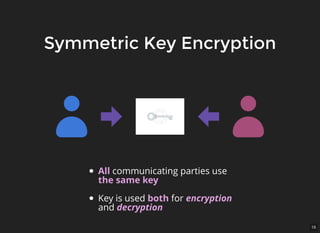
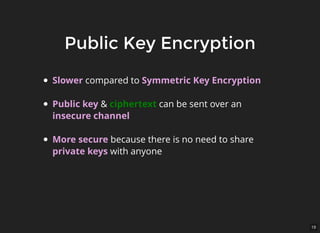
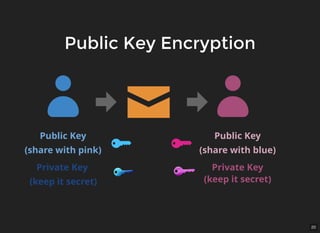
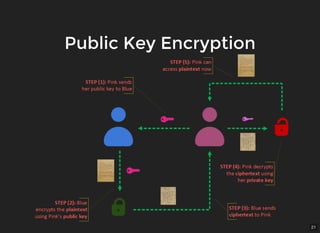
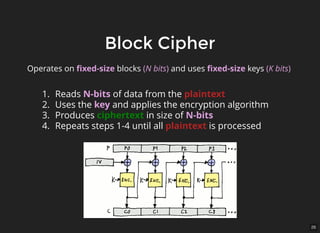
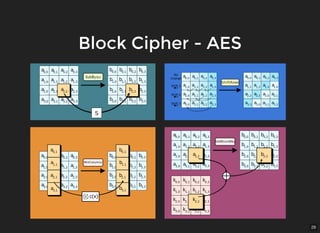
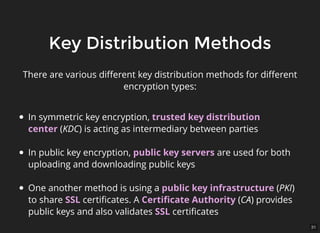
The document discusses encryption, which is the process of encoding information to ensure confidentiality and security during communication. It details types of encryption, such as symmetric and public key encryption, and the significance of encryption algorithms like block and stream ciphers. Additionally, it addresses key distribution methods and emphasizes the use of trusted centers or public key infrastructure for securely sharing cryptographic keys.