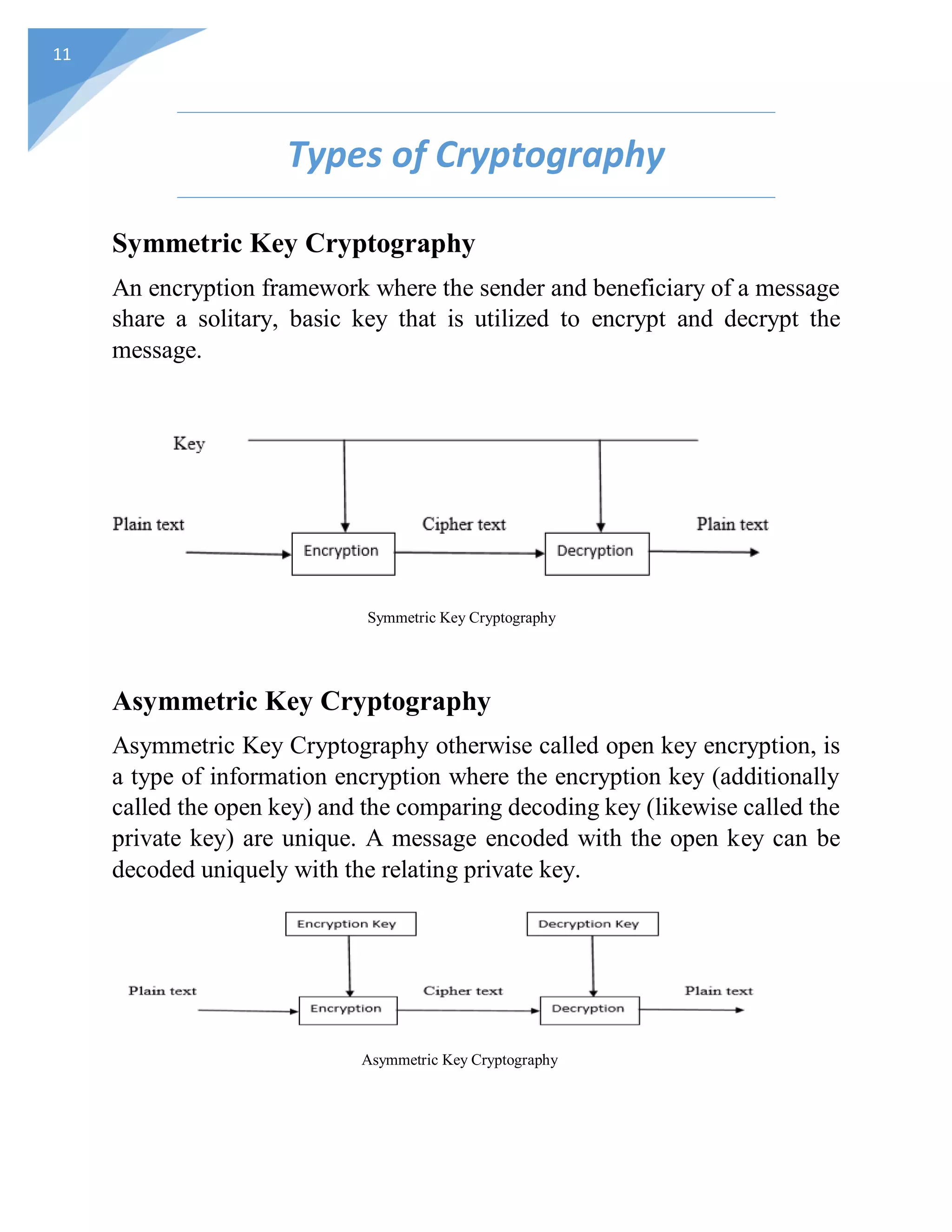
Cryptography is used to secure data by encrypting it so that only authorized users can access it. It provides confidentiality, integrity, and authentication. There are different types of encryption algorithms like symmetric key cryptography where one key is used to encrypt and decrypt, and asymmetric key cryptography where public and private keys are used. The goals of cryptography are to ensure confidentiality so unauthorized users cannot understand encrypted data, authenticate users, maintain data integrity so it is not altered without detection, and provide non-repudiation and access control.