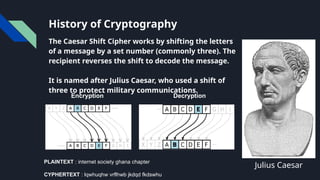
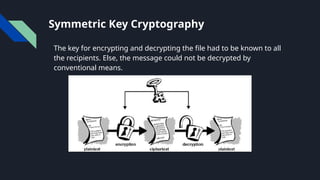
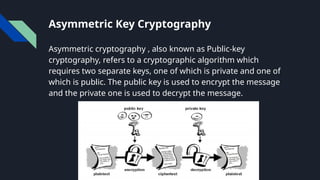
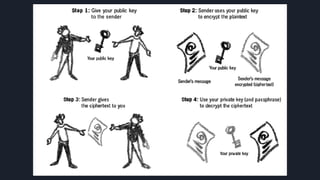
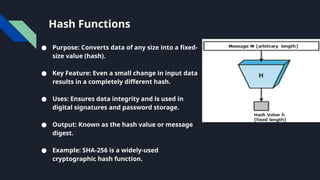
The document provides an overview of cryptography, including definitions, key concepts like encryption and decryption, and historical context such as the Caesar shift cipher. It outlines the goals, services, and types of cryptography, detailing symmetric and asymmetric methods, as well as hash functions and their applications. The importance of cryptography in securing data, alongside challenges such as key management and the potential impact of quantum computing on encryption, is emphasized.