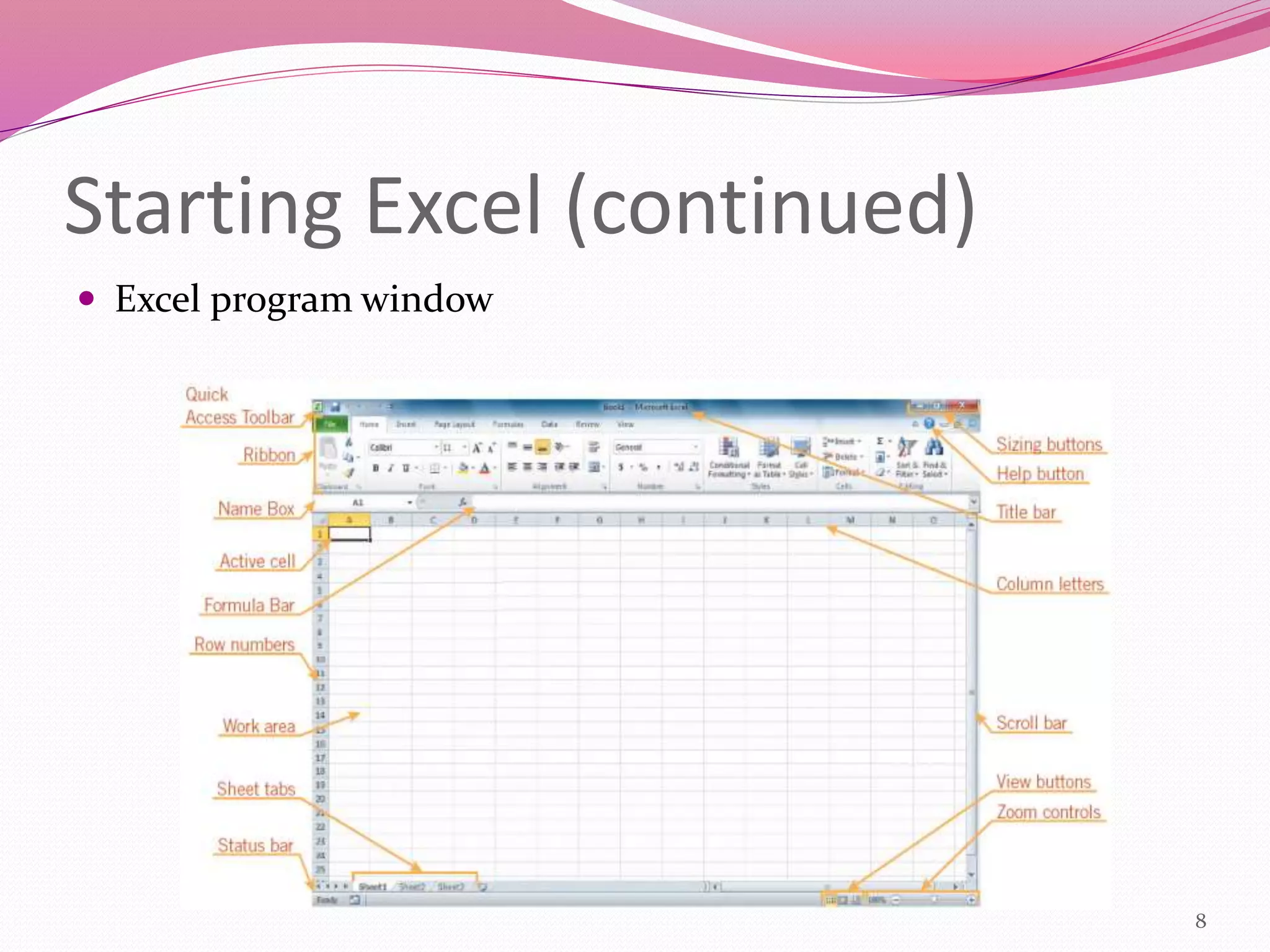
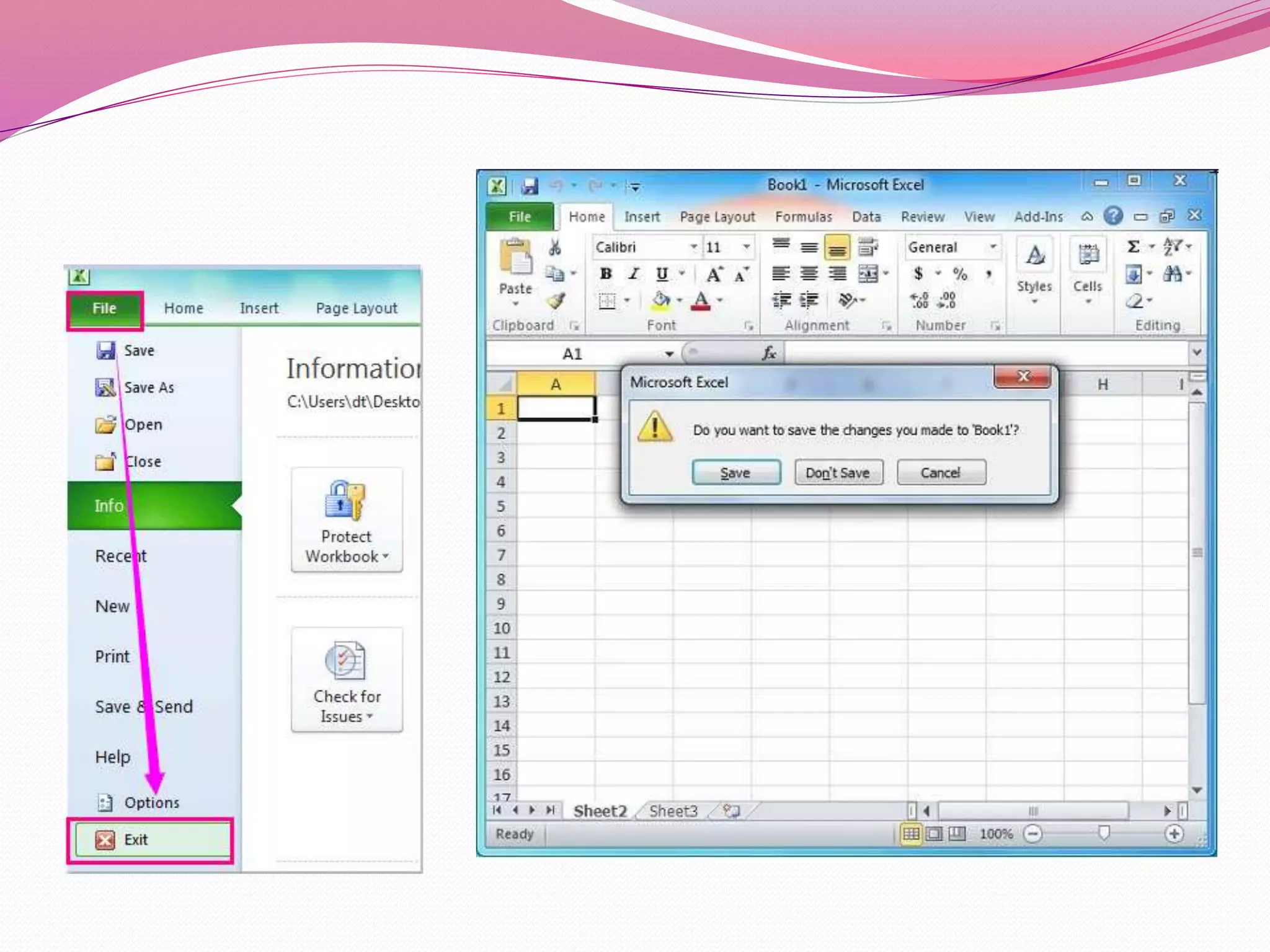
This document provides an introduction to spreadsheets and Microsoft Excel. It explains that a spreadsheet is a grid of rows and columns used to enter and analyze data. It describes how to start Excel, open and save workbooks, and explores the basic parts of a workbook like worksheets, columns, rows, and cells. Examples of using spreadsheets for finances, grades, and other purposes are provided.