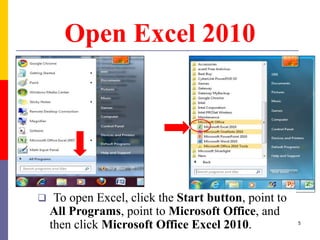
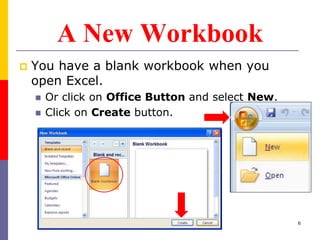
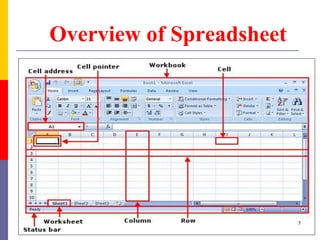
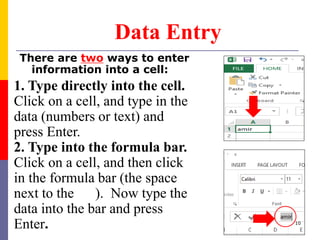
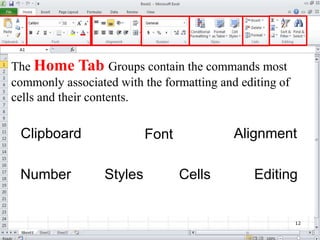
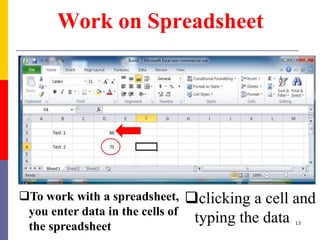
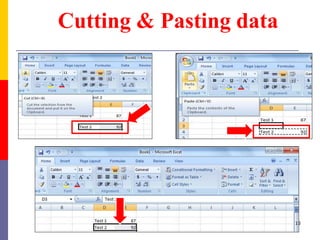
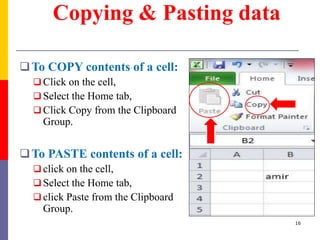
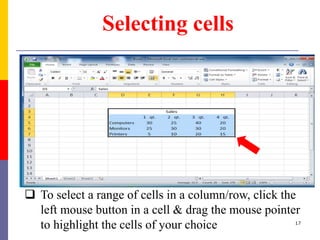
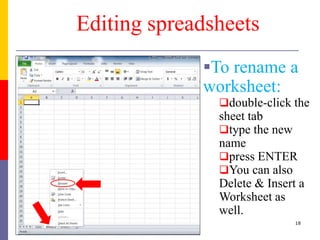
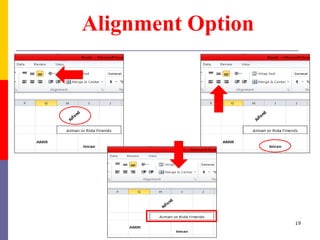
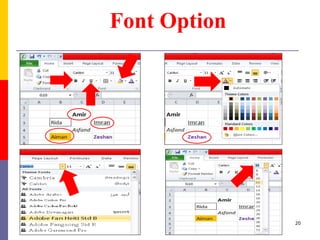
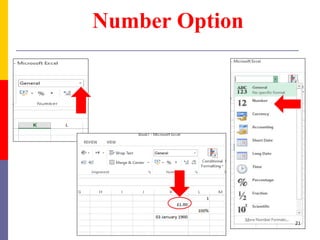
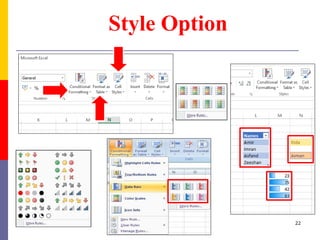
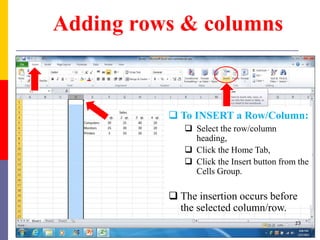
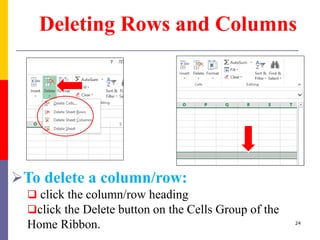
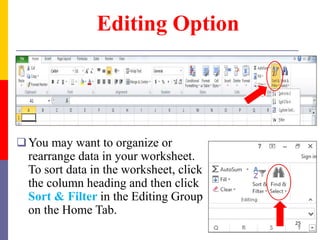
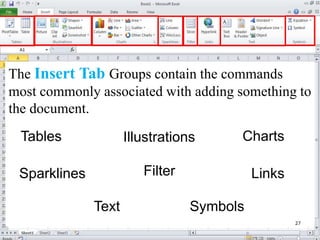
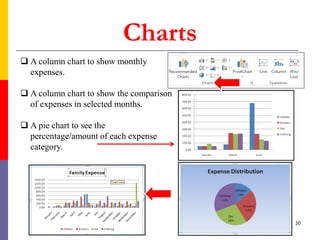
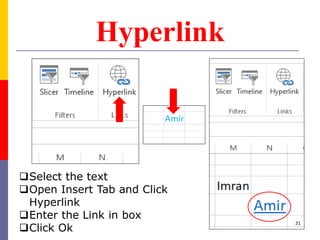
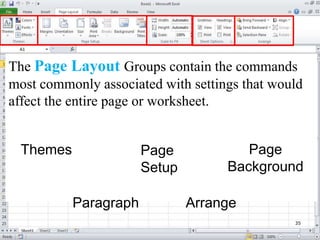
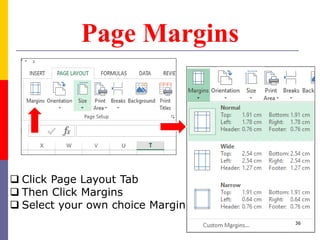
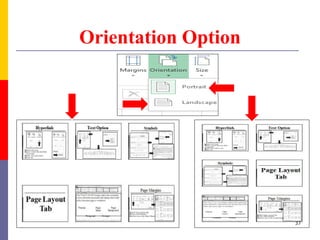
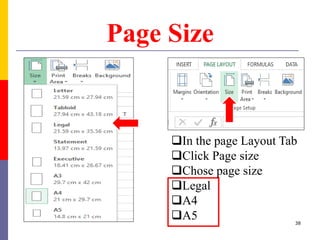
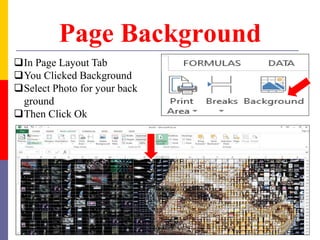
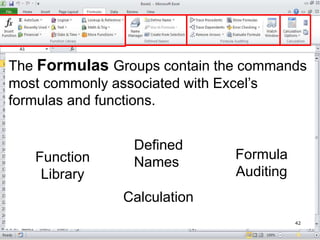
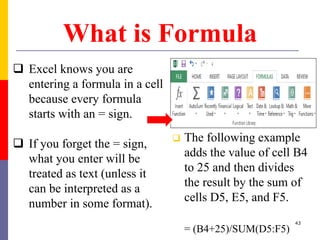
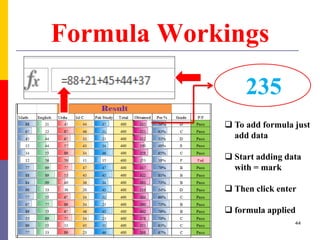
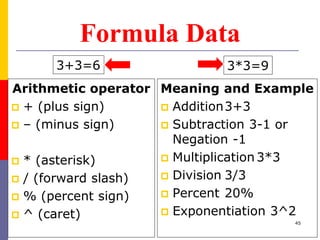
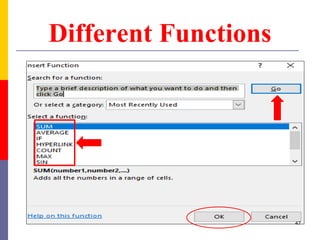
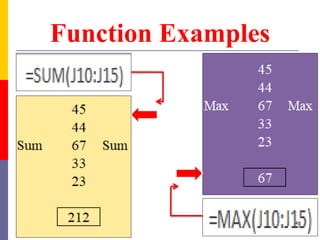
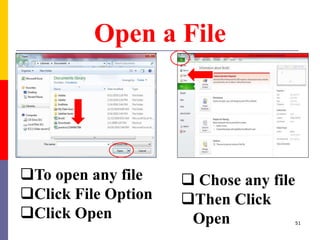
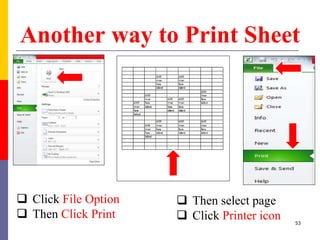
The document provides a comprehensive introduction to Microsoft Excel 2010, covering the basic components of a spreadsheet, data entry methods, and common tasks such as copying, pasting, and editing data. It includes instructions on using the home, insert, page layout, and formulas tabs, along with guidance on creating charts, organizing data, and managing worksheets. Additionally, it explains how to save and print Excel files.