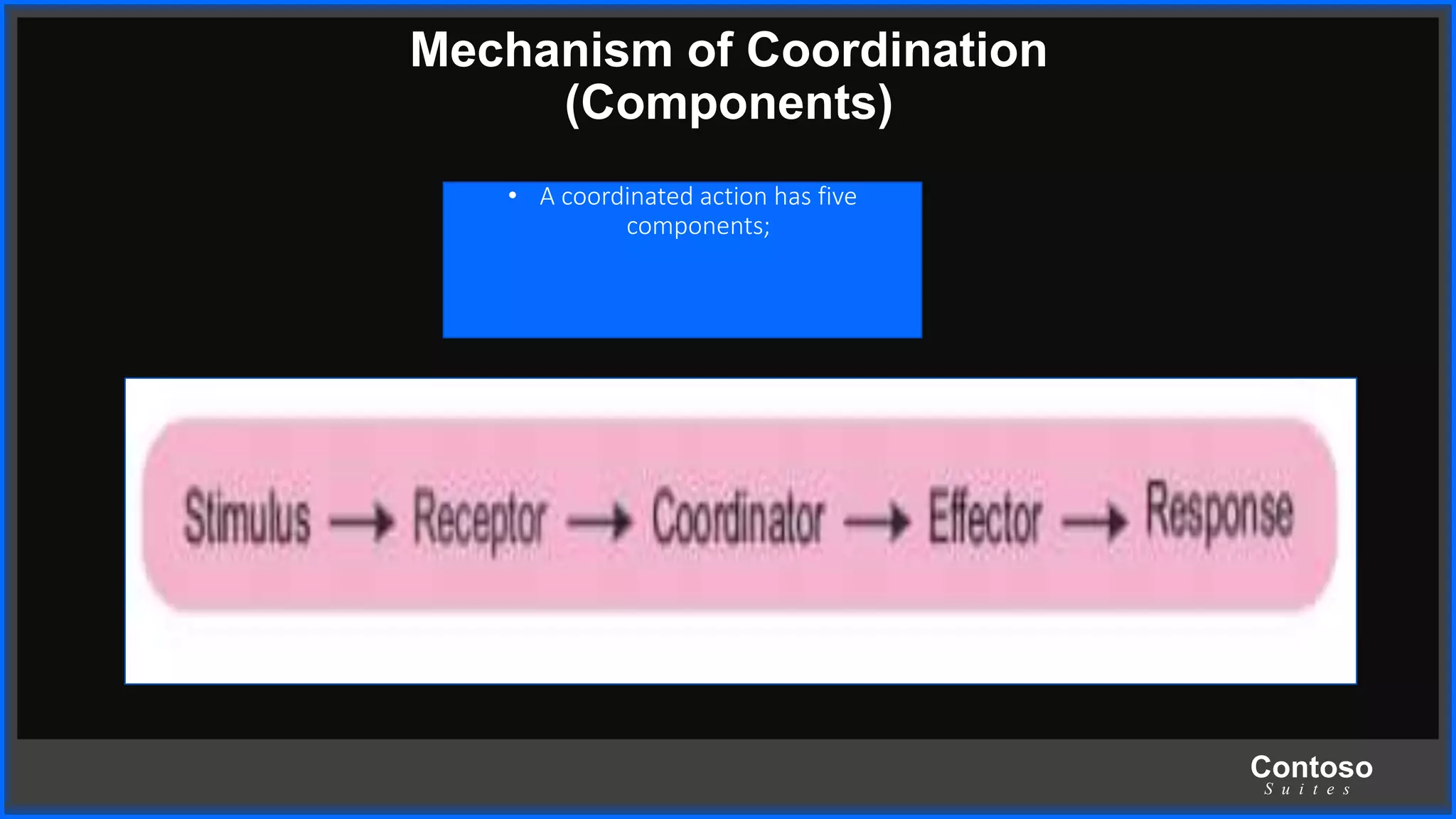
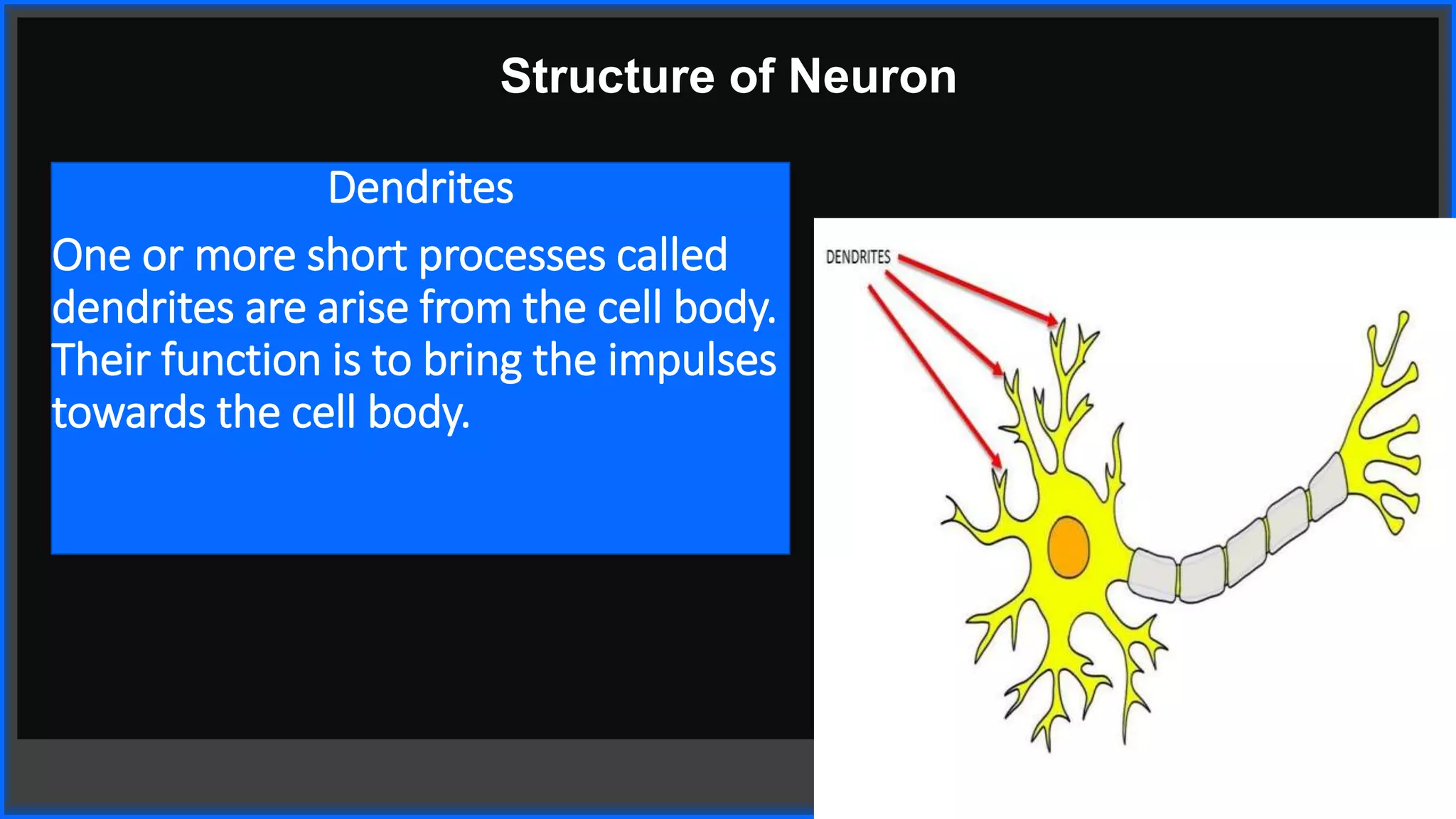
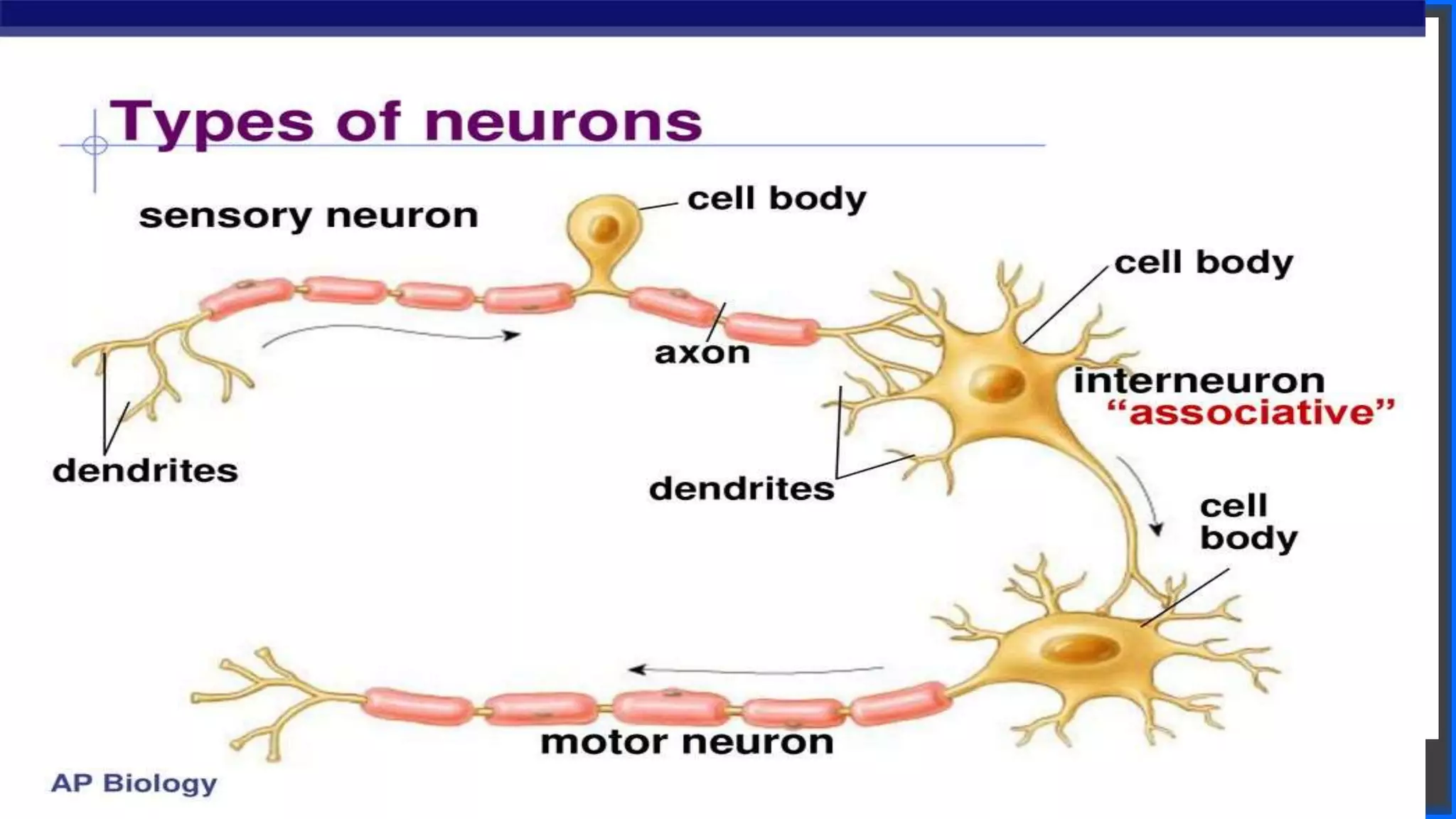
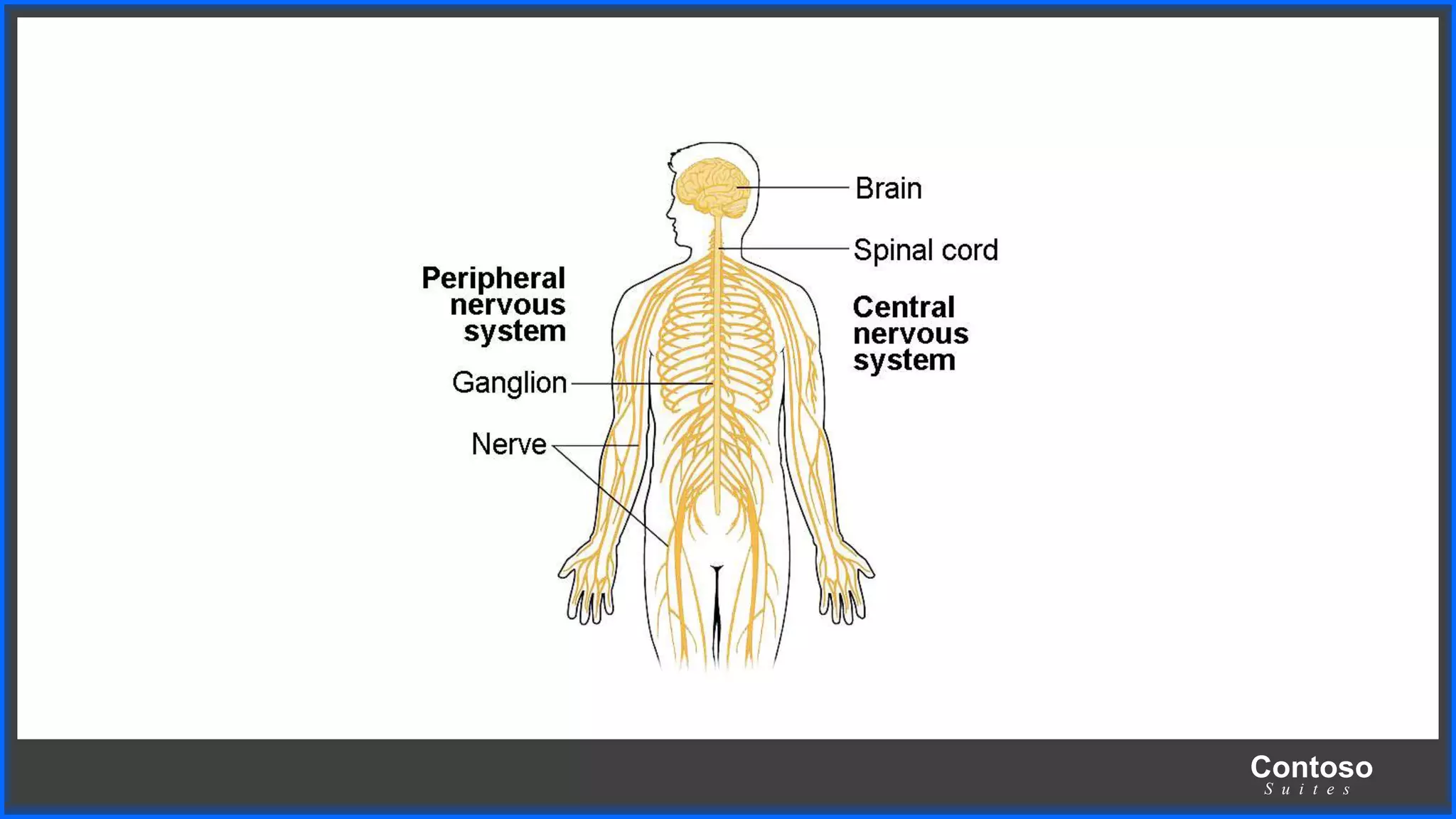
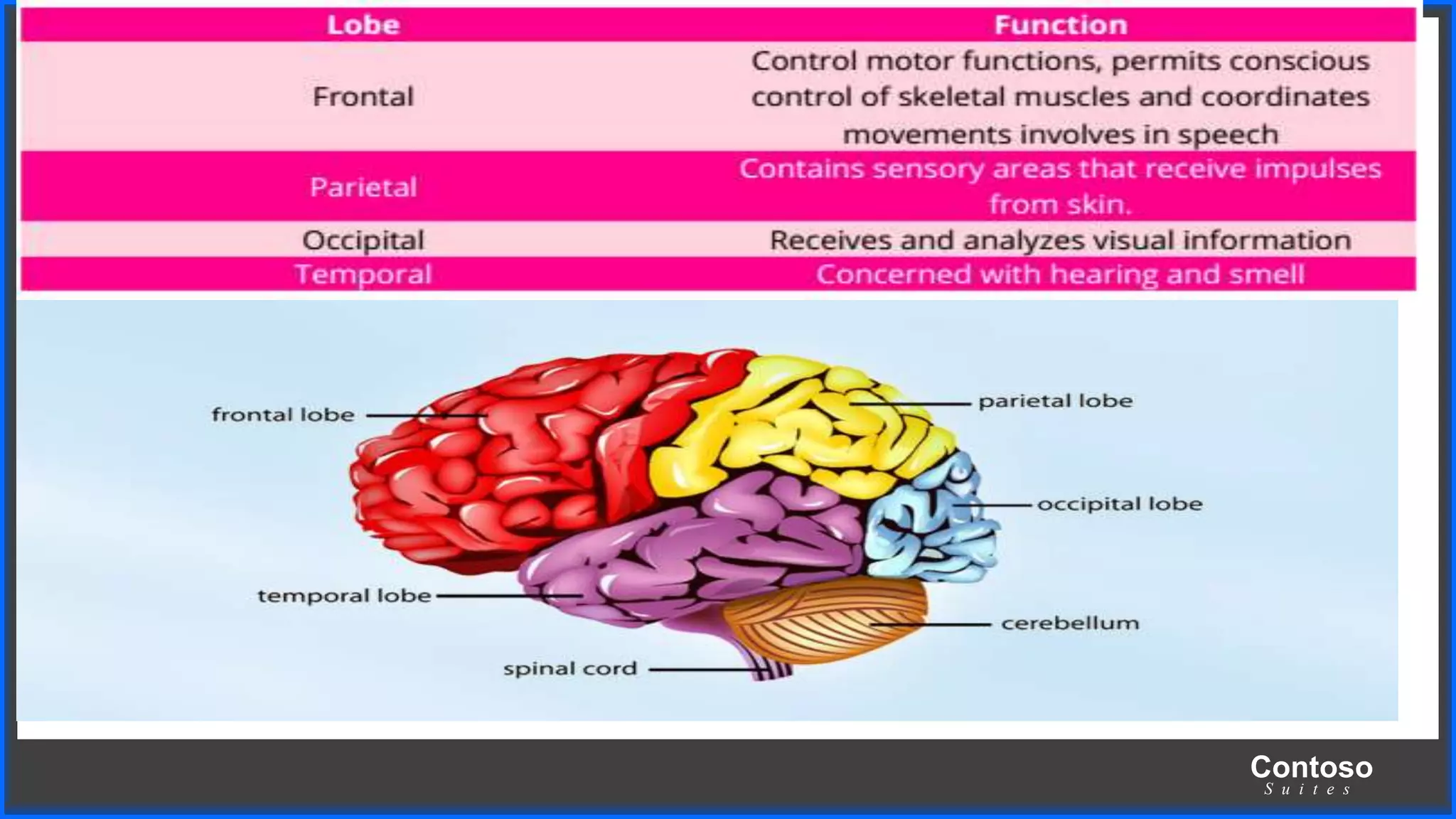
This document discusses coordination in multicellular organisms. It describes the five components of a coordinated action: stimuli, receptors, coordinators, effectors, and response. In animals, the nervous system and chemical systems work together to coordinate actions. The nervous system uses neurons, nerves, and the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) for coordination. The central nervous system receives information from receptors and sends messages to effectors through neurons to produce responses.