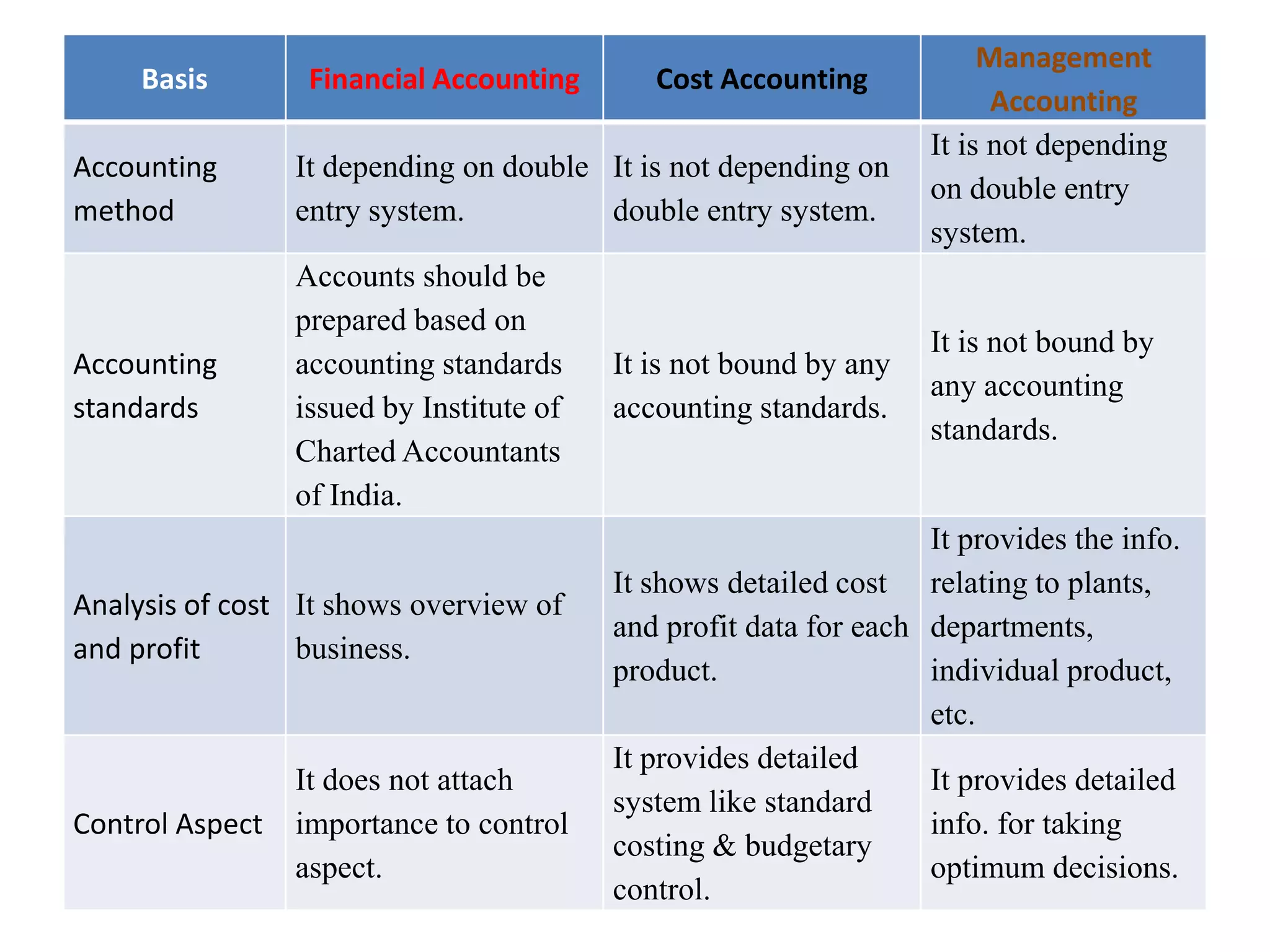
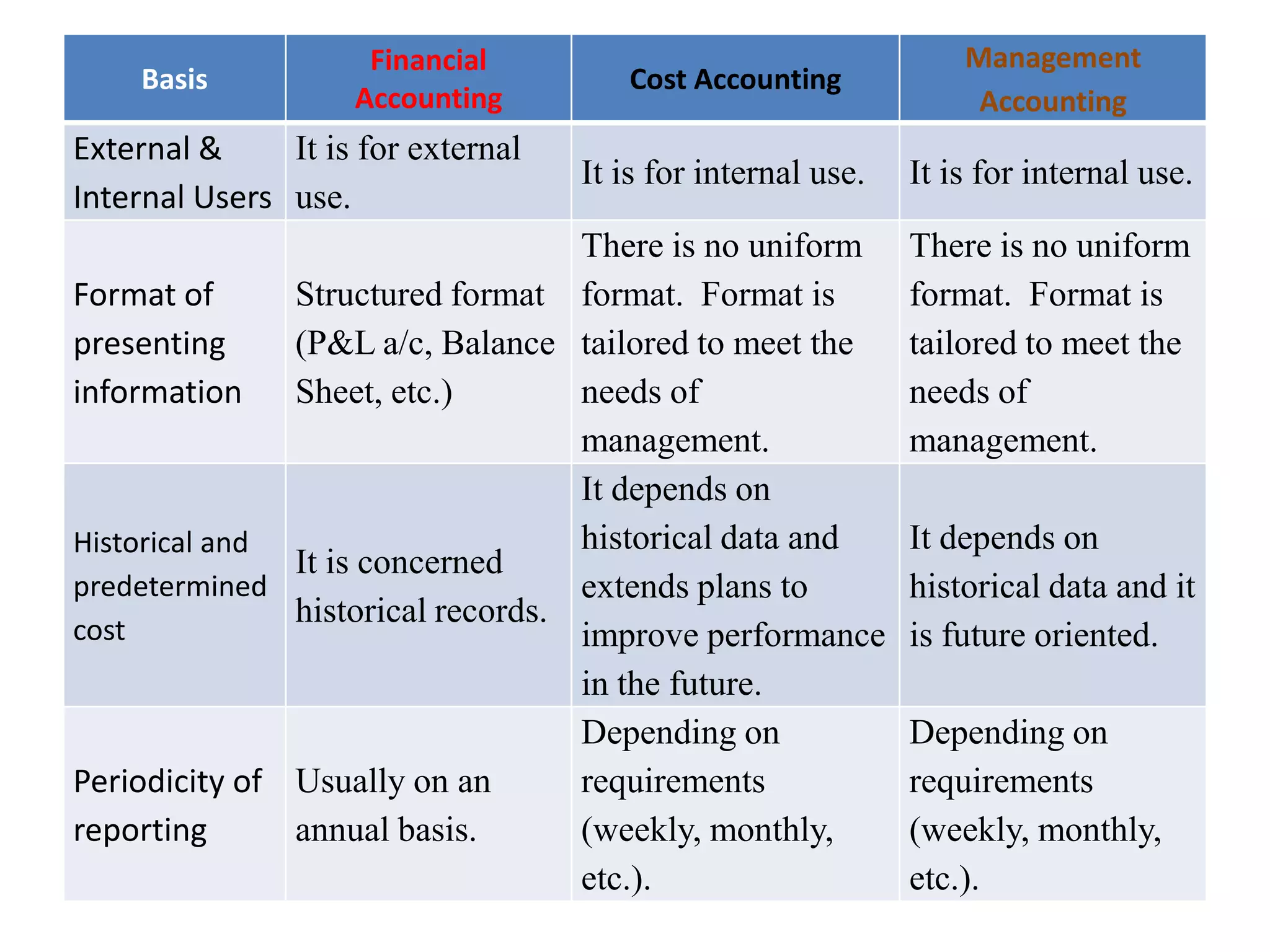
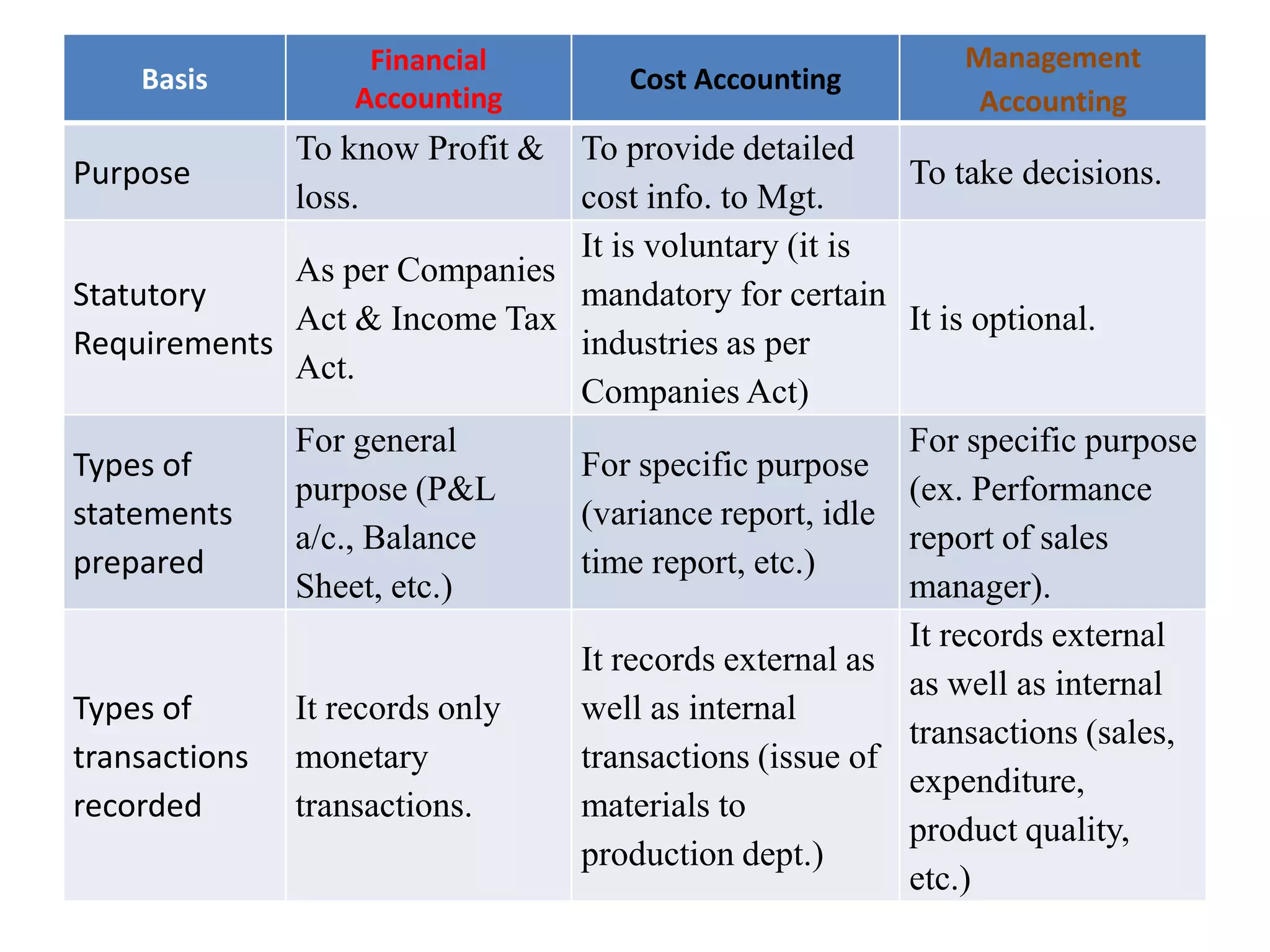
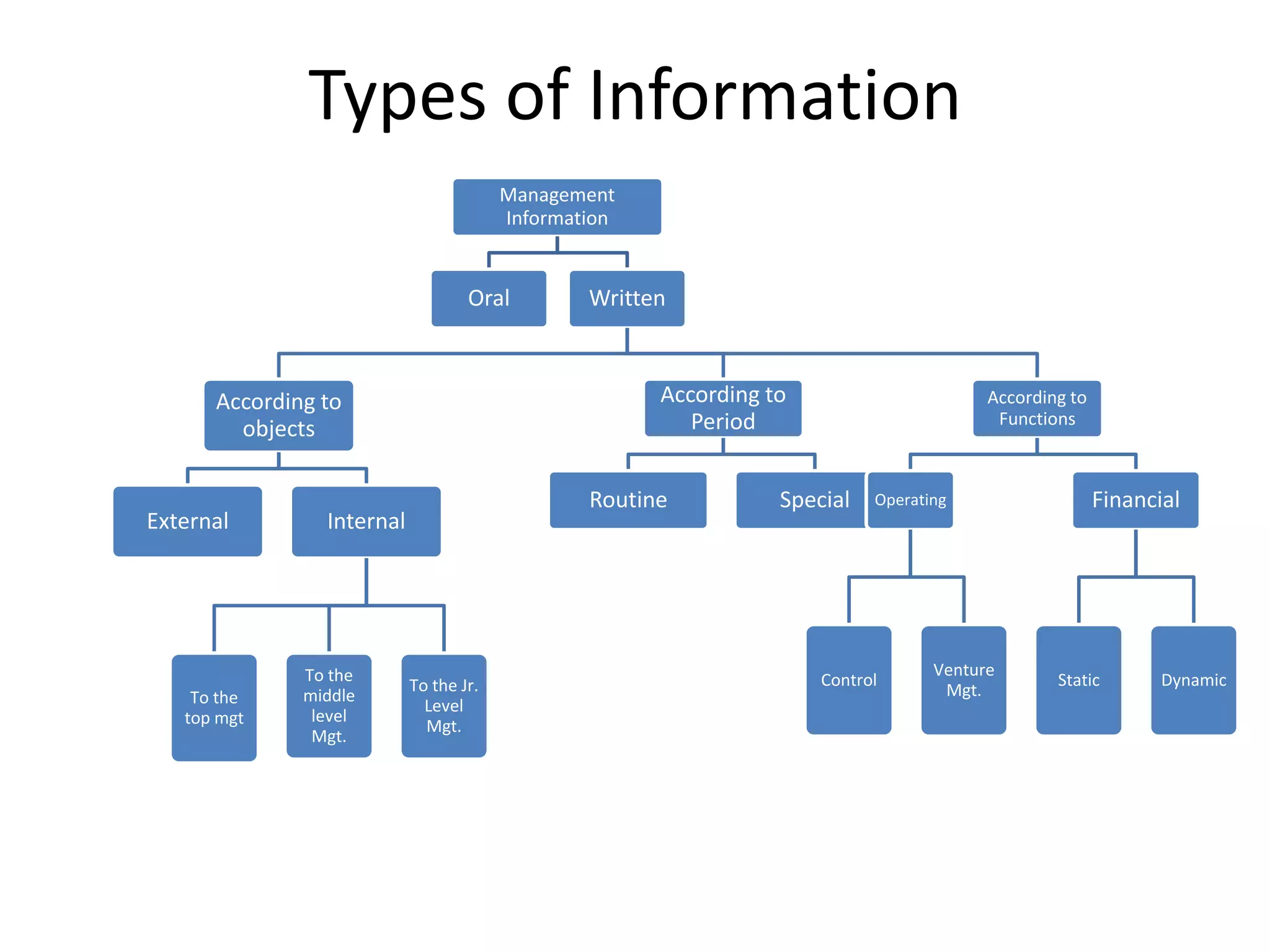
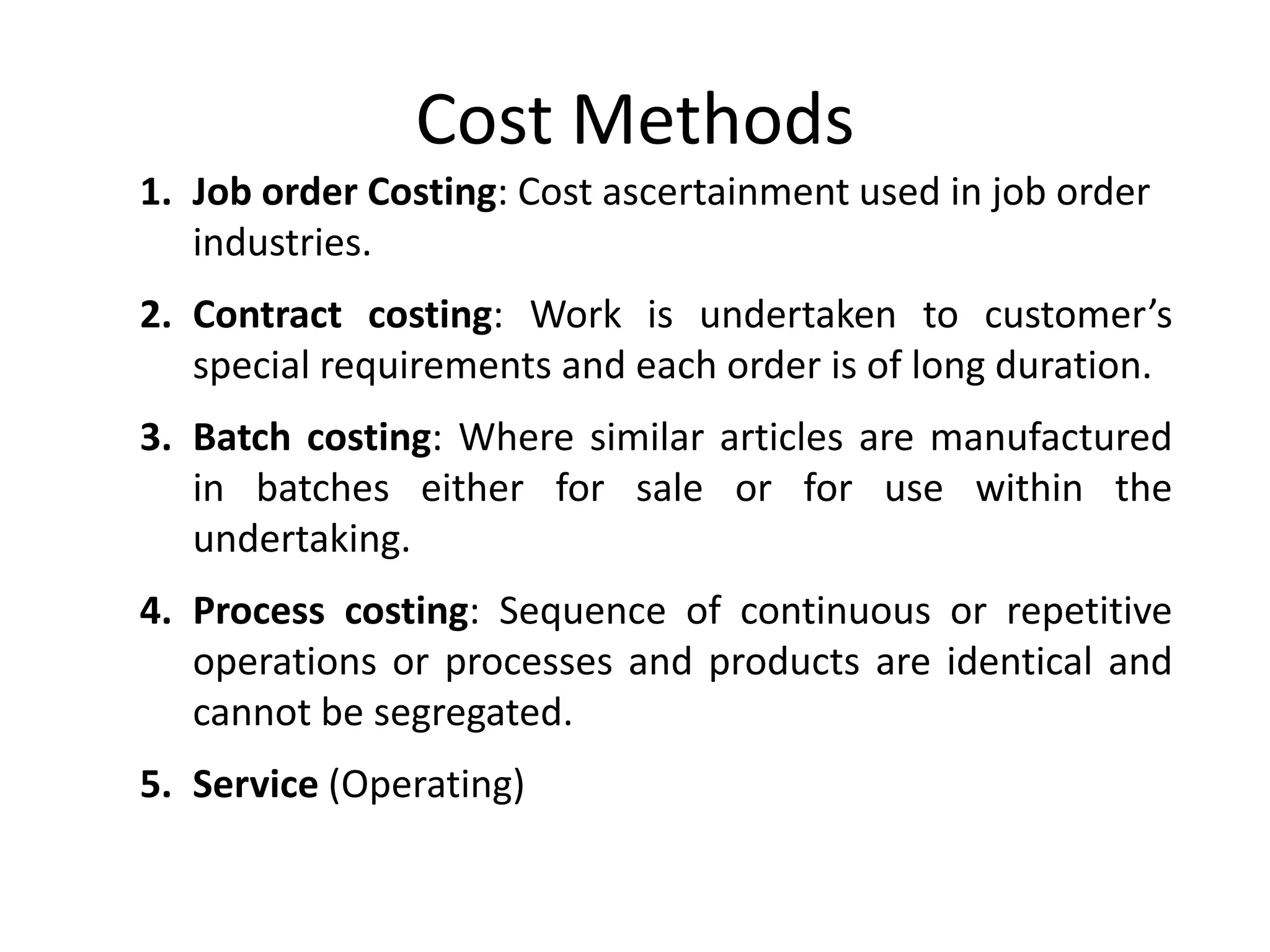
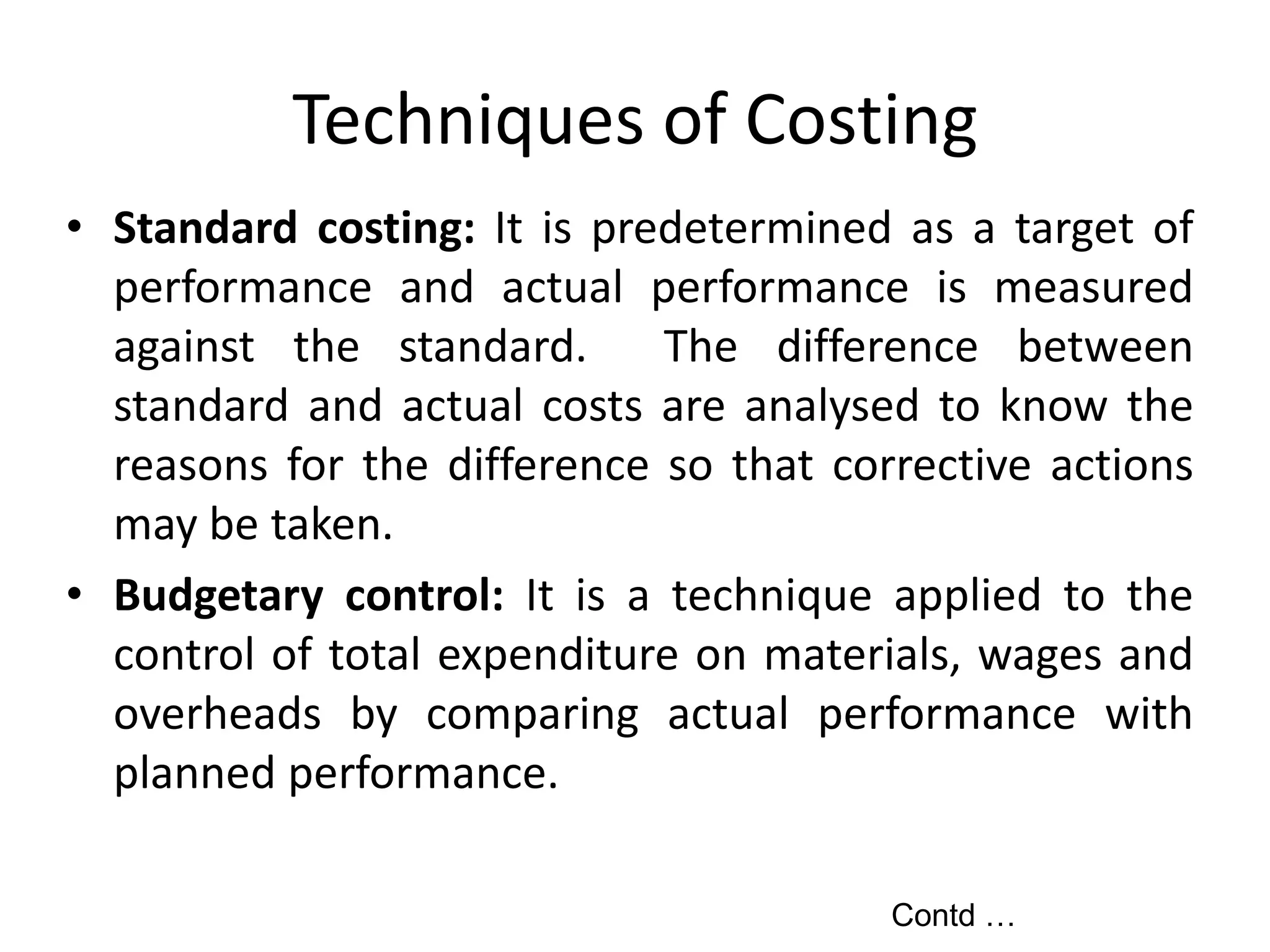
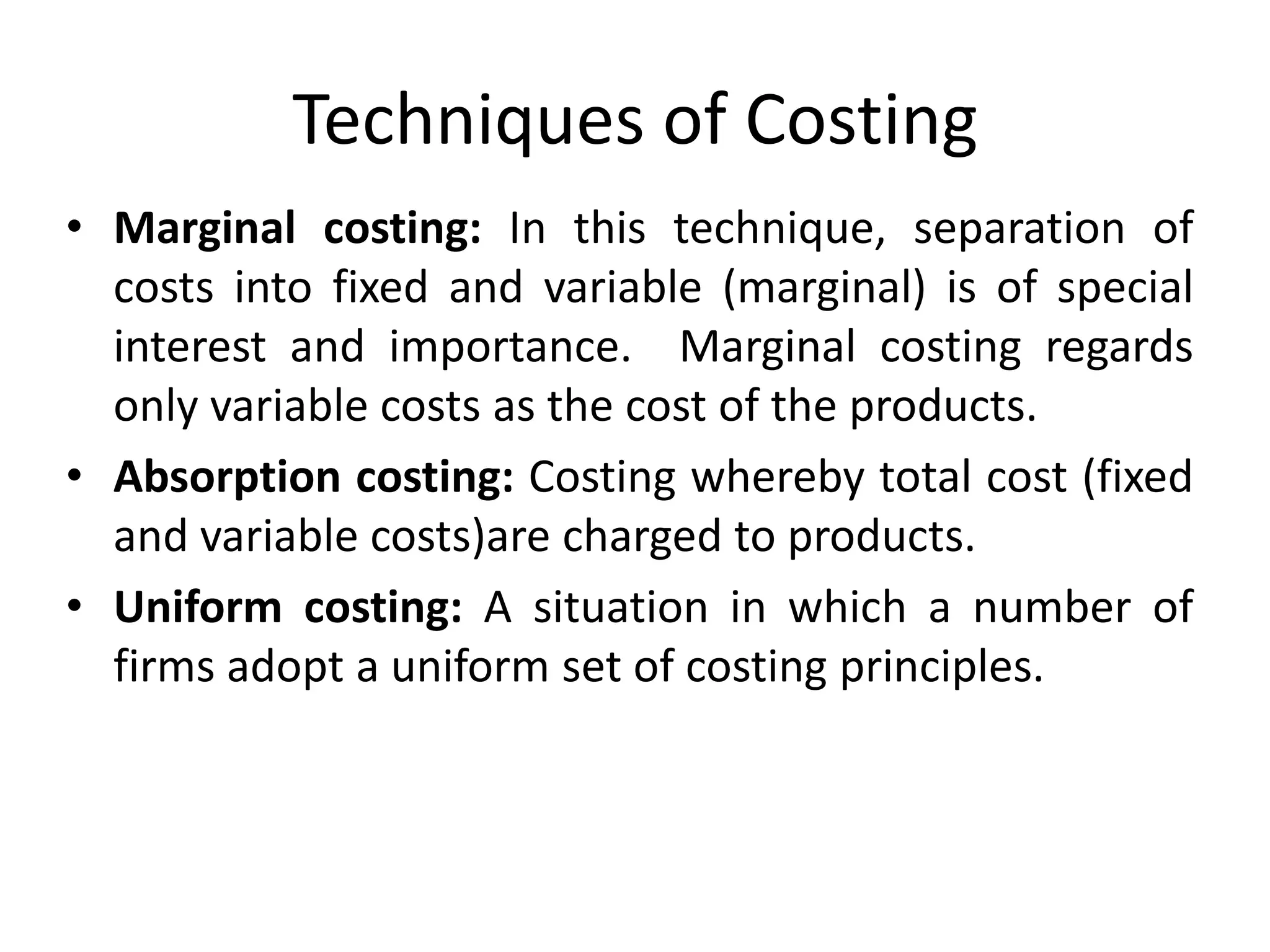
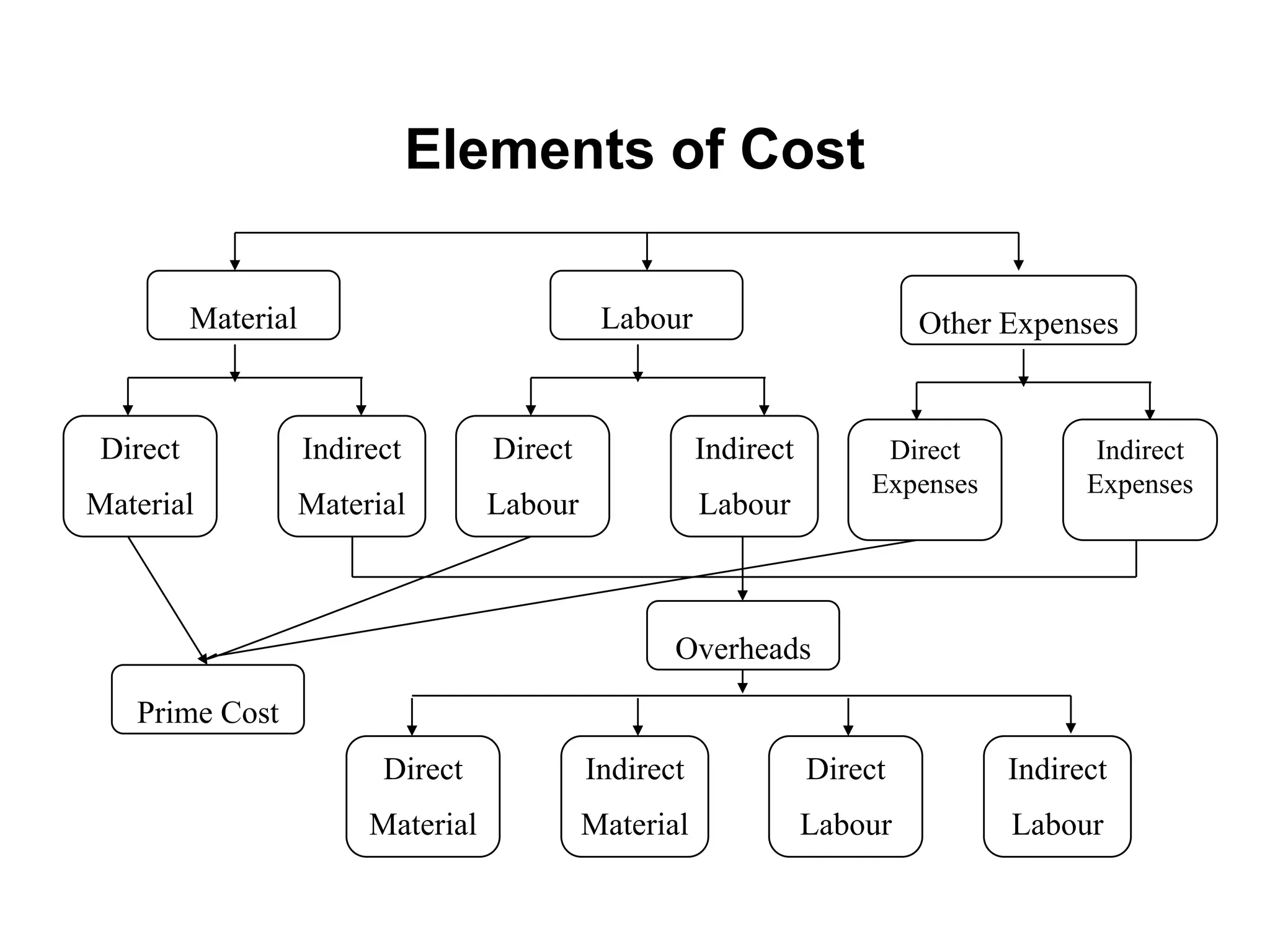
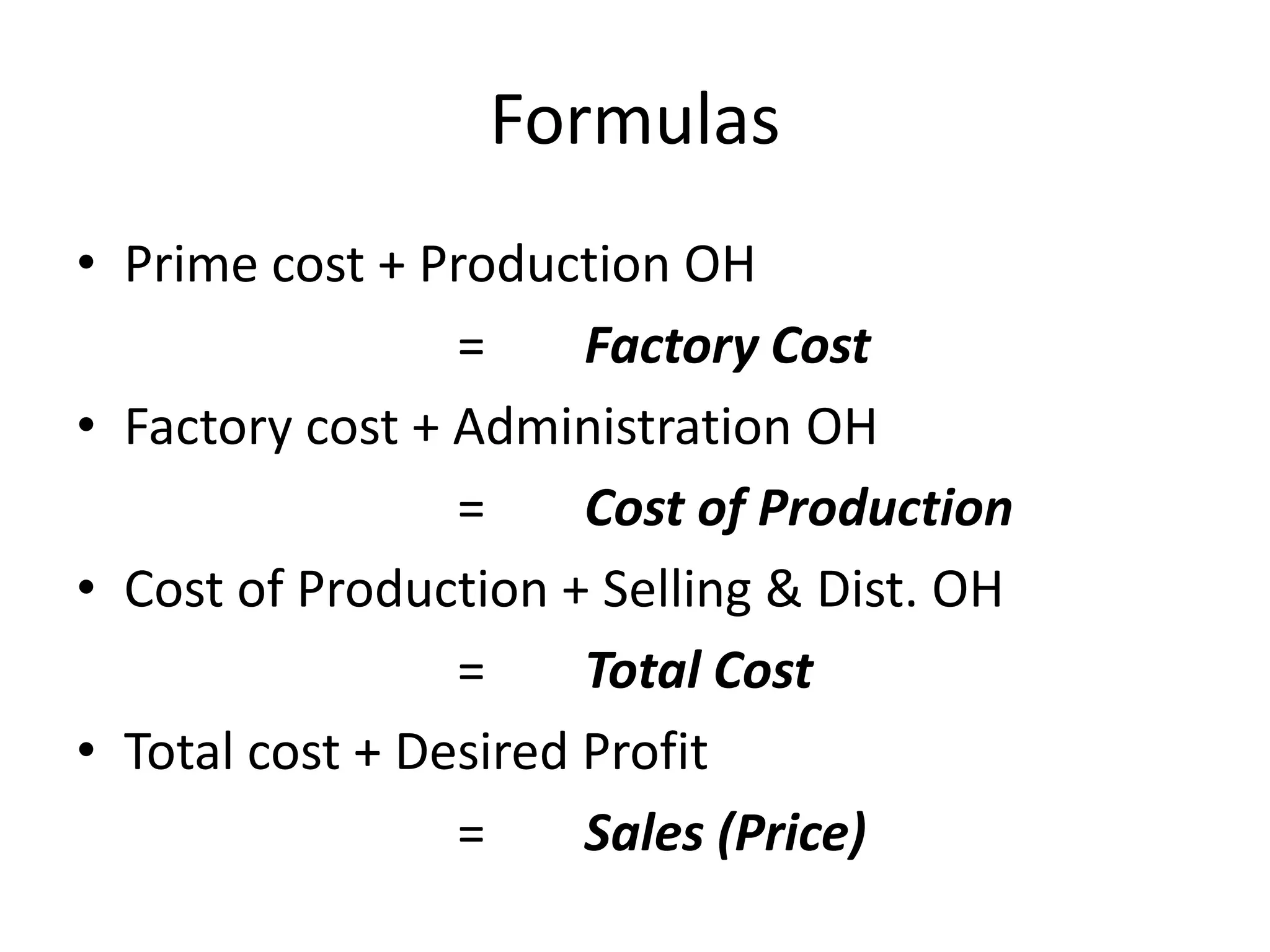
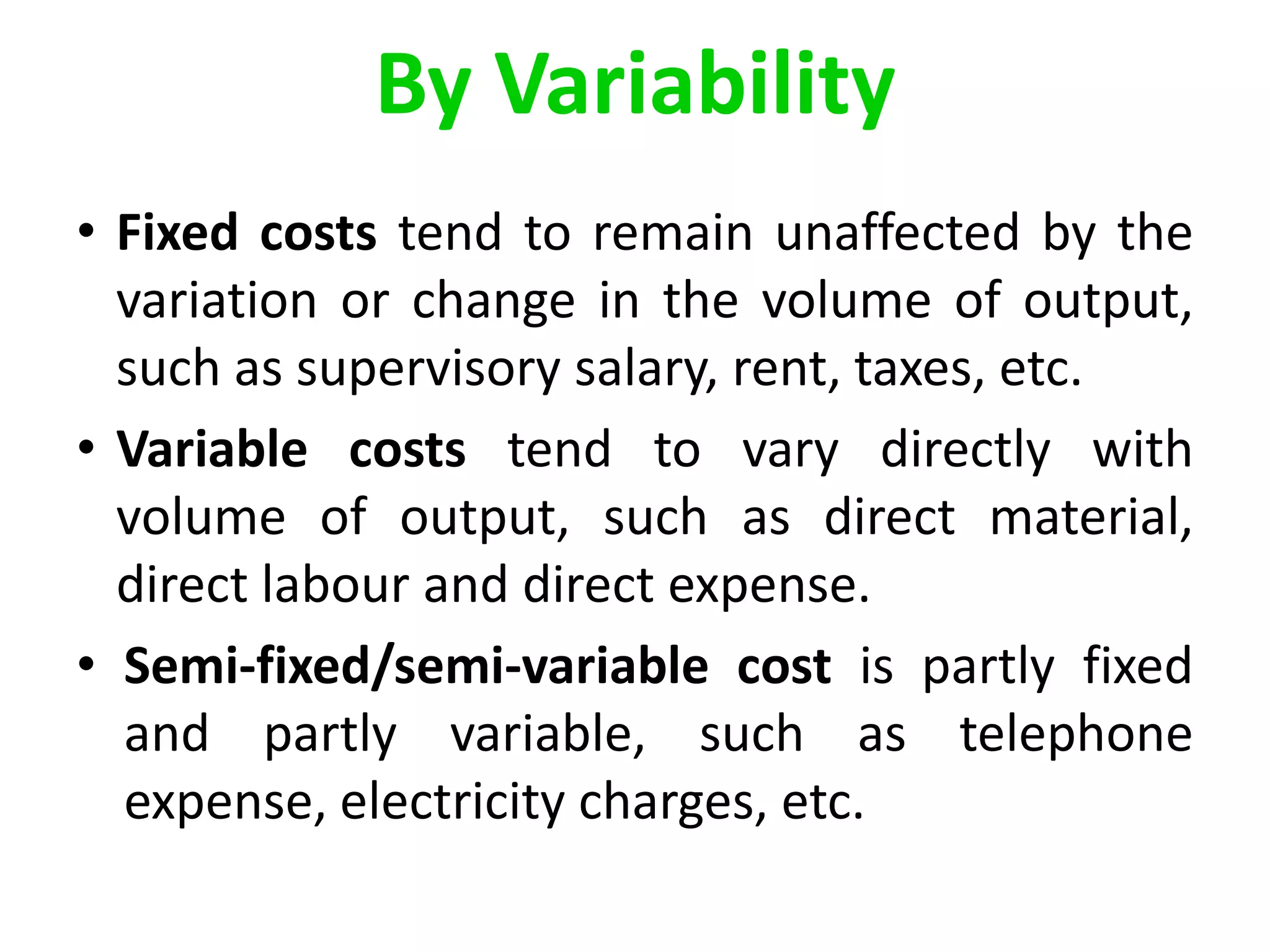
There are several types of cost accounting methods that are used for different purposes. Job order costing is used for job order industries where each job or order is treated as a cost unit. Process costing is used for industries with continuous production where the output is uniform. Standard costing sets targets and variances are analyzed to take corrective actions. Marginal costing only considers variable costs as product costs. Absorption costing includes both fixed and variable costs. Costs can also be classified as fixed, variable, or semi-variable depending on their behavior with production volume. Direct costs can be traced to a cost object while indirect costs cannot. Historical costs are actual costs incurred while predetermined and estimated costs are budgeted or forecast