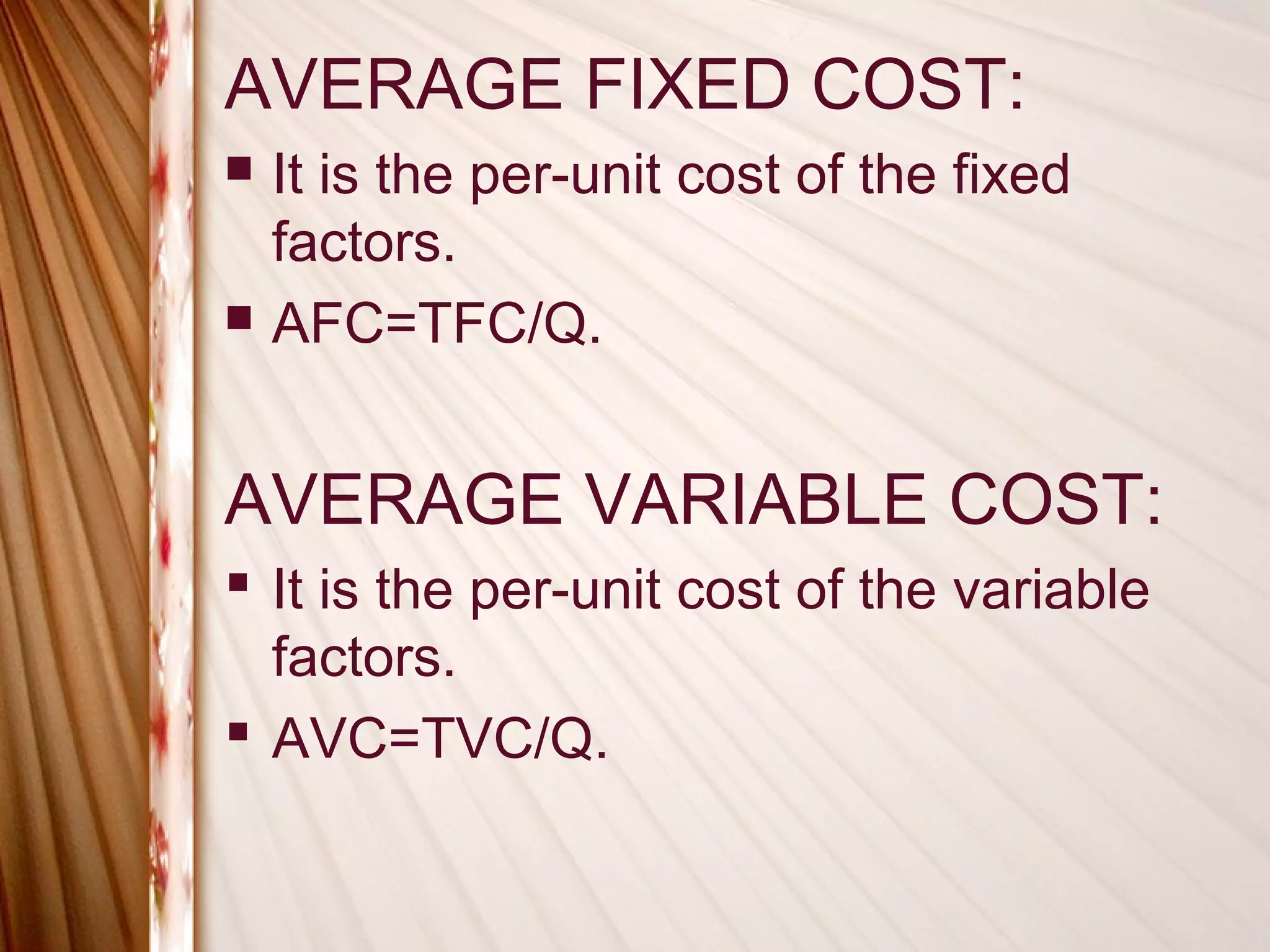
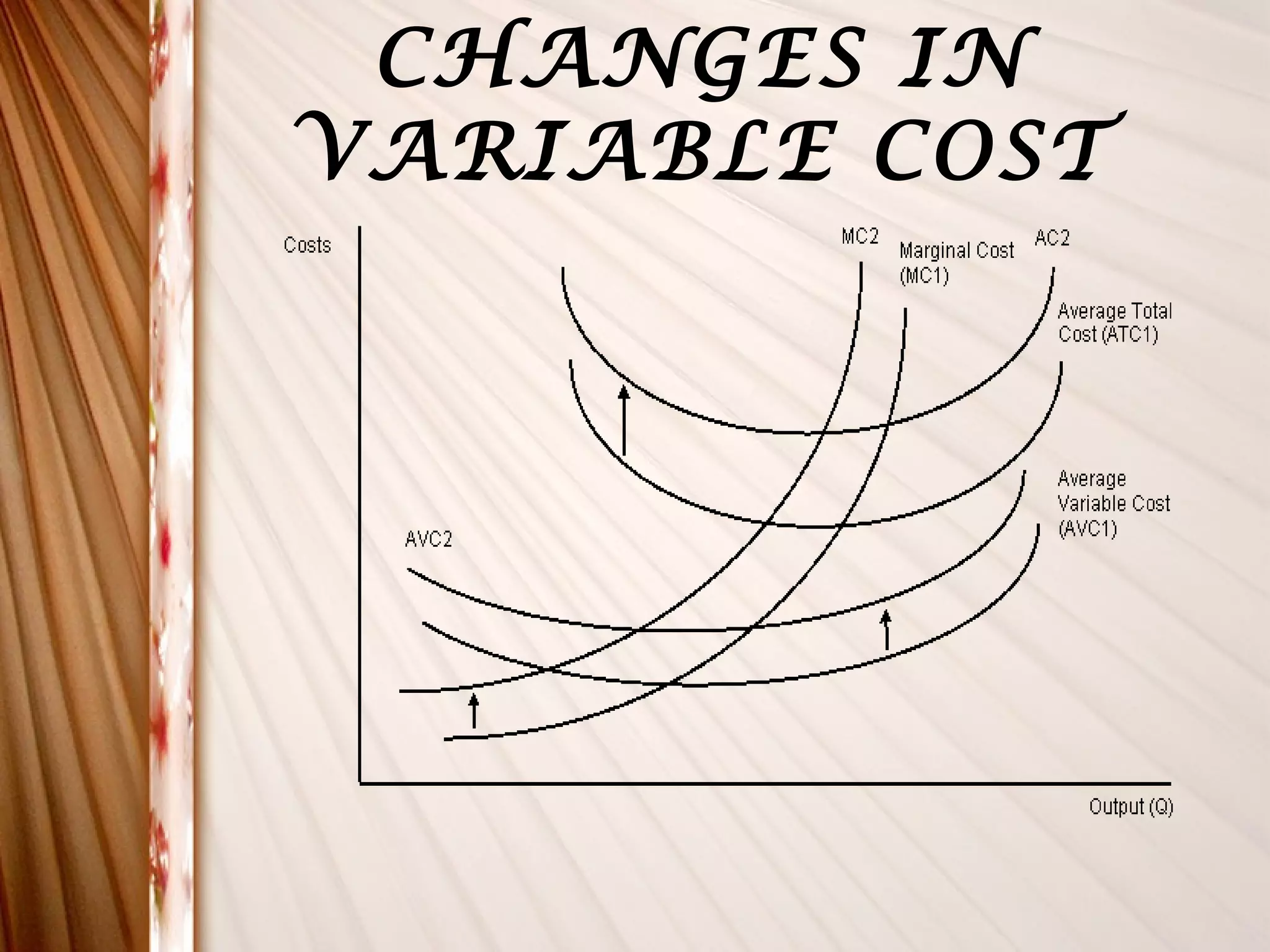
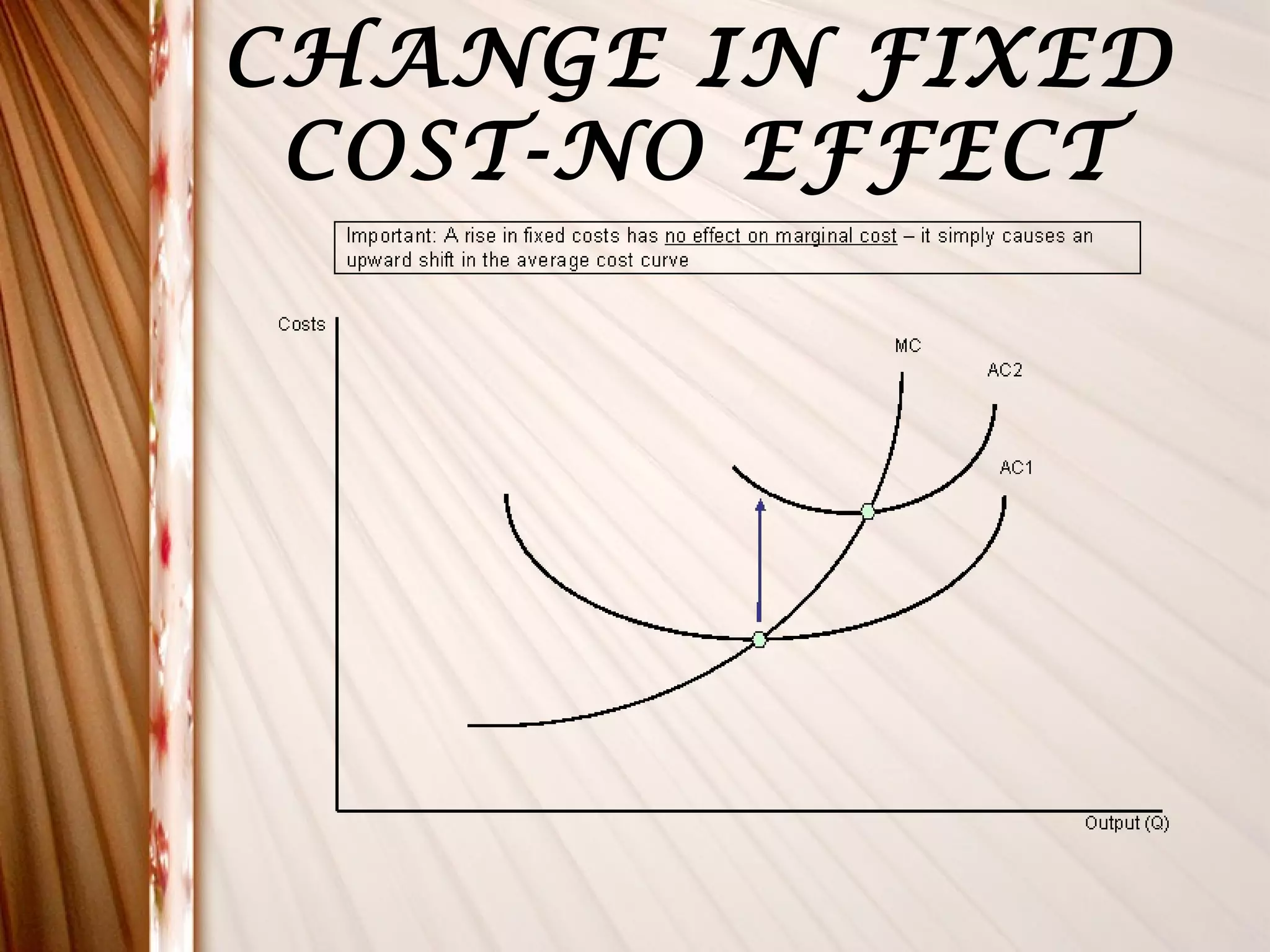
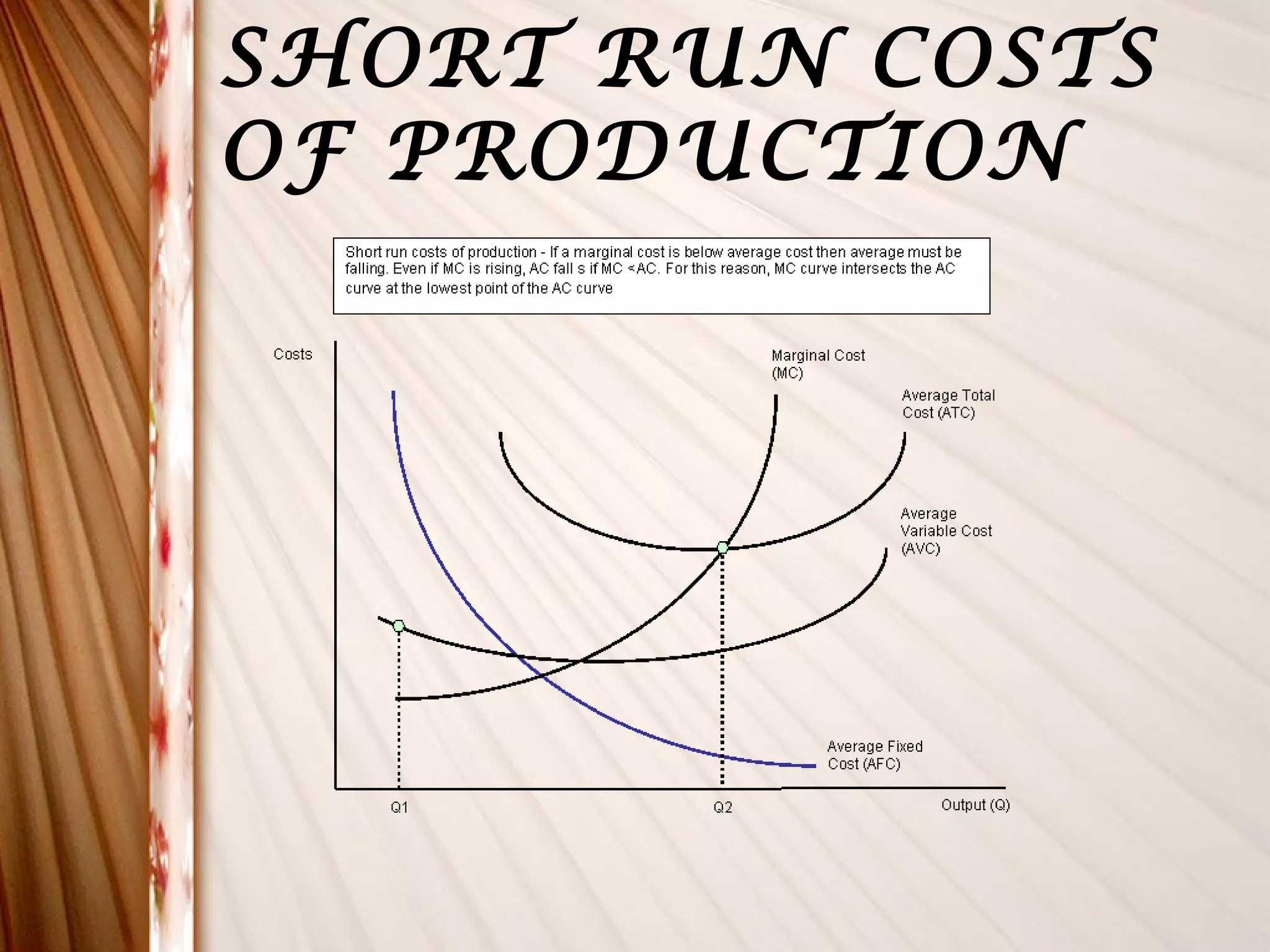
This document discusses different types of costs related to production. It defines money cost, nominal cost, real cost, opportunity cost, implicit cost, explicit cost, accounting cost, social cost, and entrepreneur's cost. It also covers classification of costs, elements of costs, short-run costs including fixed, variable, total, average and marginal costs. Finally, it discusses long-run cost curves including long-run average cost and long-run marginal cost curves.