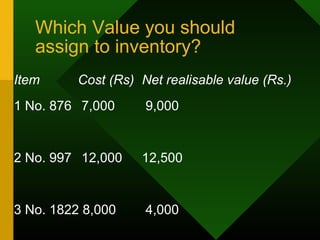
This document summarizes the key principles of IAS 2 regarding the accounting treatment for inventories. It defines inventories as assets held for sale, in production, or as materials/supplies. Inventories must be measured at the lower of cost or net realizable value, where net realizable value is the estimated selling price less costs to complete and sell. Cost includes purchase costs, conversion costs, and other costs to bring inventories to their present condition and location. Certain costs like abnormal losses or selling costs are excluded.