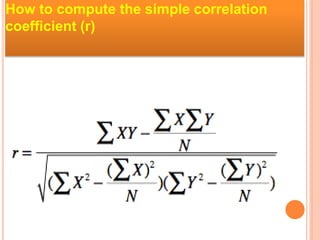
This document discusses correlation and provides examples of its applications. It defines correlation as a linear relationship between two variables and describes types of correlation including positive, negative, simple, partial and multiple correlations. Simple correlation coefficient (r) is explained, which measures the strength and nature of a relationship between two quantitative variables. An example of calculating r using age and weight data is shown. Several real-life examples of positive and negative correlations are given such as the relationships between study time and test scores, age and clothing size, and temperature and sales.