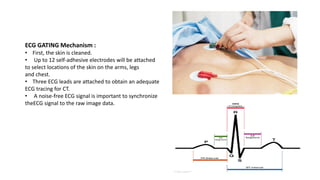
This document discusses coronary CT angiography (CCTA), a non-invasive imaging technique used to evaluate the coronary arteries. CCTA uses CT imaging with ECG gating to visualize the coronary arteries during periods of minimal cardiac motion. The document outlines the indications, contraindications, technical requirements, and procedure for CCTA. It describes how CCTA can be used to diagnose coronary artery disease, assess grafts after bypass surgery, and identify congenital coronary anomalies.