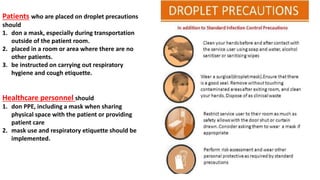
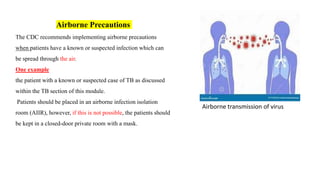
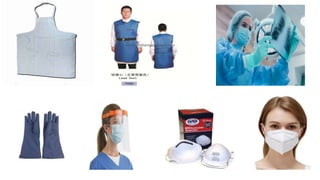
The document outlines contact, droplet, and airborne precautions for managing patients with known or suspected infections. Contact precautions include hygiene protocols and use of non-sterile gowns and gloves, while droplet precautions involve personal protective equipment and patient transport limitations. Airborne precautions require special isolation rooms and N95 respirators for healthcare personnel when dealing with highly transmissible infections like TB or measles.