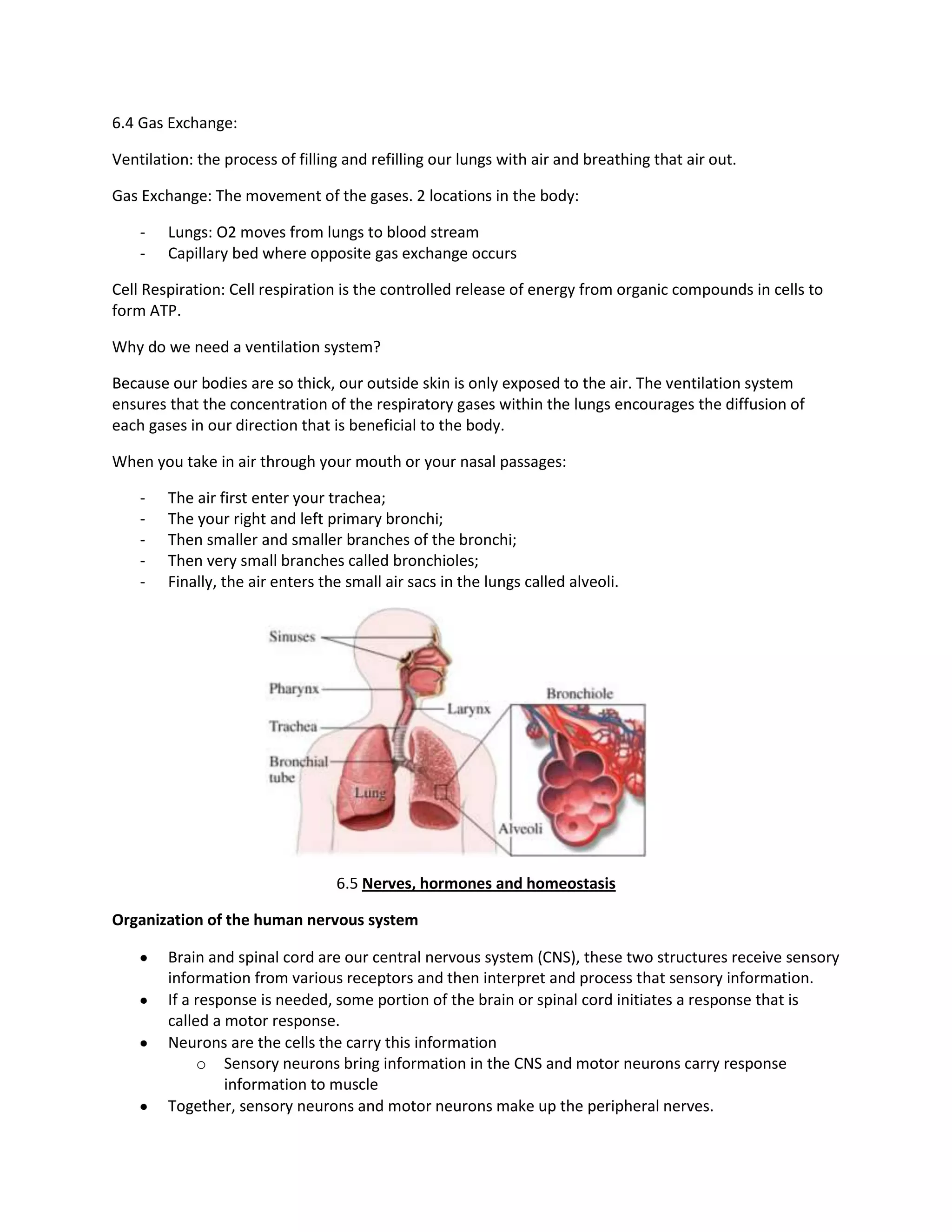
The document discusses gas exchange and the human respiratory and nervous systems. It provides details on:
1) Ventilation is the process of breathing air in and out of the lungs. Gas exchange occurs as oxygen moves from the lungs into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide moves out.
2) The nervous system includes the brain, spinal cord, neurons, nerves, and cranial and spinal nerves which transmit sensory information and motor responses.
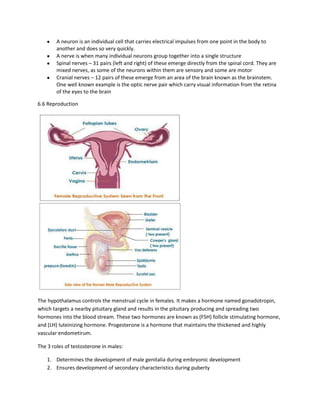
3) The document also discusses human reproduction, including the hormones that control the female menstrual cycle and roles of testosterone in males. In-vitro fertilization is summarized.