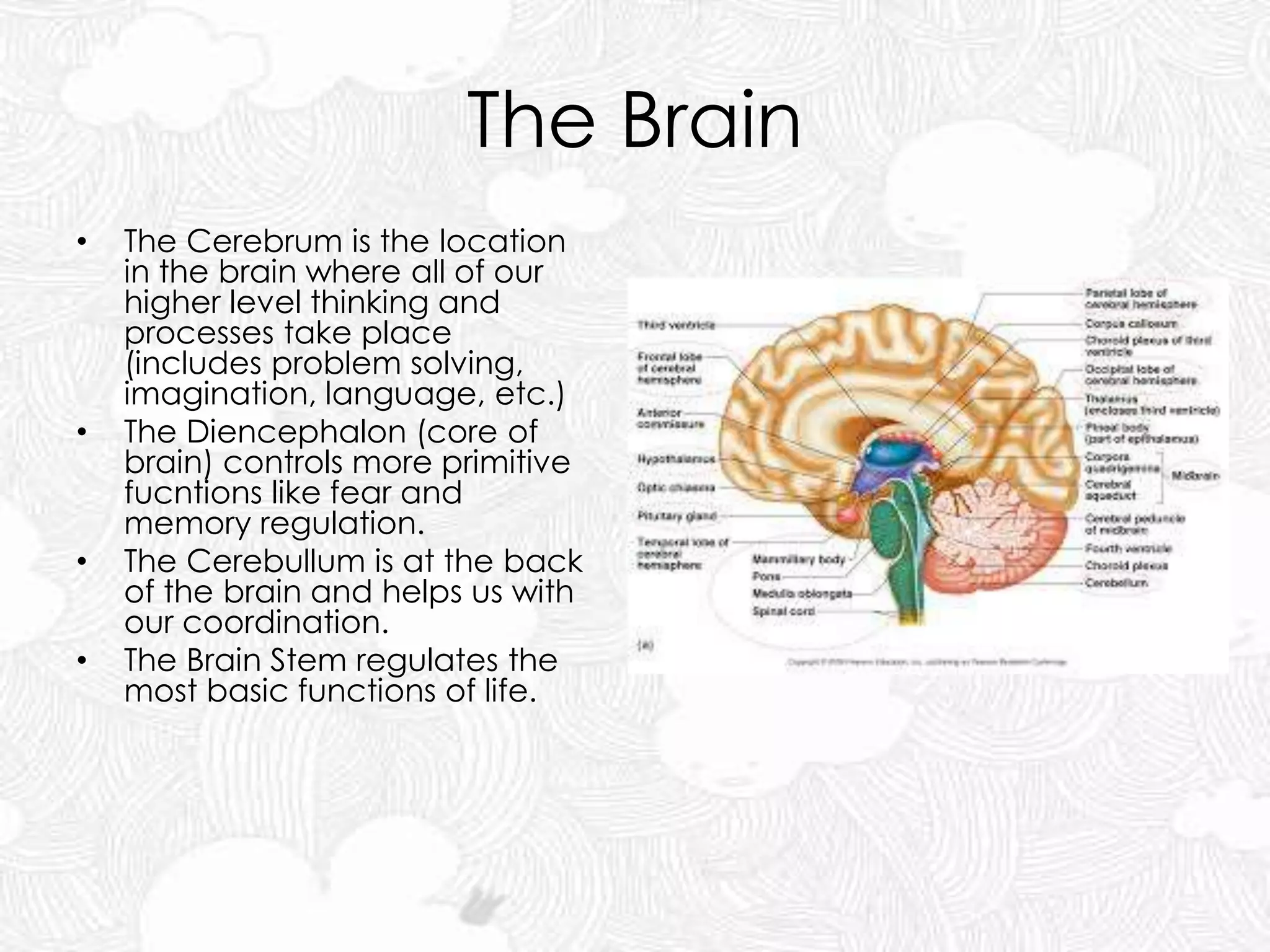
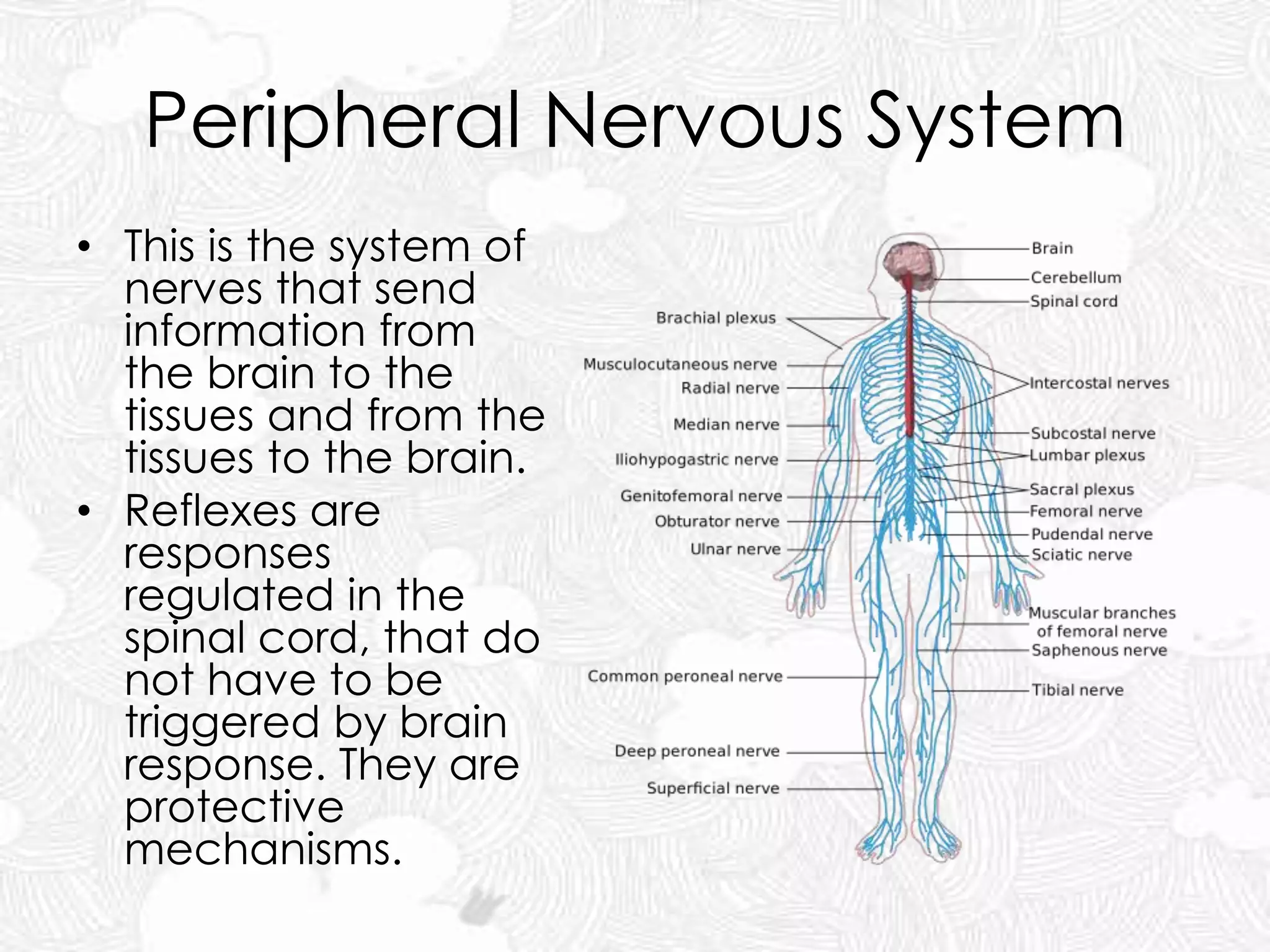
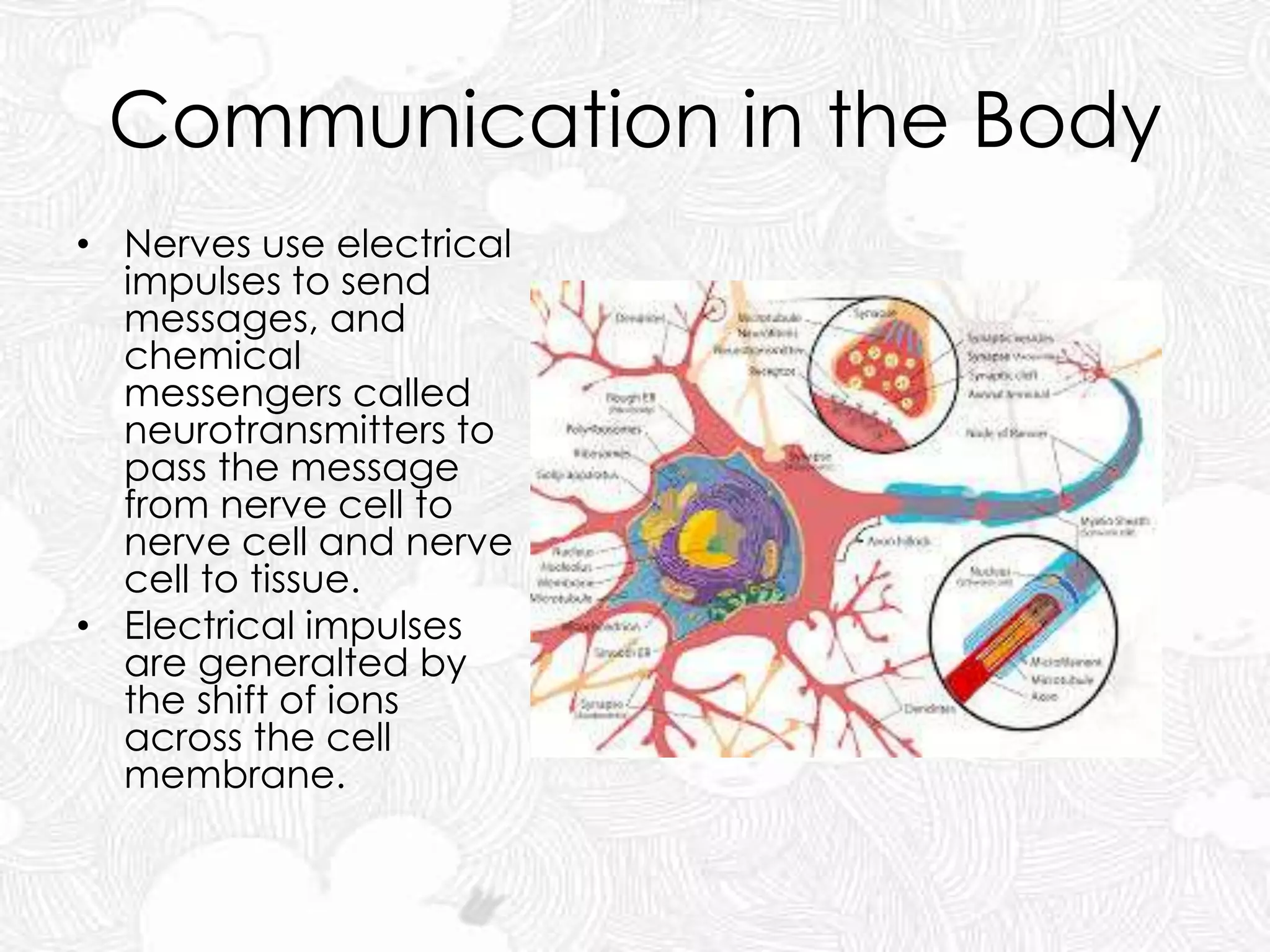
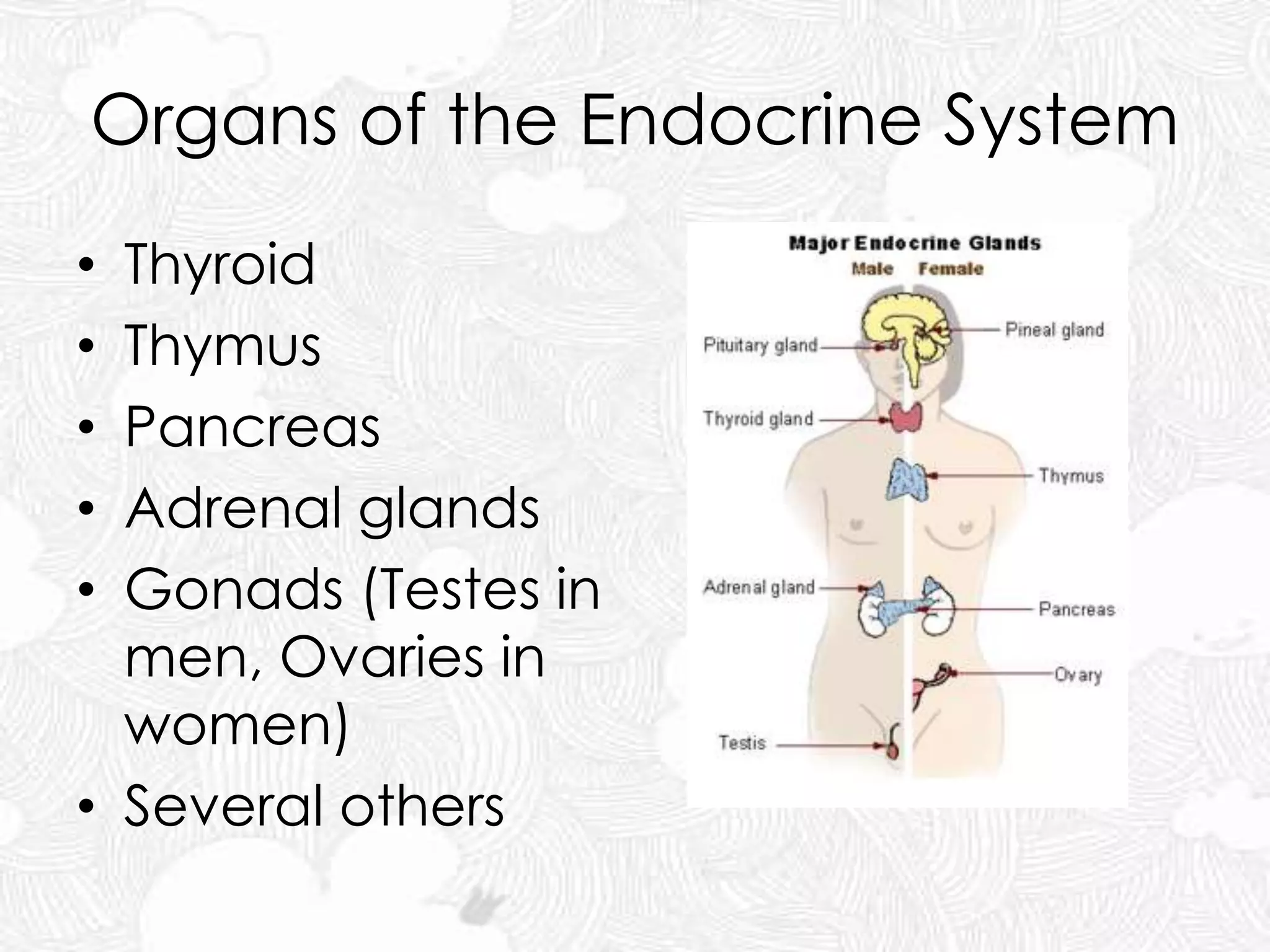
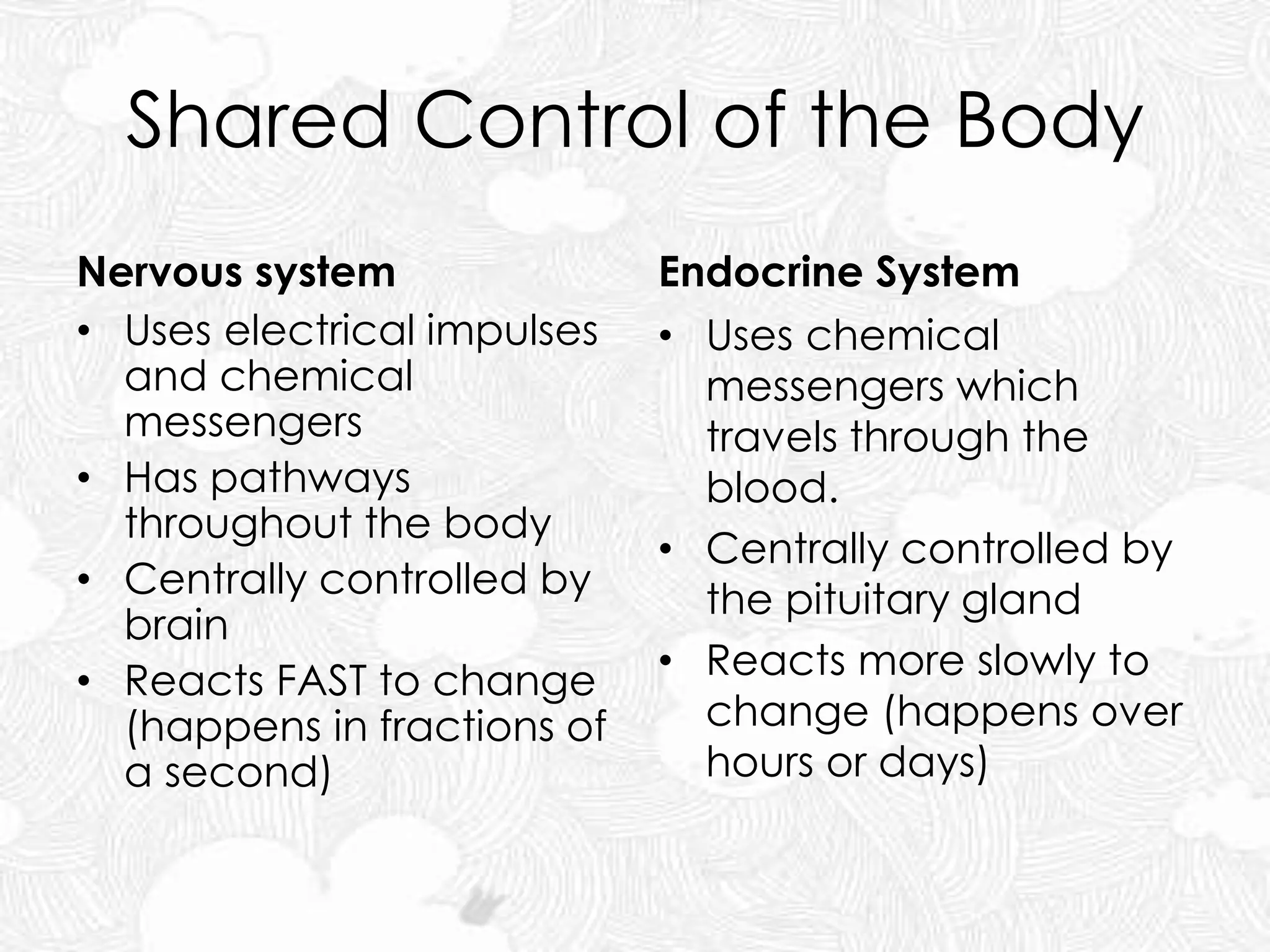
The document discusses the nervous and endocrine systems. The nervous system includes billions of neurons and is divided into the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system. The brain acts as the central control center and uses electrical impulses and neurotransmitters to communicate. The endocrine system is made up of hormone-producing glands that regulate body functions through chemicals called hormones, which are released into the bloodstream. The pituitary gland controls many other glands. The nervous and endocrine systems work together to control the body, with the nervous system reacting fast to changes and the endocrine system responding more slowly.