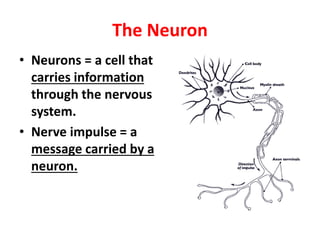
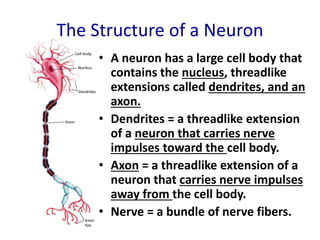
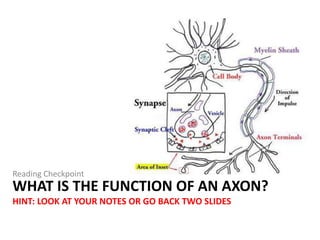
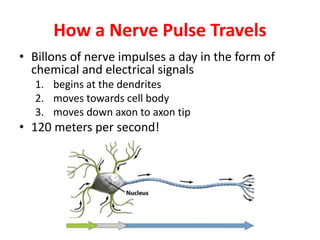
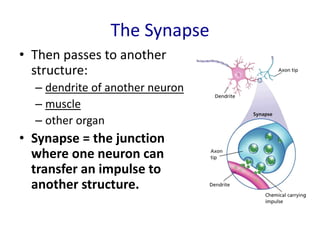
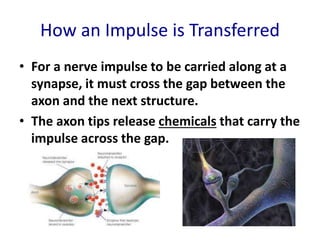
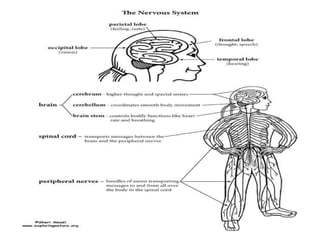
The nervous system functions to receive information from inside and outside the body, respond to stimuli, and maintain homeostasis. It is made up of neurons, which are cells that transmit electrochemical signals. There are three main types of neurons - sensory neurons detect stimuli, interneurons relay signals between neurons, and motor neurons activate glands and muscles. Nerve impulses travel along neurons when they are stimulated, moving from dendrites to the cell body and then down the axon to the axon tip via changes in electrical potential. At synapses, chemicals transmit impulses across gaps to the next neuron or structure.